This is an automatically translated article.
Biopsy is a highly accurate procedure that examines the cause and extent of the lesion. Biopsy test is especially popular in diagnosing cancer to promptly prevent risks affecting the patient's life.1. What is a biopsy?
Biopsy is a small, minimally invasive technique. The doctor will use a biopsy needle to cut or aspirate samples from suspected lesions of unknown nature for pathology, bacteriology or genetic diagnosis. Currently, this is a very effective and helpful support method for clinicians, towards the guideline of standard treatment according to evidence-based medicine.Biopsy is a medical test with high accuracy that helps diagnose most cancers. Types of imaging tests such as CT scans and X-rays can only help identify areas to be examined, but cannot distinguish between normal cells and cancer cells.
Biopsy is done by taking a sample of tissue from any part of the body such as skin, internal organs or other structures. Then the specimen will be examined under a microscope for a more accurate diagnosis. The purpose of this test is usually directed to check for abnormalities in the function of a part of the body or changes in the abnormal cell structure such as tumors, swelling, tumours...
Biopsy tests are often associated with cancer. Doctors use this test to check if abnormalities in the body are caused by cancer or other problems.
For example, if a woman has a lump in her breast, an imaging test will confirm the lump, while a biopsy will help determine if it is breast cancer or another condition.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. Types of biopsy tests
Biopsy is classified into many different types, the doctor will choose based on the condition and suspicious areas on the patient's body. Regardless of the type of biopsy, the patient will be given a local anesthetic to relieve pain in the area being performed. Here are some of the types of biopsies used in diagnosis, including:2.1. Bone marrow biopsy Inside some large bones such as the hip or femur, blood cells are produced by a spongy material called bone marrow. If the doctor suspects a problem with the blood, the patient will have a bone marrow biopsy.
Bone marrow biopsy tests can diagnose cancerous and noncancerous conditions such as leukemia, anemia, infection, or lymphoma. The test is also used to check if cancer cells from another part of the body have spread to the bones.
The bone marrow is easily accessed using a long needle inserted into the hip bone. The inside of the bone cannot be numbed, so some people may feel a dull ache during the procedure.
2.2. Endoscopic Biopsy An endoscopic biopsy is used to access tissue inside the body to collect samples from organs such as the bladder , colon , lungs...
During the procedure, the doctor will use uses a thin flexible tube called an endoscope with a small camera and light. The doctor uses a video monitor to view images that make it easier to collect samples. After the procedure, the patient may feel some discomfort, bloating, or a sore throat.
Laparoscopic biopsies can be done through small incisions in the body or through organs including the mouth, nose, rectum, or urethra. The process usually takes between 5 and 20 minutes.
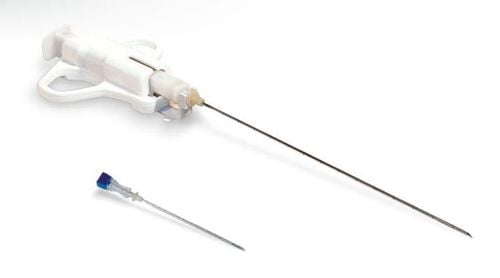
2.3. Needle biopsy A needle biopsy is used to collect skin samples, or for any tissue that can be easily accessed under the skin. There are different types of needle biopsies including:
Core needle biopsy: This test uses a large, medium-sized needle to reach the central core of tissue, for example, to remove tissue from the central core of a tumor inside the breast. Fine Needle Biopsy: This biopsy test uses a fine needle attached to a syringe, allowing fluid and cells to be withdrawn. Axial biopsy: This procedure is done for areas that are not palpable, but can be seen through x-ray images such as X-rays or CT scans so that the doctor can access specific areas, such as the lungs, liver or other organs. Vacuum-assisted biopsy: A type of test that supports a vacuum device, helping to hurt, operate and not have large scars, often used in breast testing.
Skin biopsies can be done using a local anesthetic, then removing a small part with a knife or using a punch biopsy, a special instrument that punches a small hole through the upper layers end of the skin to obtain a skin sample for biopsy.
The skin biopsy sample will be sent to a laboratory for testing for possible conditions such as infection, cancer, inflammation of skin structures or blood vessels.
2.5. Surgical biopsy Your doctor will remove a small sample of tissue to examine in a few minutes to help guide further surgery or treatment.
2.6.Excisional biopsy In an excision biopsy, part or all of the tumor may be removed to look for abnormal cells. Excisional biopsies are performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the location of the tumor. This type of biopsy can be done for a lump in the breast.
3. Effect of biopsy
Some of the effects of a biopsy test include:Cancer biopsy : If a patient has a lump or swelling somewhere in the body without an obvious cause, the only way to determine whether it is whether it is cancer or not it is through the test. Stomach biopsy: This procedure can help your doctor determine if conditions such as stomach ulcers are caused by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Small bowel biopsies may be used to evaluate patients with malabsorption, anemia, or celiac disease. Liver biopsy: This can help your doctor diagnose a tumor or cancer, cirrhosis of the liver caused by alcohol abuse, or long-term inflammation. Biopsy can also be used to assess how a patient is responding to a treatment regimen. Testing for infection: A needle biopsy can help determine if a patient has an infection and what type of organism is causing it. Inflammation test: By examining the cells, your doctor can determine what's causing the inflammation. Sometimes, biopsies are also performed on transplanted organs to determine whether the body is adapting to the transplanted organ.
Biopsy is a rather complicated technique, so doctors will only do biopsies after easier diagnostic techniques have been performed (X-ray, ultrasound, laboratory tests) that have not yet been confirmed. definitely illness. According to experts, viewing tissue or cells under the microscope always gives the most accurate diagnostic results and is very effective when determining the nature of a tumor: benign or malignant. Once it is determined that the tumor is malignant, the doctor will order a biopsy of the nearby tissues to see if the tumor has metastasized or not, so that appropriate therapy can be given to the patient.
4. The process of performing a biopsy

4.1. Before the biopsy The biopsy procedure may require some preparation on the part of the patient, such as avoiding eating and drinking for several hours before the test. Patients should tell their doctor about any medications and supplements they have taken. You may need to stop taking certain medications before the test, such as aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Patients will be tested for blood and evaluated for possible allergies to related substances. Depending on the type of biopsy, your doctor will give you more specific instructions on what to do before the procedure. The patient will need to sign a consent form to this test.
4.2. During the biopsy The biopsy tissue samples will be sent to a laboratory and will be examined by the coroner. In the case of cancer, the examiner will need to determine if the sample is malignant or benign. If the case is malignant, they will evaluate how invasive or advanced the cancer is. As for benign cases, it will depend on the size of the tumor and whether there is a risk of becoming malignant or not, the doctor will give an appropriate solution.
4.3. After a biopsy If a biopsy tissue sample is taken from an internal organ, the patient may need general anesthesia and an overnight hospital stay. The procedure to scrape a tissue sample from inside the mouth usually does not require anesthesia, the area may feel sore for a while.
If the biopsy sample is taken from a major organ, such as the liver or kidney, the patient may need to rest in the hospital for several hours before being able to go home. After a biopsy of the cervix or the lining of the uterus, you may experience light vaginal bleeding.
Possible risks include possibility of bleeding, testing in the wrong place, not taking enough samples which could lead to false results and need for re-test. A study of the results of a test used in clinical trials found that only 5.2% of biopsies resulted in complications.
Therefore, it is best to choose large, reputable medical facilities to perform. If you want to have a biopsy done at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can go directly to Vinmec medical system nationwide.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.