This is an automatically translated article.
Mast cells help protect the body from disease and aid in wound healing by releasing substances such as histamine and leukotrienes. However, for some reason, the number of mast cells in the body is too much, causing pathology.
1. What is mast cell disease?
Mast cell disease (also called Mastocytosis) occurs due to the abnormal infiltration of mast cells into the skin, other tissues and organs. Manifestations include pruritus, flushing, and gastric hypersecretion, causing dyspepsia, also known as immediate anaphylaxis, which occurs due to the release of chemical mediators such as histamine, inflammatory cytokines, heparin, and leukotrienes.
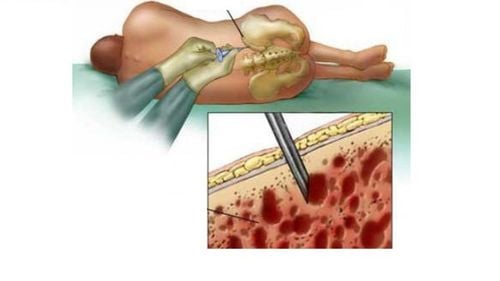
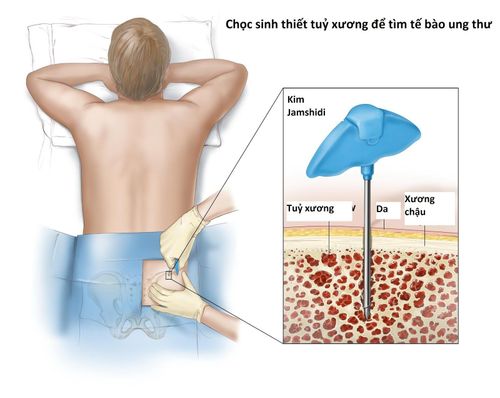
The disease can only be definitively diagnosed through a biopsy of the skin or bone marrow or a combination of both. Systemic mast cell disease is treated specifically with antihistamines in combination with the treatment of comorbid complications or disorders. Histamine is the most important chemical mediator in the pathogenesis of Mastocytosis, which can cause various manifestations of hypersensitivity and organ dysfunction.
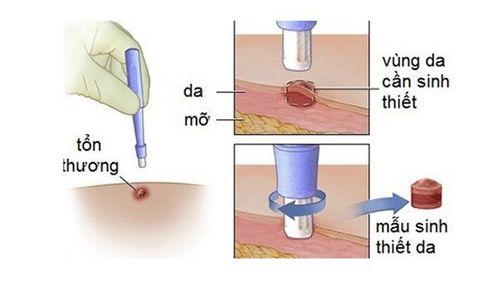
Sinh thiết da để chẩn đoán bệnh tế bào mast
2.Causes of mast cell disease
The cause of mast cell disease in many patients is an activating mutation (D816V) in the gene that codes for the c-kit receptor of the stem cells inside mast cells. The consequence is increased autophosphorylation of this receptor and uncontrolled mast cell proliferation.
3.Risk factors for disease onset
Risk factors that increase the likelihood of disease onset in patients with pre-existing mutations include:
Local anesthesia, topical anesthesia... Heat-related physical contacts such as overheating , too cold or rapid temperature changes... Massaging, massaging or scratching the skin; Alcoholic beverages such as wine, beer; Stress, both physical and mental stress; Insect bites ; Food allergy.
Dị ứng thực phẩm là một trong các yếu tố nguy cơ làm tăng khả năng khởi phát bệnh
4.Classification of mast cell disease
4.1. Mast cell disease of the skin Mast cell disease of the skin is common in children. The main manifestation of the disease is pigmented urticaria, localized or diffuse brown maculopapular skin lesions or skin rash with bullae and severe itching.
Common systemic symptoms accompanied by hot flashes, vomiting, diarrhea, headache or possibly fainting. These manifestations are caused by mast cells that invade the skin and release chemical mediators.
Skin lesions can progress to nodules and plaques. In particular, the nodular skin lesions are usually distributed locally, while the papules tend to spread throughout the body.
4.2. Systemic mast cell disease Systemic mast cell disease, also known as immediate hypersensitivity (type I) disease, is common in adults. The characteristic symptom is multifocal lesions in the bone marrow and is accompanied by lesions of other organs such as skin, lymph nodes, liver, spleen, and gastrointestinal tract. Systemic mast cell disease is subdivided into different subtypes:
Inactive systemic mast cell disease: Organ functions are not disturbed, there are no clinical symptoms, and the prognosis is good. This is the most common form of the disease. Systemic mast cell disease associated with hematological abnormalities such as myeloproliferative disease, myelodysplasia, lymphoma... This form of the disease is also relatively common after inactive systemic mast cell disease; Invasive, aggressive, fast-growing mast cell disease that causes severe organ dysfunction; Mast cell leukemia: A marrow biopsy has more than 20% mast cells in the bone marrow. Manifestations without skin lesions, multiple organ failure and poor prognosis. However, this form of mast cell disease is very rare; Symptoms of systemic mast cell disease include:
Multifocal bone marrow lesions are common in adults; Damage to various organs; Systemic symptoms are varied, the most common being flushing or sometimes anaphylactic reactions with syncope and shock; Other symptoms: peptic ulcer causing epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, persistent diarrhea, bone and joint pain, or neuropsychiatric changes (such as depression, mood instability). Ascites is caused by hepatosplenic infiltrates and portal hypertension.

Đau bụng thượng vị có thể là triệu chứng của bệnh tế bào mast hệ thống
5. Diagnosis of mast cell disease
Clinical symptoms are suggestive for the diagnosis of the disease, then the patient is indicated for skin lesion biopsy or bone marrow biopsy. Biopsy results help confirm the diagnosis of mast cell disease, which is characterized by dense infiltration of mast cells in the biopsy specimen.
Associated tests that contribute to a more accurate diagnosis include:
Quantification of elevated levels of mast cell mediators and their metabolites (eg, N-methyl histamine and N-methylimidazole acetic acid in blood and urine) Serum tryptase levels help differentiate the two forms of the disease. Systemic mast cell disease is elevated while mast cell disease is normal. Bone X-ray ; Identification of the c-kit receptor D816V mutation. Some other laboratory tests help to differentiate mast cell disease from other diseases with similar symptoms such as anaphylaxis, adrenal adenoma, carcinoid syndrome, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, etc. These include:
Measurement of serum gastrin levels in patients with peptic ulcers helps to differentiate from Zollinger-Ellison syndrome; Quantification of urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) in patients with flushing to rule out carcinoid syndrome; Measure the concentration of free metanephrines in the blood or urine to distinguish it from an adrenal tumor.
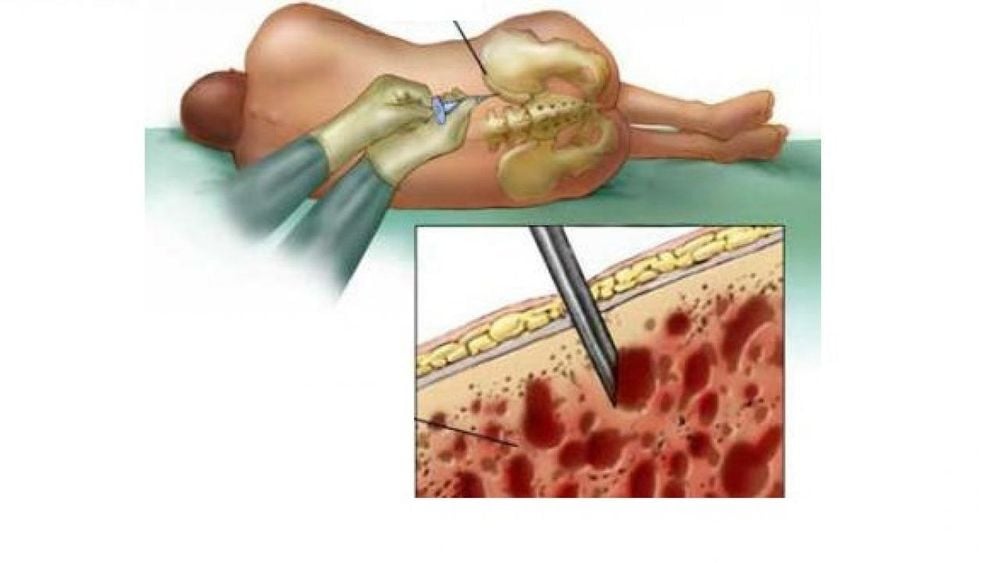
Hình ảnh sinh thiết tủy xương
6.Treatment of mast cell disease
6.1. For mast cell disease in the skin For mast cell disease in the skin, the treatment directions include:
Reducing symptoms of the disease with H1-receptor antagonists; Skin manifestations in children may resolve on their own, without treatment; In adults, treatment with psoralen in combination with ultraviolet irradiation or topical corticosteroids; Skin mast cell disease is unlikely to progress to systemic mast cell disease in children, but it is still possible to progress in adults. 6.2. For systemic mast cell disease Treatments include:
Use of H1 and H2 antihistamines; Cromolyn with a dose of 200mg for adults and 100mg for children 2-12 years old (not more than 40mg/kg/day), divided into 4 times a day;
Thuốc Prednisone 40 - 60 mg có thể được chỉ định để điều trị bệnh tế bào mast
If the patient has advanced disease, use interferon alpha-2b: A dose of 3-4 MUI injected under the skin once a week can limit bone marrow damage; Anti-inflammatory corticosteroids such as Prednisone 40 - 60 mg orally daily for 2 to 3 weeks may be indicated; Splenectomy has the potential to improve survival; Narcotic drugs such as daunomycin, etoposide, 6-mercaptopurine are indicated for mast cell leukemia. However, the effectiveness has not been tested; Imatinib (a tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor) may be indicated in some forms of mast cell disease but is less effective in those due to the D816V mutation at the c-kit receptor. Midostaurin (a 2nd generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor) is being studied for use in this patient population. Systemic mast cell disease is a disorder that results in an increased number of mast cells in the body. Mast cells normally help protect the body from disease and aid in wound healing by releasing substances such as histamine and leukotrienes.
Early medical examination and treatment will lead to a better prognosis of disease treatment, ensuring the patient's health.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has been and continues to be fully equipped with modern diagnostic facilities such as: PET/CT, SPECT/CT, MRI, X-ray, ultrasound..., testing blood test, histopathology, immunohistochemistry, gene test, molecular biology test,... to diagnose diseases.
After having an accurate diagnosis of the disease and stage, the patient will be consulted to choose the most appropriate and effective treatment methods. The treatment process is always closely coordinated with many specialties: Diagnostic Imaging, Biochemistry, Immunology, Cardiology, Stem Cell and Gene Technology; Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Department of Endocrinology, Department of Rehabilitation, Department of Psychology, Department of Nutrition... to bring the highest efficiency and comfort to the patient. After undergoing the treatment phase, the patient will also be monitored and re-examined to determine whether the treatment is effective or not.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.