This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Nguyen Hong Tram - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital1. What is duodenal diverticulum?
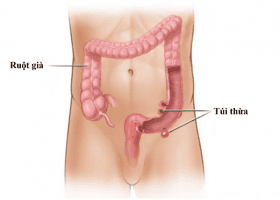
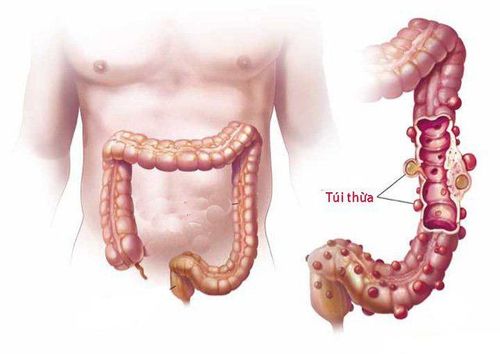
Beside colonic diverticulum, duodenal diverticulum is also very common in clinical practice, most commonly at D2, rarer in D3 and D4 and in D1 account for an extremely small percentage. Duodenal diverticulum is usually about 2 - 3 cm in size, it is also possible to meet duodenal diverticulum larger than 10 cm, but this rate is very low. Duodenal diverticulum may present as multiple pouches or be associated with other diverticula such as colonic diverticulum or esophageal diverticulum. In addition, when the body appears duodenal diverticulum, it is accompanied by damage to other surrounding organs such as duodenal ulcer, duodenal stricture, duodenal stasis, gallstones or even inflammatory disease. acute pancreas.
In terms of classification, duodenal diverticulum is divided into 2 types as follows:
Congenital duodenal diverticulum: This is a primary duodenal diverticulum, with the most common location being opposite the blood vessels leading to the intestinal wall. , consisting of layers of the duodenum. Acquired duodenal diverticulum: Also known as a secondary duodenal diverticulum, it can be at the site of the vascular access to the intestinal wall or a healing ulcer, the structure often lacks the muscular layers of the duodenum. The symptoms of duodenal diverticulum are often poor and difficult to detect before the age of 30, and are detected more often between the ages of 50 and 65. The disease can manifest through a number of signs as follows:
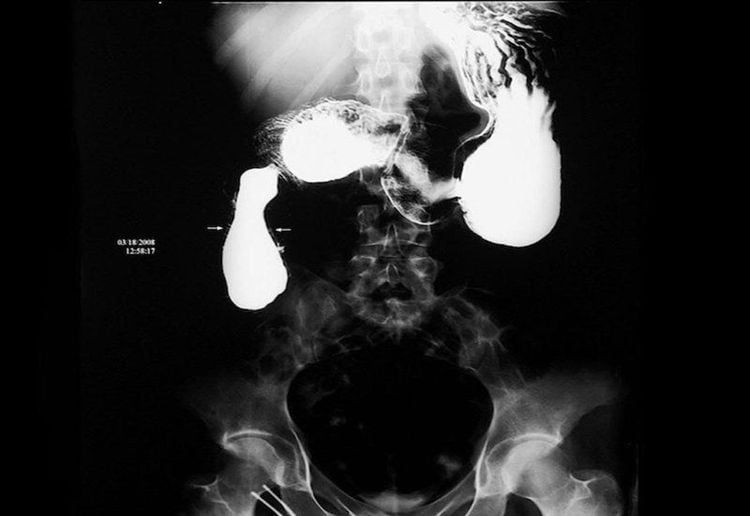
Abdominal pain, pain above the navel, does not spread, appears after eating, pain increases when changing positions, if changing positions can relieve pain , the pain occurs frequently during the day. Nausea, vomiting, possible bile vomiting Anorexia Not digesting food Weight loss Jaundice Diarrhea Diarrhea Constipation Bleeding and pyloric stenosis To diagnose duodenal diverticulum, the most important method is X-ray, On unprepared X-ray, there is an image of the water vapor level in the side of the duodenum. The clinical symptoms of duodenal diverticulum above can be confused with gastric ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, pyloric stenosis... so the X-ray film plays a very necessary role. in making a definitive diagnosis and providing the most effective treatment. In addition, the patient may be assigned to perform a few other valuable laboratory techniques, including endoscopy.
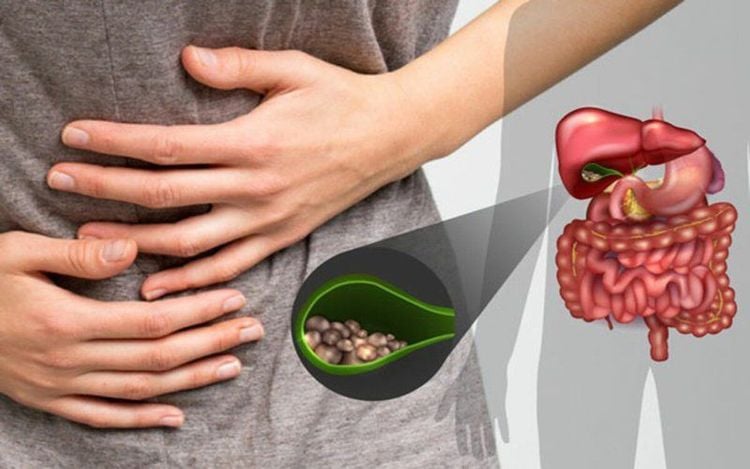
2. Bile obstruction due to duodenal diverticulum
Cholestasis is a condition caused by a number of factors such as gallstones, pancreatic head tumors, cholangiocarcinoma, or duodenal diverticulum. In particular, duodenal diverticulum is a condition causing biliary obstruction that is rarely mentioned and easily overlooked in clinical practice.
The cause is explained that duodenal diverticulum often has few obvious symptoms, only a few common symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain. Because duodenal diverticulum can be misdiagnosed with some other diseases such as gastritis, gallstones, etc., ultrasound as well as X-ray to diagnose biliary obstruction is extremely important.
The mechanism of duodenal diverticulum causes biliary obstruction is explained specifically as follows: duodenal diverticulum makes bile cannot escape into the duodenum, causing the common bile duct to dilate, gradually bile will be stagnant. . Because bile is stagnant, the patient will have an infection, the causative agent of which is beta-glucuronidase-producing bacteria, which is a factor in the formation of bile pigment stones.
In addition, when food remains in the duodenal diverticulum, the bag will tend to stretch, compressing some structures such as bile ducts, pancreatic ducts, causing acute pancreatitis and biliary obstruction. In some cases of patients with duodenal diverticulum at the papillary position, at this time, the muscle tone and contraction of the sphincter will be lower than in normal cases, so this will be the cause. gallstones more easily.
There are many methods to treat duodenal diverticulum, including:
Conservative treatment: This method is applied to patients with small diverticula, less stasis and few symptoms of disorder. function. The patient will be advised on a suitable diet to prevent inflammation and spasms, and will conduct duodenal lavage.

Surgery: This is a radical surgical treatment that is applied to cases of duodenal diverticulum causing perforation, bleeding or patients with severe functional disorders, complications such as Acute pancreatitis, peritonitis, duodenal fistula, damage to biliary structures, ampulla of vater as well as conservative treatment are ineffective. Some surgical techniques can be applied such as gastrectomy for diverticulum at the ampulla of Vater or diverticulum adherent to the common bile duct, duodenal diverticulectomy in case the diverticulum appears in D3, D4, lateral aspect of D2, proximal to Vater, with no biliary involvement or Kocher motility of the duodenum. Duodenal diverticulum is one of the few causes of obstructive gastrointestinal disease or is neglected in clinical practice. ready. Although not a frequent cause, if left undetected duodenal diverticulum can lead to biliary obstruction as well as other gastrointestinal diseases such as cholangitis or gallstones. Therefore, when there are any symptoms that suspect the presence of duodenal diverticulum, the patient should actively go to the medical facility to be examined and diagnosed.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.