This is an automatically translated article.
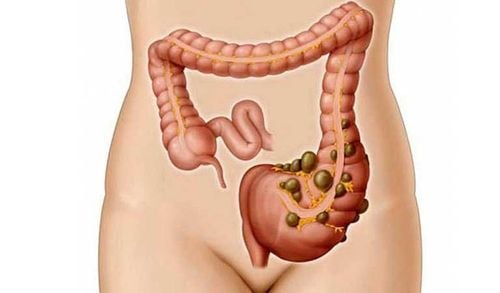
This article was professionally consulted by Doctor Vu Van Quan, Department of General Surgery and Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.In the West, half of people over 60% have diverticulitis, but only 10%-25% of people continue to have diverticulitis. Diverticulitis usually develops when the waste outlet in the sacs is blocked, the stagnation allows bacteria to accumulate and cause infection. Inflammation spreads to surrounding fatty tissue, sometimes perforation of the diverticulum leads to abscess formation or peritonitis. Rarely, a colonic fistula may form with the bladder, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
1. Complications of diverticulitis
Serious complications can occur from diverticulitis. Most of them are the result of the development of a tear or perforation of the intestinal wall. If this happens, intestinal waste can leak out of the intestines and into the surrounding abdominal cavity causing the following problems:
1.1 Peritonitis
Diverticulitis can cause necrosis of the diverticulum, the digestive contents of the colon spilling into the abdominal cavity, leading to peritonitis. Peritonitis is a surgical emergency that requires immediate surgery to clear the abdominal cavity. Part of the colon that has ruptured may need to be removed. If peritonitis is not treated in time, the patient can die.
1.2 Abscess and diffuse inflammation (Abscess and Phlegmon)
Diverticulitis can progress to an abscess (a ball of pus).
If the abscess is small, it can be successfully treated with antibiotics. If it's large or doesn't respond to treatment, doctors will need to surgically drain the pus and may even need to remove some of the damaged bowel tissue.
1.3 Intestinal obstruction
Infection can lead to colon scarring, and scar tissue can cause partial or complete obstruction. A partial obstruction does not require emergency surgery. However, surgery is needed with complete obstruction.
1.4 Bleeding diverticulum

Diverticular bleeding is not common, occurring only in about 17% of people with chronic diverticulitis. The condition is usually painless and the bleeding usually stops on its own. But in rare cases, the bleeding can be severe enough to require a blood transfusion or surgery. If you experience bleeding, contact your doctor immediately.
1.5 Fistula
Fistula is an abnormal shortcut formation between two organs. In diverticulitis, a fistula can form and often connects the colon to the bladder, small intestine, or vagina. Symptoms include: air or stool in the urine, pain when urinating, or abnormal vaginal discharge.
After a sudden episode of diverticulitis, about 14% of patients are at risk of developing a fistula. When a fistula is found, surgery is often required to treat the condition and to avoid further complications.
2. Factors that increase the risk of complications of diverticulitis
Aging and genetics are major factors in the development of diverticulitis and diverticulitis, but diet also plays an important role. A diet low in fiber and high in refined foods may increase the risk. Indeed, in Western societies, an estimated 10% of people over the age of 40 eventually develop diverticulosis; this figure reaches at least 50% in people over 60 years old. Diverticulitis occurs in about 10%-25% of people with diverticulitis.
Although it has not been proven, some researchers think that if you are frequently constipated and often strain during bowel movements, you may be creating enough pressure in the intestinal walls to weaken them and start early development of the diverticulum. Another school of thought is not enough fiber in the diet. The lack of fiber leads to increased strain on the intestinal wall to move stool through the colon. That then causes increased local pressure that leads to the formation of vesicles at weak points in the colon wall. The increased pressure with undigested food caught in these sacs can erode the diverticulum wall, causing inflammation and bacterial infection, which can lead to diverticulitis.
People who have had acute diverticulitis have a higher risk of complications than other groups. About 5 to 10 years after the first outbreak, the risk of a second complication is about 50%.
The best way to avoid serious complications of diverticulitis is to see a gastroenterologist as soon as you notice symptoms, follow treatment guidelines, and continue to have regular checkups.
3. Treatment of diverticular disease at Vinmec Hai Phong
Most patients with diverticulosis have minimal or no symptoms and do not require specific treatment. A high-fiber diet and fiber supplements are recommended to prevent constipation and the formation of multiple diverticula.
When diverticulitis symptoms - abdominal pain, fever, ... if mild, oral antibiotics are usually sufficient. When pain is worse, a liquid diet to allow the colon and intestines to recover may also be indicated. When the pain gets worse, or when you have a high fever or you can't drink fluids, you may need to stay in the hospital, along with intravenous antibiotics, and not eat or drink for several days.
Diverticulitis unresponsive to medical treatment requiring surgery. Surgery usually involves draining the pus and removing the segment of the colon that contains the diverticulum. Resection of the bleeding diverticulum is necessary for patients with persistent bleeding. Surgery may also be needed for any diverticula that have eroded into the bladder, causing severe, recurrent urinary tract infections and passing gas during urination, and to treat intestinal blockages.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.