This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Tran Quynh Trang - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International General HospitalBilirubin is the end product of hemoglobin metabolism and is derived mainly from the breakdown of red blood cells, to a lesser extent from cytochromes and myoglobin.
1. Overview of Bilirubin
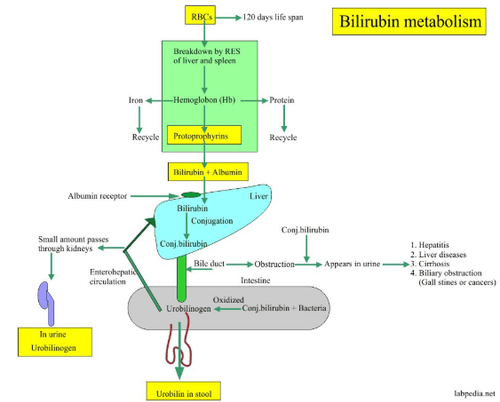
Bilirubin exists in many different forms in the blood, but is largely bound to serum albumin, commonly referred to as free or indirect bilirubin because it is necessary to use an indirect method to quantify this protein (in combination). adding a substrate to accelerate the colorimetric reaction). Because bilirubin is indirectly bound to albumin, it is not filtered by the glomerulus.In the liver, indirect bilirubin undergoes a 3-stage metabolism:
It is retained by liver cells. Conjugation to glucuronide by hepatic enzyme glucuronyltransferase. Excreted into the bile ducts.
Tổng quan về Bilirubin
Direct Bilirubin:
Make up 20% of total bilirubin circulating in the blood. Not bound to proteins, soluble in water, so filtered by the kidneys. 20% of direct bilirubin is reabsorbed into the blood, while 80% is eliminated in the biliary tract and then into the intestine. In the intestine, under the action of bacteria, bilirubin is converted to urobilinogen and then to stercobilin and is eliminated in the feces. Only a small fraction of urobilinogen present in the gastrointestinal tract will be reabsorbed into the portal venous system for the enterohepatic cycle and can be detected in the urine. Bilirubin TP = Bilirubin GT + Bilirubin TT
2. Bilirubin index and jaundice
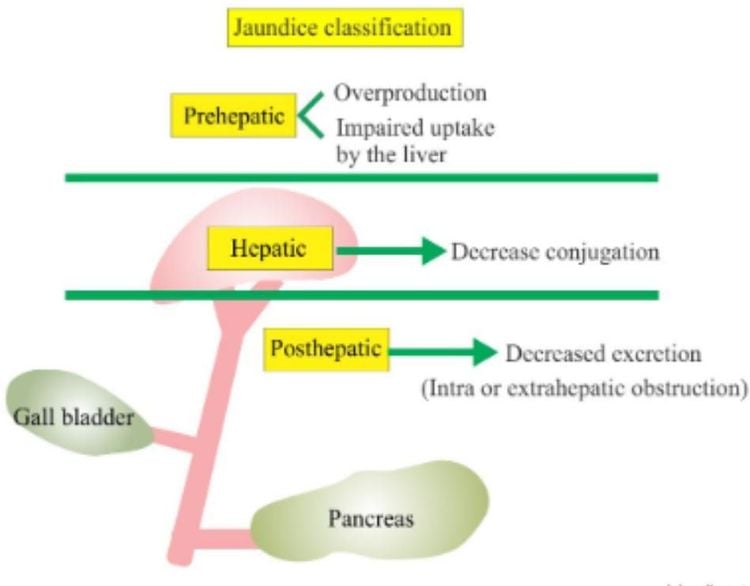
Bilirubin is a yellow substance found in bile, a liquid that helps you digest food. If your liver is healthy, it will remove most of the bilirubin from your body. If your liver is damaged, bilirubin can leak out of your liver and into your bloodstream. When too much bilirubin enters your bloodstream, it can cause your skin and eyes to turn yellow.People divide jaundice into 3 types:
Pre-hepatic jaundice: Usually caused by hemolysis, elevated indirect bilirubin. In Vietnam, common causes: malaria, hemolysis from congenital or toxic causes, bacteremia. Jaundice in the liver: often associated with pathology of liver cells, reducing and preventing the transport of bilirubin into the body's circulation. Common: viral hepatitis, toxic hepatitis caused by drugs, bacteria and parasites. Jaundice behind the liver: Usually obstructive jaundice such as gallstones, cancer, worms (very common in Vietnam).
Bilirubin có liên quan mật thiết đến tình trạng vàng da
The bilirubin blood test is used to check the condition of the liver, bile and hemolysis. This test is also commonly used to help diagnose neonatal jaundice. Many healthy babies develop jaundice because their livers are not mature enough to remove enough bilirubin. Neonatal jaundice is usually harmless and resolves within a few weeks. But in some cases, high bilirubin levels can lead to brain damage (also called Kernicterus), so babies are usually screened just in case.
3. Normal value Total Bilirubin:
Neonates: < 10 mg/dL or < 171 μmol/L. 1 month: 0.3 - 1.2 mg/dL or 5.1 - 20.5 μmol/L. Adults: 0.2 - 1.0 mg/dL or 3.4 - 17.1 μmol/L. Direct bilirubin: 0.0 - 0.4 mg/dL or 0 - 7 μmol/L.
Indirect Bilirubin: 0.1 - 1.0 mg/dL or 1 - 17 μmol/L.
Ratio of direct bilirubin / total bilirubin : < 20%.
Kết quả xét nghiệm mấu phần nào phản ánh tình trạng sức khoẻ của người bệnh
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, including a quantitative Bilirubin test, which helps detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/cause liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory, subclinical; risks affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer To register for examination and treatment of hepatobiliary diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.