This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi My - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.In the process of destroying red blood cells and secreting in bile, a yellow pigment called bilirubin is produced. Patients with hepatobiliary disease or children after birth often have jaundice, yellow eyes, however, there are many other diseases that also lead to this symptom. Bilirubin test helps to diagnose specifically the cause of jaundice and yellow eyes in patients.
1. What is a bilirubin test?
Bilirubin is a yellow-orange pigment that is a waste product of the normal breakdown of red blood cells in the blood. Bilirubin passes through the liver and eventually leaves the body. The Bilirubin test is used to check the level of bilirubin in the blood.Most laboratories will measure bilirubin levels directly. Then, the total amount of bilirubin in the body is subtracted from the direct amount, thereby estimating the amount of indirect bilirubin or can do 3 types of total, direct and indirect Bilirubin.
Direct or indirect bilirubin levels greater than normal suggest a variety of liver diseases. Usually, a high bilirubin level indicates an increased rate of red blood cell damage.
Types of Bilirubin test:
Blood Bilirubin: is a form of testing Bilirubin levels through Bilirubin blood index Amniocentesis: is a test for pregnant patients, Bilirubin can be measured through fluid amniotic fluid. Bilirubinuria: Can be measured in the urine (urine bilirubin test). Normally the urine will not contain Bilirubin, but if the results indicate yes, the doctor will order further tests to find out the specific cause. The amount of Bilirubin that appears in the urine often predicts a state of stagnant Bilirubin, which has not been eliminated from the body by the liver. Either way, the risks associated with a bilirubin test are minimal.
2. What is the bilirubin test for?
Sometimes bilirubin is measured as part of routine tests. The concentration of bilirubin in the blood of men may be slightly higher than that of women. African-Americans have lower blood bilirubin levels than other American groups.In older children and adults, the bilirubin test is done to:
Diagnose and monitor liver-related diseases such as gallstones, cholecystitis, cholestatic hepatitis, cholangiocarcinoma, .. Evaluation for sickle cell disease or other conditions causing hemolytic anemia. Some genetic diseases, such as Gilbert's syndrome, affect how the liver processes bilirubin. Although jaundice can occur in some people with Gilbert's syndrome, the condition is not usually dangerous. Diseases that cause obstruction of the biliary tract such as gallstones, cholangiocarcinoma, cholestatic hepatitis or pancreatic cancer. Rapid destruction of red blood cells in the blood, such as sickle cell disease or an allergy to blood received from a blood transfusion. In neonates:
Bilirubin is used to diagnose jaundice in the first 24 hours after birth; Severe bruising at birth; Testing Bilirubin blood levels for timely treatment before excess unconjugated bilirubin causes damage to the child's brain cells, resulting in mental retardation, impaired learning and development. development, hearing loss, eye movement disorders, and even death. In the fetus:
Bilirubin may be measured in the amniotic fluid if the doctor thinks the fetus has a condition that destroys red blood cells.

3. When should a bilirubin test be performed?
Doctors usually order a bilirubin test along with other tests when there are unusual signs of:Symptoms of jaundice; History of excessive alcohol consumption; Suspected drug poisoning; Hepatitis virus exposure; Dark amber urine; Nausea, vomiting; Suspected abdominal pain (right lower quadrant, head of the pancreas, common bile duct,...); Fatigue and lethargy accompany chronic liver disease. If hemolytic anemia is suspected, this should be done with other tests to evaluate hemolysis.
4. Attention when performing Bilirubin test?
4.1. Before the test Before testing the bilirubin level in the blood, it is necessary to:Avoid strenuous exercise because it can increase the bilirubin level. Drugs such as barbiturates, penicillins, and high doses of salicylates should be avoided because they lower blood bilirubin levels, and the HIV antiviral drug Atazanavir can increase bilirubin levels indirectly. You should not eat or drink for 4 hours before the test. No special preparation is required in young children when testing for bilirubin. Tell the doctor if the patient is allergic to the medicine; or bleeding; taking anticoagulants such as aspirin, clopidogrel (Plavix), or warfarin (Coumadin); There is a risk of pregnancy. 4.2 Procedure for performing a bilirubin test Step 1: Wrap a bandage around your arm to stop the blood from circulating.
Step 2: Disinfect the injection area with medical alcohol
Step 3: Inject a needle into the vein to get the right amount of blood for the test
Step 4: Remove the bandage around the hand after taking enough blood. Apply an alcohol-soaked gauze or cotton swab to the injection site.
Step 5: Stick a bandage on the injection site for 10-20 minutes to help stop bleeding, avoid lifting objects with your hands after testing.
Step 6: Collect blood into sterile test tubes for storage.
Step 7: Blood is sent to a laboratory to determine Bilirubin levels.
5. How to read the results
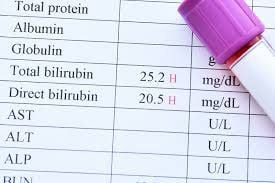
Normal values for direct bilirubin range from: 0 – 0.3 mg/dl. Normal values for total bilirubin (both direct and indirect) range from: 0.3 to 1.9 mg/dl. Indirect Bilirubin Values: 0.1 - 1.0 mg/dL In Newborns:
Normal Bilirubin: Less than 5 mg/dl, but more than 60% of newborns have jaundice and bilirubin levels more than 5 mg /dl. 5.2 When is an abnormal result Bilirubin is abnormal when:
Direct Bilirubin is greater than 0.3 mg/dL Total Bilirubin is greater than 1.9 mg/dL. These results vary slightly by laboratory and are mostly for adult men.
Normal results for women and children may vary slightly, and results will be affected by certain foods, medications or strenuous exercise.
Master. American doctor has more than 6 years of experience as an internal medicine doctor at Hue Central Hospital, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital; Tam Tri Da Nang Hospital; Danang Hospital. Currently, he is a General Internal Medicine Doctor at Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.














