Article by Master of Science, Doctor Mai Viễn Phương - Endoscopy Specialist, Department of General Medicine & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Pain on the right side of the chest can occur for several reasons. However, most chest discomfort is not related to the heart. In fact, right-sided chest pain is rarely a result of a heart attack. So, what are the main causes of chest pain?
1. Potential Risks Causing Chest Pain
The chest houses several organs and tissues that can become inflamed or injured, resulting in pain. Most discomfort in this area is likely due to muscle strain, infection, stress, or anxiety, rather than heart-related issues.
Left-sided chest pain is often associated with heart attacks. If you feel pain on the right side, it is less likely to be heart-related. However, you should seek immediate medical attention if you:
- Experience severe, unexplained, and sudden chest pain.
- Feel pressure, tightness, or squeezing in the chest.
- Have intense pain radiating to the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Break into a cold sweat.
- Feel weak, dizzy, or nauseous.
- Experience shortness of breath.
Any of these symptoms may indicate a serious or life-threatening condition, and urgent medical care is essential.
2. Stress or Anxiety Causing Chest Pain
Certain anxiety disorders or extreme stress can trigger panic attacks, often mimicking heart attack symptoms. Panic attacks may occur randomly or be triggered by stressful or traumatic life events. Symptoms of anxiety and panic attacks include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Chest pain.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Dizziness.
- Numbness in the hands or feet.
- Sweating.
- Trembling.
- Fainting.
Panic attacks can cause chest pain due to hyperventilation (rapid or deep breathing), which leads to muscle spasms in the chest wall. Anxiety or stress-induced pain can occur on either side of the chest. Since the symptoms of panic attacks resemble those of heart attacks, seeking immediate medical evaluation to rule out heart-related issues is recommended.

3. Muscle Strain Causing Chest Pain
Injury or overexertion can strain muscles, which is one of the most common causes of pain on either side of the chest. Muscle strain can occur due to intense upper body activity, such as playing sports, overusing muscles while painting a ceiling, chopping wood, or performing other strenuous activities. Muscle pain can also develop gradually due to stress or anxiety.
In most cases, over-the-counter pain relievers and rest are sufficient to alleviate symptoms.
4. Chest Trauma
Chest pain can also result from tearing of the chest muscles, often caused by indirect trauma or a direct blow to the chest. Blunt trauma can also lead to rib fractures or potential rib displacement. Symptoms of chest trauma or rib displacement include:
- Chest pain worsening with coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
- Shortness of breath.
- Bruising.
- Swelling.
- Tenderness.
- If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a doctor to determine whether your injury will heal on its own or requires treatment.
5. Indigestion or Heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest after eating, bending over, exercising, or lying down at night. This condition is usually caused by acid reflux, where stomach acid backs up into the esophagus.
In addition to chest pain, you may feel a burning sensation in the throat, difficulty swallowing, or a sensation of food being stuck in the throat or chest. You may also notice a sour, salty, or acidic taste at the back of the throat. While indigestion rarely causes chest pain, it may accompany heartburn. Symptoms of indigestion include:
- Nausea.
- Feeling full too quickly and discomfort after eating.
- Pain, discomfort, and burning in the upper abdomen.
- Bloating.

6. Acid Reflux
Acid reflux occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus. This condition can cause:
- Heartburn.
- Abdominal pain.
- Burping.
- A sour taste in the mouth.
If you experience acid reflux more than twice a week, you may have developed gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Symptoms of GERD, in addition to chest pain, include:
- Heartburn.
- Sore throat or hoarseness.
- A lump-like sensation in the throat.
- Dry cough and difficulty swallowing.
Though home remedies may provide relief, it is best to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Medications may be prescribed to treat or prevent symptoms.
7. Costochondritis
Chest pain is a primary symptom of costochondritis, which occurs when cartilage in the rib cage becomes inflamed. The pain may range from mild to severe and is usually felt on the left side of the chest, but it can also occur on the right.
The discomfort caused by costochondritis may resemble that of a heart attack or other heart-related conditions. Seeking emergency care to rule out life-threatening causes is recommended.
8. Cholecystitis (Gallbladder Inflammation)
Cholecystitis occurs when bile builds up in the gallbladder, often due to gallstones blocking the exit duct. Inflammation can also result from bile duct issues or tumors.
If your gallbladder is inflamed, you may feel intense pain in the upper right abdomen, which can radiate to the right side. Other symptoms include:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Fever.
- Sweating.
- Loss of appetite.
- Tenderness when the abdomen is touched.
If you experience these symptoms, consult a doctor for diagnosis.
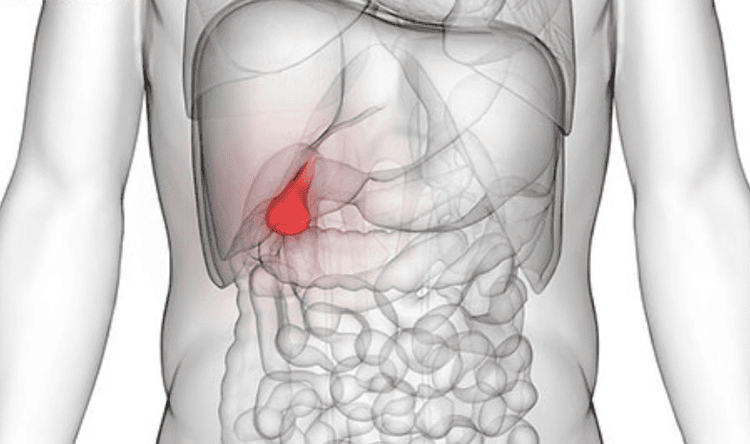
9. Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis occurs when digestive enzymes activate while still in the pancreas, causing inflammation. Common causes include alcoholism or gallstones. Although chest pain is not a symptom of pancreatitis, upper abdominal pain may radiate to the back, increasing chest discomfort. Additional symptoms of acute pancreatitis include:
- Abdominal pain worsening after eating.
- Fever and rapid pulse.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Abdominal tenderness.
Chronic pancreatitis may lead to greasy stools and unexplained weight loss.
10. Shingles
Shingles is an infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which also causes chickenpox.
While shingles does not directly cause chest pain, it may mimic heart or lung issues depending on the affected area. Symptoms, apart from a rash, include:
- Pain.
- Burning.
- Tingling or numbness.
- Sensitivity to touch.
- Fluid-filled blisters that rupture and crust over, causing itching.
Though home remedies may provide some relief, it is advisable to consult a doctor for diagnosis and antiviral medication.
11. Pleurisy
Pleurisy occurs when the pleura (the lining of the chest cavity) becomes inflamed, causing pain on either side of the chest during breathing. Pain may also occur in the shoulders and back. Symptoms include:
- Chest pain worsening with coughing, sneezing, or laughing.
- Shortness of breath if you limit breathing to minimize discomfort.
- Fever or cough if the pleurisy is caused by a lung infection.
Seek medical evaluation to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
12. Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an infection of one or both lungs, often causing coughing, sometimes with phlegm, leading to pain on either side of the chest. Pain may also occur during breathing. Other symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Fever.
- Sweating.
- Shaking chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
If left untreated, pneumonia can be fatal.
13. Pneumothorax (Collapsed Lung)
Sudden, sharp chest pain is a key symptom of pneumothorax, which can occur on either the right or left side of the chest, often due to trauma. Additional symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath.
- A feeling of chest tightness.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Fatigue and coughing.
14. Inflammation in the Heart
Two types of heart inflammation can cause chest pain: myocarditis and pericarditis. Myocarditis refers to inflammation of the heart muscle, while pericarditis involves inflammation of the pericardium (the sac-like tissue surrounding the heart). Both conditions are typically caused by infection and may result in mild to severe chest pain.
Symptoms of myocarditis and pericarditis overlap and include:
- Fever.
- Weakness.
- Shortness of breath.
- Cough.
- Rapid heartbeat.
- Fatigue.
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen.
Pericarditis can cause chest discomfort intense enough to feel like a heart attack. Seek emergency care for severe chest pain.
15. Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension refers to high blood pressure in the heart-lung system. This condition can force the heart to work harder, causing widespread chest pain. Symptoms include:
- Shortness of breath during regular activity.
- Lightheadedness, especially during physical exertion.
- Fatigue.
- Pain in the upper right abdomen.
- Loss of appetite.
- Fainting.
- Swelling in the ankles or legs.
- Bluish skin or lips.
If you experience these symptoms, seek a diagnosis to manage symptoms and prevent complications.

16. Pulmonary Embolism
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot travels from a vein in the leg to the lungs, causing a sudden blockage in the artery. This can result in chest pain that may radiate to the arms, jaw, shoulders, and neck.
Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening if untreated. Seek immediate medical care if you experience these symptoms.
If you are concerned about right-sided chest pain lasting more than a few days, consult a doctor. While mild causes like acid reflux are common, serious conditions such as pulmonary hypertension should not be ruled out. A thorough evaluation will enable proper treatment of the underlying cause.
Chest pain can be caused by a wide variety of factors. Therefore, if you experience any unusual health symptoms, it is advisable to undergo a comprehensive health examination to assess your overall health status. This will allow for an accurate evaluation and the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital, with a team of experienced specialists and state-of-the-art equipment, has achieved significant success in diagnosing and treating various conditions, earning trust from both professionals and patients.
To arrange an appointment, please call … or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.