This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, eating raw meat has become an unfamiliar habit in many culinary cultures around the world. However, there are certain concerns and implications for us in terms of food safety.
1. Dangers of eating raw meat
Based on nutritional and biochemical reports, in general, when eating rare, raw meat, the greatest risk you can face is food poisoning.
The cause of food poisoning is largely due to ingesting food contaminated with bacteria, viruses, parasites or toxins. Usually, this contamination occurs during slaughter, if an animal's intestines are accidentally punctured and the spread of harmful pathogens to the meat or storage conditions are inadequate.
Common pathogens that can cause botulism in raw meat include Salmonella , Clostridium perfringens , E. coli , Listeria monocytogenes and Campylobacter .
Symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach cramps, fever and headache. These symptoms usually appear within 24 hours and can last up to 7 days - or longer in certain cases depending on the causative agent.
Certain groups of people are at high risk for food poisoning when eating raw meat, such as children, pregnant or lactating women, and the elderly.
2. Some popular raw meat dishes
Currently, in the world, there are some typical raw meat dishes such as:
Steak tartare: Minced raw beef steak mixed with egg yolks, onions and spices Tuna tartare: Uncooked chopped tuna mixed with herbs and spices Carpaccio: Italian dish made with thinly sliced raw beef or fish Pittsburgh Steak: Steak that's been undercooked on the outside and whole on the inside. Mett: A German dish of raw minced pork seasoned with salt, pepper and garlic or caraway Several types of sushi : Traditional Japanese dish Made with lean fish, vegetables and avocado, sushi can be one way Good for vitamins and omega-3 fatty acids. But sushi can have bacteria and parasites that cause vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain. Ceviche: Minced raw fish marinated with citrus juices and spices. Like sushi, it has the potential to have bacteria and parasites that can cause food poisoning Torisashi: A Japanese dish consisting of thin pieces of chicken that are lightly cooked on the outside and raw on the inside.
These dishes are found on the menus of many restaurants, including high-end, but that does not mean they are safe. Often, raw meat dishes in restaurants will come with the small warning "Eating raw or undercooked meat, poultry, seafood, shellfish or eggs may increase your risk of food poisoning. "
Besides, raw meat dishes can still be prepared at home. In this case, a hygienic source of raw materials is extremely important.
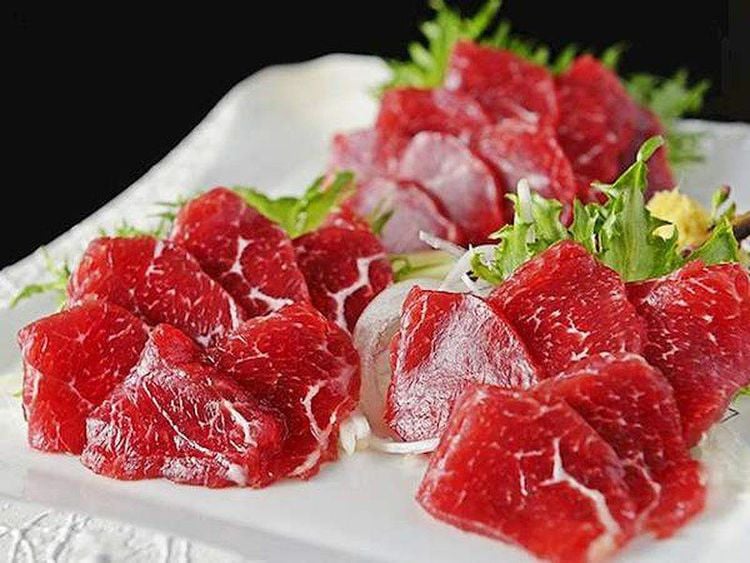

Ăn thịt sống cần đảm bảo an toàn vệ sinh thực phẩm
3. The truth about eating raw meat
Although many people believe that eating raw meat is better than cooked meat in terms of nutritional value and health, there is little evidence to support this view.
Some anthropologists theorize that cooking food, especially meat, played an important role in human evolution, as cooked food would contain more protein than size shorter, making it easier to chew and digest.
Although processing can reduce levels of several vitamins and minerals, including thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium and phosphorus, levels of copper, zinc and iron will increase after cooking.
Remember, any benefit of eating raw meat needs to be weighed against the higher risk of illness from raw food.
4. What can be done to reduce the risk of eating raw meat?
Although eating raw meat is not guaranteed to be safe, there are some tips to reduce the risk of disease.
When enjoying raw meat, choose whole cuts of meat, such as steak or home-ground meat, instead of prepackaged minced meat. This is because pre-minced beef can contain more impurities or the area at risk of contamination is greater than whole cuts of meat.
The same phenomenon holds true for other meats, such as fish, chicken and pork.
In a way, choosing raw fish is another way to reduce risk. Raw fish is likely to be safer than other types of raw meat, as it is often frozen immediately after being caught to limit the growth of some harmful pathogens.
On the other hand, chicken if eaten raw will be more dangerous. Compared to other meats, chicken tends to contain more harmful bacteria like Salmonella. Chicken also has a more porous structure, allowing pathogens to penetrate deep into the meat. Therefore, even cooking the surface of raw chicken will not kill all pathogens.
In summary, to completely avoid the risk of certain diseases caused by eating raw meat, cook pork, beef and fish to a minimum internal temperature of 63°C, ground meat to 71°C and poultry to at least 74 degrees Celsius.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: healthline.com, webmd.com