This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by MSc Vu Thi Duyen, Doctor of Nephrology - Endocrinology, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International Hospital
Diabetes mellitus is a heterogeneous metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia due to both defects in insulin secretion and insulin action. People with diabetes for a long time and poor blood glucose control will cause a lot of complications for themselves. Includes acute and chronic complications.
1. Dangerous acute complications with the risk of death
1.1. Ketoacidosis Ketoacidosis is a toxic state caused by acidosis of the blood, due to increased acidity, which is the product of incomplete metabolism caused by insulin deficiency. The patient can die if not treated promptly. This is a medical emergency requiring aggressive treatment. Common in patients with type 1 diabetes who quit treatment or have type 1 diabetes that has not been detected and treated in time.
Clinical
Signs of diabetes: frequent urination, increased thirst, increased appetite, and weight loss Signs of ketoacidosis include: + Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and hyperventilation (breathing rapidly and deeply, Kussmaul breathing pattern).
+ Severe generalized dehydration.
+ More severe with hypothermia, disturbances of consciousness at different levels.
Nhiễm toan ceton với biểu hiện mất nước toàn thể nặng
1.2. Increased osmotic pressure Too high blood sugar can cause coma due to increased osmotic pressure, this is the most serious and very fatal complication that requires the patient to be treated immediately.
Clinical:
Signs of diabetes: frequent urination, increased thirst, increased appetite and weight loss, varying degrees of consciousness disorder.
Signs of increased osmolality include:
+ Blood glucose > 33.3 mmol/L (> 600 mg/dL)
+ No ketones in urine or very mild
+ Blood osmolality > 330 mOsm/kg
+ Severe total dehydration
1.3. Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia is abnormally low blood sugar that is potentially damaging to patients with a blood glucose threshold of ≤ 70 mg/dL (≤ 3.9 mmol/l). This is a very common complication in diabetic patients. Complications of hypoglycemia: + Death if not detected and treated early.
+ Coma.
+ Cardiovascular complications.
+ Loss of consciousness.
+ Dementia, reduced quality of life.
When you have low blood sugar, you must immediately put a sugar into the body by mouth (eating sweets, drinking milk, sugar water ...) or glucose infusion. Immediately discontinue antidiabetic drugs and consult an endocrinologist for dose adjustment.

Khi bị hạ đường huyết người bệnh nên bổ sung nước ngay
2. Chronic complications
2.1 Cardiovascular complications Diabetes increases the risk of high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, causing paralysis or death.
2.2 Kidney Complications Diabetes causes damage to the small blood vessels in the kidneys leading to kidney failure or kidney failure. Kidney disease is more common in people with diabetes than in those without. Maintaining normal blood glucose levels and blood pressure significantly reduces the risk of kidney disease.
2.3 Nerve complications Nerve damage: is a common complication and often appears early in people with diabetes. Diabetes can cause nerve damage throughout the body when blood glucose and blood pressure are too high. Manifestations in the extremities: numbness, loss of sensation or disturbances of sensation, muscle atrophy, pain, malnutrition and ulceration due to malnutrition are the risk of infection leading to amputation (removal of part of a limb). .. Injury to the cranial nerve can cause ptosis, strabismus, and facial paralysis. Damage to the autonomic nerves can also cause myocardial infarction, bladder paralysis, impotence, digestive disorders... Visual complications: Most people with diabetes will develop some type of disease. vision loss or blindness. Persistently high blood glucose levels along with elevated blood pressure and high cholesterol are the main causes of retinopathy. This condition can be controlled through regular eye exams, keeping blood glucose levels and blood pressure close to or normal. 2.4 Risk of infection High blood sugar is a favorable environment for bacteria to grow, and at the same time weakens the body's immune system, so it is easy to get infections such as gum, urinary or genital infections, long-lasting sores... Inflammation is often long-lasting, persistent and difficult to treat...
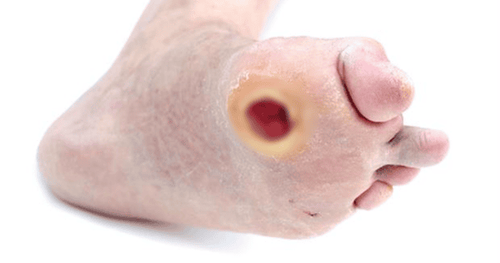
Vết loét lâu liền là biến chứng mạn tính của đái tháo đường
3. Complications during pregnancy
High blood glucose during pregnancy can lead to an overweight fetus. This easily leads to obstetric complications for children and mothers; the risk of sudden hypoglycemia in the newborn baby; Children exposed to high blood glucose during pregnancy have a higher risk of developing diabetes in the future than other children.
In addition to the above complications, high blood sugar can also damage many other organs of the body such as bones, joints, brain, memory loss or skin diseases...
In order to limit complications, all diabetic patients need to see an endocrinologist periodically to screen for early complications and advise on follow-up treatment.
If there are signs of suspicion of diabetes, you should immediately see an endocrinologist.

Mẹ bầu nên đên gặp bác sĩ để được tư vấn và điều trị kịp thời
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE ALSO:
Ketosis in patients with diabetes The role of blood glucose measurement What does the glucose test during pregnancy mean for the fetus and pregnant woman's health?