This is an automatically translated article.
What does Zodalan do, is it an anesthetic? In fact, Zodalan is an anesthetic, used for pre-anesthesia, anesthesia and maintenance of anesthesia. Zodalan is also combined with other sedatives to perform diagnostic procedures.
1. What does Zodalan do?
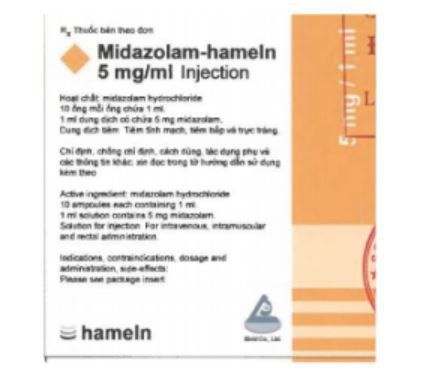
Zodalan belongs to the group of anesthetics and anesthetics, with the main ingredient being Midazolam 5mg. Midazolam has a sedative effect, calms anxiety. In addition, it has muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects.Zodalan is prepared in the form of a solution for injection and is indicated for use in pre-anesthesia, anesthetic induction or maintenance anesthesia. In addition, the drug is also used alone or in combination with other sedative drugs to conduct diagnostic, endoscopic, and cardiac catheterization procedures.
2. How to use and dose Zodalan
Zodalan is administered by injection, can be injected intramuscularly or intravenously. To make sure medication is safe for the patient, it needs to be injected by a healthcare professional or doctor.
Depending on the purpose of use, the specific dose of Zodalan is as follows:
Pre-anesthesia: About 5 - 10 minutes before the procedure, intravenously with a dose of 2.5mg. In case it is necessary to have a repeat injection with a dose of 1mg, the maximum total dose should not exceed 5mg. Elderly patients take a dose of 1 - 1.5 mg. Or can be injected intramuscularly 30 minutes before surgical surgery for surgery, the dose of Zodalan is calculated according to the patient's weight, specifically adults use a dose of 0.07 - 0.1mg/kg, children use a dose of 0. ,15 - 0.20mg/kg. Induction: Intravenous 10 - 15mg. Children injected intramuscularly at a dose of 0.15 - 0.20 mg/kg body weight in combination with ketamine 4 - 8 mg/kg body weight. Maintenance of anesthesia: The maximum dose is from 0.05 to 0.4mg/kg body weight/hour.
3. Zodalan side effects
Zodalan medicine can cause some unwanted side effects with seriousness such as apnea, respiratory failure, cardiac arrest. This side effect can occur when the drug is taken in high doses or given too quickly.
Here are some possible side effects when taking Zodalan with an unknown frequency:
Immune system: Angioedema , increased sensitivity, anaphylaxis. Nervous, psychiatric: Hyperactivity, convulsions, epilepsy, sedation, drowsiness, decreased alertness, dizziness, headache, memory loss, confusion, ataxia. Anxiety, delusions, euphoria, excitement, aggression, substance abuse, withdrawal syndrome. Cardiovascular: Zodalan may cause bradycardia, cardiac arrest, hypotension, vasodilation, venous occlusion, thrombosis. Respiratory: Respiratory depression, hiccups, laryngospasm, dyspnea, apnea. Gastrointestinal: Dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, constipation. Skin: Itching, urticaria, rash, pain or erythema at the injection site. Bones: Broken bones, easy to fall. If you have any strange symptoms after taking Zodalan, you should report it to your doctor immediately.
4. Some notes when using Zodalan medicine
Do not use Zodalan in people with hypersensitivity to the ingredients of the drug, people with liver failure, alcohol poisoning, acute or chronic lung disease, respiratory failure, congestive heart failure, coma, shock or side effects. Women who are pregnant in the first 3 months. Zodalan should not be injected into the arachnoid or epidural space. If Zodalan is taken regularly in high doses or abused, it can cause drug dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Zodalan can cause forgetfulness for a short period of time, patients do not remember the most recent events, when the drug has the strongest effect. Zodalan should be used with caution in patients with respiratory failure for the purpose of conscious sedation. Using Zodalan in children under 6 months of age can cause airway obstruction and reduce ventilation. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust the dose to a low level to both ensure clinical effectiveness and keep the child's breathing rate, and at the same time, it is necessary to monitor oxygen saturation. Monitor patients after injecting Zodalan as pre-anesthesia, because each patient's sensitivity to the drug is different. Elderly people, people with chronic diseases (respiratory, kidney failure, liver failure, heart failure), children under 6 months old, need to be very careful when using Zodalan. Particular caution should be exercised in patients with myasthenia gravis. If stopping Zodalan suddenly can cause withdrawal syndrome with manifestations such as muscle pain, headache, irritability, insomnia, nervousness, nervousness, restlessness, confusion, convulsions, hallucinations, mood change. In order not to experience withdrawal symptoms, it is best to reduce the dose slowly before stopping using the drug. If Zodalan is used in high doses and injected quickly, it can cause symptoms such as hyperactivity, anxiety, aggression, anger, and excitement. Adjust the dose of Zodalan in patients receiving concomitant medications that induce or inhibit CYP3A4, hepatic impairment, neonates, and patients with low cardiac output. Premature infants and patients with a history of preterm birth should be used with caution when taking Zodalan because of the risk of respiratory arrest. It is necessary to monitor the patient's ventilation status for prompt emergency management. Do not give rapid injections to infants, especially children with cardiovascular disease. Zodalan is not indicated for resuscitation and intensive care in infants under 6 months of age because of the risk of airway obstruction and hypoventilation. Zodalan must not be used together with alcohol or other central nervous system depressants. Do not drink alcohol or alcoholic beverages for at least 12 hours after the injection. If pain medication is required, the patient should take it before injecting Zodalan. People with a history of alcoholism or drug abuse should avoid taking Zodalan. Do not drive or operate or operate machinery for at least 12 hours after injecting Zodalan. An increased risk of increased intracranial pressure may occur with the use of Zodalan in patients with acute nerve damage. Co-administration of Zodalan with sedatives or CNS depressants may increase sedation and respiratory depression. Zodalan also reduces alveolar concentrations when administered with inhalation anesthetics. The use of Zodalan is pre-anesthesia, anesthesia and maintenance anesthesia. Zodalan can be used together with other sedative-hypnotics for diagnostic medical procedures.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.