This is an automatically translated article.
Volatile anesthetics through inhalation due to their volatile properties, easy absorption into the body and quick effects, the drug is often used to induce anesthesia, replacing injectable drugs.
1. Anesthesia evaporates through inhalation
Depending on the method of giving anesthetics into the body, they are divided into 2 types, including:
Intravenous anesthetics Inhalational anesthetics Inhalational anesthetics are used to maintain anesthesia but drugs can also used to induce anesthesia, especially in children. Inhalation anesthetics include 2 types:
Gaseous Volatile: Isofluran, halothan, sevoran... Volatile anesthetics through inhalation due to their characteristics of being volatile, easily absorbed into the body, and fast acting. Therefore, the drug is often used to induce anesthesia, instead of injectable drugs. In addition, anesthetic volatile through inhalation also has a sedative effect, has a muscle relaxant effect. Compared with other anesthetics, inhalation anesthetics also act more quickly. In some recent studies, inhalation anesthetics, especially volatile anesthetics, are widely used in the treatment of insomnia. However, if used more than 3 times, it will have a bad effect on the patient.
Thuốc mê bay hơi qua đường hô hấp Halothan
2. Indication of volatile anesthetics via inhalation
Indications for the use of volatile anesthetics through inhalation include:
Use to maintain anesthesia in surgery for adults and children Use for outpatient anesthesia Can be used to induce anesthesia
3. Contraindications for inhalation anesthetics
Contraindications to the use of volatile anesthetics through inhalation in the following cases:
Patients with a history of malignant high fever after taking the drug Allergy to the drug Sensitivity to the drug Patients with increased intracranial pressure Patients with porphyria Patients with jaundice Patients with chronic liver disease Women under 6 months of pregnancy Patients with hepatitis caused by halothan Patients with heart failure Women who are breastfeeding

Bệnh nhân bị vàng da không nên sử dụng thuốc mê bay hơi qua đường hô hấp
4. Mechanism of action of volatile anesthetics through inhalation
Currently, the mechanism of action of volatile anesthetics through inhalation has not been determined. In the CNS, various ion channels are thought to play a role and have been shown to be sensitive to volatile anesthetics.
Although the exact mechanism of volatile anesthetics has not been determined, several factors are considered to affect absorption, including:
Blood gas distribution coefficient: Absorption of anesthetic into blood will be lower when the drug has a lower solubility in the blood. When body temperature is lowered and blood lipids increase, the solubility of volatile anesthetics in the blood will be increased. Concentration of inhaled anesthetic: Circulatory ring size, rate of new air flow and anesthetic gas uptake by circuit components will affect the concentration of inhaled anesthetic Air alveolar ventilation: Anesthesia transport or absorption can be altered by increasing minute ventilation, keeping other parameters Concentration effect: If large amounts of anesthetic are absorbed by the body, alveolar space is created for inhalation As a result, the tidal volume is increased and the anesthetic concentration in the alveoli is also increased. Second gas effect: The density effect leads to this result Cardiac output: An increase in cardiac output will increase anesthetic absorption and vice versa. In particular, this is more pronounced for highly soluble anesthetics or closed breathing systems. Difference between alveolar and venous blood concentrations of anesthetic: If there is a difference in partial pressure of the drug anesthesia between the alveoli and the pulmonary blood stream, the absorption of anesthetic into the blood is reduced.
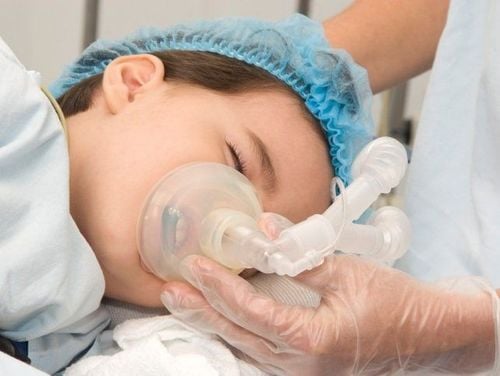
Bệnh nhân được hít thuốc mê bay hơi qua đường hô hấp
5. Undesirable effects when using volatile anesthetics through inhalation
Anesthetics are usually quite safe if used in the right dosage, but if used in excess, side effects can occur and the severity will depend on the dose used.
Volatile anesthetics through inhalation can cause some unwanted effects on patients, for example:
May cause patients to forget and lose consciousness Inhibits electrical and nerve activity Central causes respiratory depression, dose-dependent respiratory depression Patient may develop cough, hiccups Patient has bronchospasm Patient blood pressure drops Patient has cardiac arrhythmias Vomiting, nausea after awakening Chills Sugar stimulated breathing under superficial anesthesia causes coughing, constriction of the larynx or trachea, especially in patients with asthma or a smoker Increased myocardial sensitivity Inhibits and causes systemic vasodilation
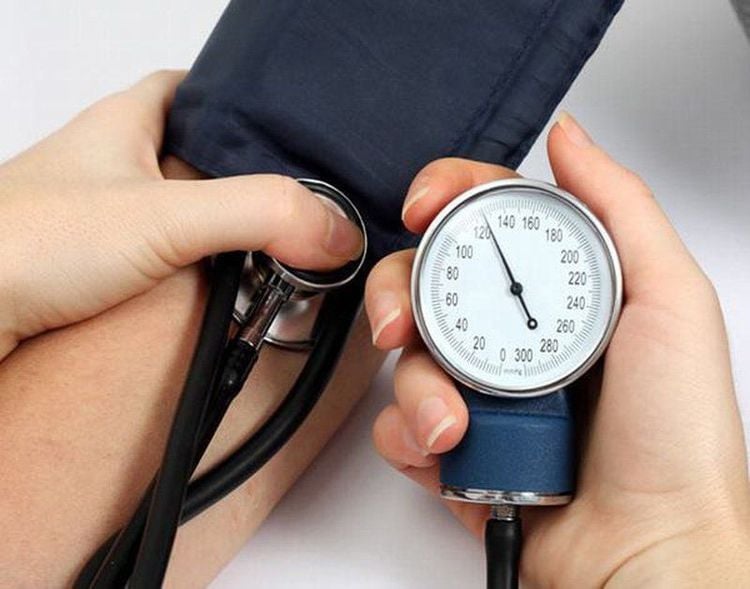
Bệnh nhân có thể bị hạ huyết áp
In fact, anesthetics are considered quite safe to use. However, the lack of knowledge about the drug as well as the incorrect use of the drug will lead to unwanted effects, which can even be life-threatening. Therefore, it is necessary to be very careful and careful when using volatile anesthetics through inhalation in particular and anesthetics in general.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.