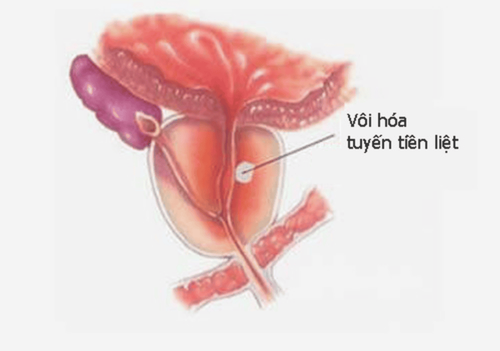
Prostate calcification is the condition of calcium deposits in the prostate gland. Usually, this condition does not cause any symptoms and does not require treatment. However, if complications arise or the condition is associated with other prostate diseases, treatment is necessary.
1. Prostate Calcification and Treatment Options
Prostate calcification is often related to chronic prostatitis, a relatively common condition in middle-aged men. When the calcification nodules are small or in early stages, they usually do not cause discomfort and are often discovered incidentally during ultrasound or X-ray examinations.
If the calcified nodules are small and asymptomatic, treatment is not necessary. Instead, preventive measures against prostate infections and regular monitoring for the progression of calcification are recommended.
When calcification leads to prostatitis or coexists with other prostate conditions, treatment becomes necessary. The available treatment options include medical (non-surgical) and surgical methods.
1.1 Medical Treatment
Calcified nodules in the prostate can harbor microorganisms, increasing the risk of prostatitis.
- Oral Antibiotics
Oral antibiotics are primarily used to eradicate bacterial infections, particularly effective in acute cases. However, for chronic cases, the efficacy of oral antibiotics is limited due to poor penetration of prostate tissue and bacterial resistance.
For chronic prostatitis, recurrence is possible after stopping antibiotic treatment.
Patients are advised not to self-medicate by altering the drug or dosage, as this can harm liver and kidney function. In cases of recurrent infections, surgical intervention may be considered.
- Injectable Antibiotics
Injectable antibiotics are administered directly into the prostate to support oral antibiotics, as oral drugs have limited tissue penetration. Despite its effectiveness, prolonged injectable antibiotic therapy can also lead to bacterial resistance. Similar to oral antibiotics, injections can treat bacterial infections but cannot dissolve calcified nodules.
Intraprostatic injections are considered an adjunct to oral antibiotics. Because oral antibiotics are not absorbed to sufficient concentrations in the prostate, intraprostatic injections provide higher concentrations. However, clinical cases over the years have shown that intraprostatic injections are also discouraged because they do not completely heal prostate calcifications.
- Physical Therapy
In addition to medication, physical therapy methods also provide significant benefits. These techniques improve blood circulation within prostate tissue, facilitating better antibiotic penetration, relieving congestion, and reducing the risk of infections.
Physical Therapy such as Local Massage Therapy
Or Ultrasound Therapy. The UT method delivers deep heat to prostate tissue, improving blood circulation. However, it may aggravate inflammation and cannot eliminate bacteria. Therefore, ultrasound therapy serves as a supportive measure during treatment and helps prevent complications.
1.2 Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for prostate calcification is indicated when:
- Large calcified nodules cause complications, such as impaired sexual function or recurrent chronic prostatitis that is unresponsive to medical treatment.
- Prostate calcification is associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) requiring surgical intervention. In such cases, calcified nodules are removed simultaneously during prostate surgery.
- Biopsy reveals malignant cells within calcified nodules.
Surgical Methods: Depending on the specific condition, options include transurethral resection (endoscopic surgery) or open surgery.
2. Preventive Measures for Prostate Calcification

Preventive measures include:
- Adequate Hydration: Drink sufficient water daily.
- Personal Hygiene: Maintain regular hygiene of the body and genital area to minimize infections.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Limit alcohol, caffeine, tobacco, and other stimulants.
- Sexual Health: For individuals with partners, maintaining regular sexual activity can reduce prostate congestion.
- Physical Exercise: Daily physical activity, especially pelvic-focused exercises like walking and yoga, is beneficial.
Regular follow-up is essential to detect abnormal symptoms early and initiate timely treatment. Treatment is only considered when calcification causes adverse symptoms.
Currently, there are no medications proven to dissolve calcified nodules; surgical removal remains the definitive treatment.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, the Urology Screening Package enables early detection and effective treatment of urinary diseases. The package includes
- Urology Specialist Consultation
- Ultrasound Examination of the Urinary System
- Total PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Measurement
- Free PSA Measurement
- Urine Culture
This screening package helps identify prostate-related conditions such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate cancer, and urinary stones, allowing for preventive measures and timely treatment to avoid severe complications.
For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.