This is an automatically translated article.
Hypoglycaemic coma is a medical emergency that can be serious and fatal. If low blood sugar is detected and treated in time, the patient can improve very well.
1. Recognize symptoms of coma due to hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is usually defined when blood sugar levels fall below 3.9 mmol/l (70 mg/dl). When the blood sugar level is below 2.8mmol/l (50mg/dl), severe symptoms of hypoglycemia appear.
Symptoms suggestive of hypoglycemia in the patient are: sudden fatigue, feeling of intense hunger, possibly accompanied by dizziness, headache, feeling anxious, panicky or agitated, psychosis.
The heart rate of people with hypoglycemia is often fast, sinus tachycardia, ventricular tachycardia or supraventricular tachycardia may be experienced, systolic blood pressure increased, may be accompanied by angina pectoris.
Hypoglycaemic coma is a severe stage of hypoglycemia, coma appears suddenly and without warning, followed by symptoms of hypoglycemia if not treated promptly. Hypoglycaemic coma is usually a quiet coma and a deep coma.
Symptoms often accompany coma such as: appearance of Babinski's focal neurologic signs on both sides, deep coma, decreased tendon reflexes, may appear generalized or partial convulsions, increased muscle tone.
Most cases have to think of hypoglycemic coma first when seeing a patient in a coma of unknown cause. If the patient is comatose due to hypoglycaemia, after intravenous administration of hypertonic sugar solution, the patient will wake up.
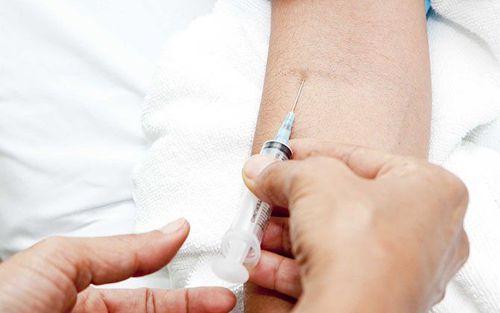
Tiêm đường ưu trương vào tĩnh mạch giúp bệnh nhân hạ đường huyết tỉnh lại
2. Causes of hypoglycemia leading to coma
Causes of hypoglycemia:
Fasting hypoglycemia Drug-induced hypoglycemia Alcoholic hypoglycemia β-cell tumor of the pancreas (Insulinoma) Hypoglycemia in liver and kidney disease... Malnutrition... , infection, dialysis Postprandial Hypoglycemia 2.1 Fasting Hypoglycemia Occurs 5-6 hours after eating with low glycemic index. Whipple triad appeared. The test shows that the blood sugar is low, the patient will wake up after making up for the sugar.
2.2 Drug-induced hypoglycemia History of using antidiabetic drugs, salicylates that inhibit glucose production, increase insulin secretion, quinine drugs, propranolol drugs, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide drugs...
2.3 Alcohol-induced hypoglycemia Decreased glycogen stores due to alcohol metabolism in the liver leads to decreased NAD, decreased gluconeogenesis, coma often smells of alcohol, and vitamin B1 deficiency may be present.

Rượu là một trong những nguyên nhân gây hạ đường huyết dẫn đến hôn mê
2.4 Hypoglycemia due to pancreatic β-cell tumors. β-cell tumors of the pancreas cause increased insulin secretion, inhibiting glycogenolysis. High blood insulin concentration, When the 72-hour fasting test showed that 75% of patients with hypoglycemia had an insulin concentration > 5 mcgU/mL, the amount of C peptide increased.
2.5 Postprandial Hypoglycemia The role of GLP, GLP-1 is to reduce the peak of insulin secretion in prediabetes, causing hypoglycemia after eating a lot of carbohydrates.
3. Treatment of hypoglycemia
Immediately stop the drug suspected to be the cause of the hypoglycaemia. Test capillary blood sugar immediately and take blood for venous blood sugar test.
In case the patient is awake (mild and moderate hypoglycemia), immediately give the patient sugar water or drinks containing sugar (honey...), do not use chemical sugars reserved for Diabetics, give the patient food to eat right after drinking sugar water.
In case of coma due to hypoglycaemia (severe): need to give emergency care by slow intravenous injection of 20% or 30% hypertonic glucose solution (due to coma, patient cannot drink sugar water), re-inject again until the patient regains consciousness. Formula for calculating the amount of glucose administered intravenously directly to the patient:
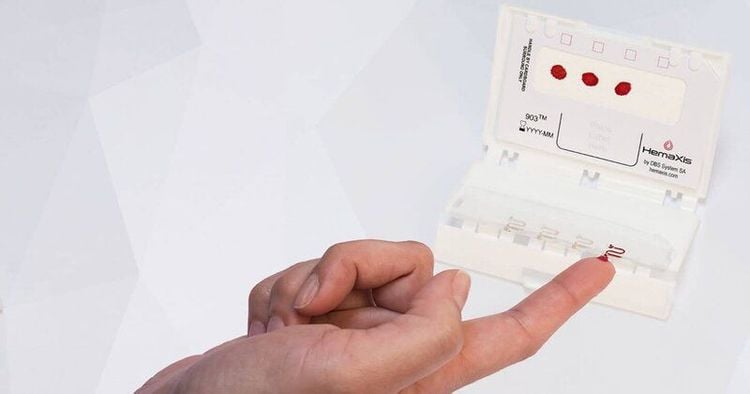
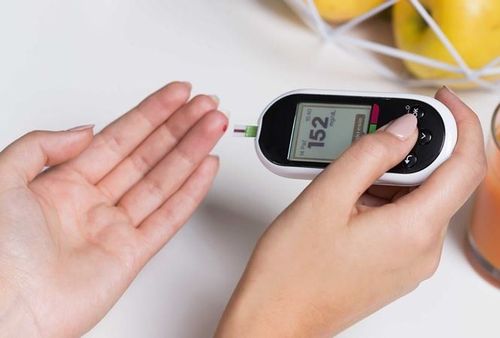
Xét nghiệm máu mao mạch đầu ngón tay để xác định tình hình hạ đường huyết
Amount of Glucose to be compensated = Patient weight (kg) x 0.2 x [Gbt - Gh] In which:
Gbt: plasma Glucose concentration to be achieved (eg 1 g/L) Gh: blood Glucose concentration at hypoglycaemia (eg, 0.2 g/L) Instituting an intravenous line of 10% or 5% glucose solution to maintain blood glucose above 5.5 mmol/l (100 mg/dl), avoiding the risk of recurrent hypoglycaemia .
Note, if the patient is using long-acting antidiabetic drugs, the hypoglycemia may persist, so maintain glucose infusion and blood sugar monitoring for at least 24-72 hours. depending on the pharmacokinetics of the drug used by the patient.
After emergency hypoglycemia, it is necessary to actively treat diseases that cause hypoglycemia such as liver failure, adrenal insufficiency, hypothyroidism, surgery, insulinoma secretagogue...
4. Prevention of coma due to hypoglycemia
Relatives and patients need to know the symptoms and early treatment of low blood sugar at home. Patients who are being treated with blood sugar-lowering drugs, if they appear lethargic, suspect hypoglycemia, they must stop the drug, immediately drink sugar water, suck on candy, etc. Hospital Diabetic patients need to follow the doctor's instructions on diet, drug use, and exercise regimen to avoid hypoglycemia complications during treatment. To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website for service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.