This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.I. Biopsy of vegetable spines
1. What is a spina bifida?
A placental biopsy is a procedure performed in the early stages of pregnancy to check for abnormalities in the fetus.The procedure is performed when the mother or father of the baby has a hereditary disease or the mother is over 35 years old, because when the mother is over 35 years old, it will increase the risk of the baby having birth defects.
Some of the diseases that can be detected by the spine biopsy include:
Chromosomal pathology: such as Down syndrome (mental retardation and some other physical features) or Edward's syndrome (disordered may lead to miscarriage, premature birth or loss of development); Genetic disorders: cystic fibrosis makes the body's secretions thicker and more sticky, hindering the functioning of certain organs; Musculoskeletal system disorders: Duchenne myasthenia gravis - a genetic disorder that leads to progressive progressive muscle weakness and malformations; Blood disorders: thalassemia - a condition that affects the body's ability to make red blood cells, or anemia that affects how red blood cells carry oxygen around the body; Disorders in metabolism: deficiency of antitrypsin makes the body unable to produce alpha-1 antitrypsin protein, phenylketouria; Neuropathy: Fragile X syndrome, a condition that affects appearance, intelligence, and behavior. In addition to the above conditions, there are other less common conditions that are diagnosed by performing a chorionic villus biopsy.
Placental biopsy cannot find congenital neural tube defects, and is not used to check if fetal lungs have developed.
2. Time to biopsies vegetable spikes
Chorionic villus biopsies are performed early in pregnancy between 10-12 weeks gestation rather than 15-20 weeks gestation. This allows you to check your baby's health and make an early decision to stop or continue the pregnancy. Placental biopsy results will be available faster than amniocentesis test results.Your doctor will not usually recommend a routine chorionic villus biopsies during pregnancy, it is only used when other test results show that your baby is at high risk for genetic diseases.
3. Procedure for performing a biopsy of vegetable thorns
3.1. Before performing a biopsy of the spines
You must stretch your bladder to make it easier to have a chorionic villus biopsy, so drink plenty of fluids before the test; Sign the consent form for the procedure.3.2. The process of performing a biopsy of vegetable spines
There are two methods of chorionic villus sampling, transperitoneal and transcervical. Which method to choose will depend on the position of the fetus and placenta in the uterus.Transabdominal spine biopsy: You will lie on your back on an examination table and pull the shirt off your abdomen. The doctor will apply a lubricant to the abdomen using an ultrasound instrument. The ultrasound machine will show images of the uterus, fetus and placenta on a screen. The doctor will look at the image on the screen to insert the needle to take a biopsy of the chorion; The doctor will disinfect the skin where the needle was inserted and numb it with medicine. The doctor inserts the biopsy needle into the abdomen and uterus to the placenta and collects a sample of the placenta; After collecting the sample, your doctor will listen to your baby's heartbeat and check your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing rate. Transcervical biopsy: Your doctor will ask you to remove clothing below your waist and cover with a cloth around your waist. Then lie on the examination table with both legs raised and extended. This position makes it easier for the doctor to see the vagina and perform the procedure; Your doctor will insert an instrument called a speculum into your vagina. The speculum will separate the vaginal wall to better see the inside of the vagina and cervix. The cervix will be washed with a special soap; An ultrasound is done to help the doctor insert the catheter through the cervix into the placenta. The ultrasound device will put pictures around the uterus, fetus and placenta on the screen; Once the correct catheter is in place, a biopsy sample of the placenta is taken; After collecting enough samples, your doctor will listen to your baby's heartbeat and check your blood pressure, pulse, and breathing rate.

3.3. After performing a biopsy of the spines
After taking a sample of the placenta, the medical professional will use an ultrasound machine to monitor the fetal heart rate. You will see some vaginal bleeding after the sample is taken; The tissue sample will be analyzed in the laboratory. Results will be available in a few days or weeks, depending on the complexity of the analytical method; If it is found that the fetus's medical condition cannot be cured or there are serious defects in the baby, the parents may decide to terminate the pregnancy; If the parents choose to continue nursing the baby, a chorionic villus biopsy will help diagnose what the disease is so you know in advance and prepare to deal with it after the baby is born.II. Amniocentesis
1. What is amniocentesis?
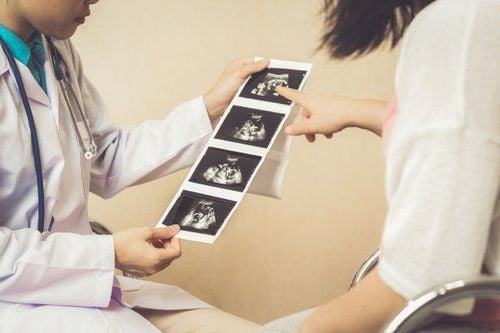
Like chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis is a prenatal test in which a small amount of amniotic fluid is drawn from the uterus through the abdominal wall with a very fine needle, under ultrasound guidance. This amniotic fluid will be sent for genetic analysis.Amniocentesis is a prenatal test that allows a doctor to collect information about your baby's health from a sample of amniotic fluid from the mother. The purpose of the test is to determine if the fetus has certain genetic disorders or chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome.
Only perform amniocentesis on mothers with high risk of genetic abnormalities, including:
Abnormal ultrasound images: thickened nape of the neck, umbilical hernia...; Having given birth to a child with a chromosomal genetic defect; Mother's age over 35.
2. Time to have amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is performed at >16 weeks gestation to check for genetic disorders.Amniocentesis can be performed in the last 3 months of pregnancy in cases where it is necessary to determine the maturity of the fetal lungs when termination of pregnancy is necessary due to conditions such as pre-eclampsia or is done to diagnose an infection ooh.
The accuracy of amniocentesis is up to 99.4%.
3. Amniocentesis procedure
3.1. Before performing amniocentesis
Before the procedure, the doctor will do an ultrasound to measure the size and basic anatomy of the fetus, as well as determine the amniotic sac to assess the safe distance of the baby and the placenta. Pregnant women lie on the examination table and the abdomen will be disinfected with an iodine alcohol solution to reduce the risk of infection.3.2. Amniocentesis test procedure
The doctor inserts a long, thin, hollow needle through the abdominal wall into the amniotic sac around the fetus to withdraw about 15 to 20 milliliters (about three teaspoons) of amniotic fluid. This process takes about 30 seconds; Normally, the amount of amniotic fluid that needs to be taken is 15-30 ml. Your body will immediately rebuild the amount of amniotic fluid removed and your baby will not be short of amniotic fluid after the test; When a woman is pregnant with twins (2 amniotic sacs), she may need to insert a needle twice into the uterus to collect amniotic fluid from two separate amniotic chambers; You may be asked to have anesthesia; This amniotic fluid sample will then be subjected to the necessary diagnostic tests; Next, the doctor checks the baby's heart rate through the image on the ultrasound screen.
3.3. After performing amniocentesis
Some women will have mild abdominal pain after amniocentesis, the doctor will give oral medication and the pregnant woman should rest on the day of amniocentesis. The next day the pain in the stomach will subside.3.4. Is amniocentesis dangerous?
Pregnant women who are facing the risk of having amniocentesis must be wondering if amniocentesis is dangerous. According to recent research, complications and risks of amniocentesis are possible miscarriage, amniotic fluid leakage, infection with the rate of 1/500 (meaning 1 in 500 women having amniocentesis will have a miscarriage). .But when the mother has the following problems may increase the risk of miscarriage, although there is no concrete evidence for these associations:
Fibroids; Uterine malformations; The amniotic membrane has not yet merged with the chorion; subchorionic hematoma; Mother has a history or recent bleeding; Obesity (BMI > 40) [BMI: body mass index]; Multiple births (>3 times); Are suffering from vaginitis; History of >3 miscarriages. Amniocentesis and chorionic villus biopsies are prenatal diagnostic methods with high accuracy, but they carry many potential risks to the fetus, especially the risk of miscarriage.
In order to get accurate diagnosis results while ensuring maximum safety for the health of pregnant women and their unborn babies, the International General Hospital has applied the NIPT Non-Invasive Prenatal Screening Method - considered as a safe "key" to help decipher fetal malformations.
The team of genetic experts at Vinmec will provide professional advice to pregnant women before making a decision whether to have NIPT testing. Vinmec Gen Technology Center is equipped with modern machinery system, giving accurate results while ensuring safety.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.