This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with MSc. Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Doctor of Nephrology - Endocrinology, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The C-peptide test is a test that evaluates the body's insulin production status. This index is a basis that can help diagnose patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes and also this index tells us whether the patient has insulin resistance or not? Therefore, it is very valuable to decide on drug selection as well as treatment regimen for patients.
1. What is C- Peptide?
Index C- Peptide is a peptide consisting of 31 amino acid residues that are biosynthesized by beta cells of the islets at the same time as insulin from proinsulin. Peptide - C has a long half-life, so it lasts longer than insulin in the peripheral blood. Therefore, when you want to evaluate the activity of beta cells in the pancreatic islets, you can measure insulin directly or measure it through C-peptide, both because the content of these two indicators is nearly equivalent.The value of the C peptide test
C peptide has no effect on blood sugar but as a byproduct is produced when insulin is produced, the C peptide test can be used to diagnose various types of diabetes . For example, type 1 diabetes is caused by the pancreas not producing enough insulin for the body, so there will be low levels of insulin and C-peptide in the blood. In contrast, patients with type 2 diabetes have insulin and C-peptide produced by the pancreas as normal or even higher than normal people because of this diabetes the cells have become resistant to insulin. and is the mechanism of type 2 diabetes.
The C peptide test value is also used to determine the cause of hypoglycaemia, such as an overdose of a therapeutic drug or a pancreatic islet tumor (called an insulin secretagogue). In essence, synthetic insulin will not contain C-peptide, patients with complications of hypoglycemia due to excessive use of synthetic insulin, when tested, have very high insulin levels while the C-peptide index is low. In the case of patients with pancreatic islet disease, when the pancreas produces too much insulin, causing hypoglycemia, both insulin and C-peptide blood levels will be elevated. This test can be used to differentiate these 2 causes of hypoglycemia as well as diagnose insulin-secreting pancreatic tumors that cause hypoglycemia complications.
Xét nghiệm peptide C còn được dùng để xác định nguyên nhân gây hạ đường huyết
2. When should the C peptide test be done?
Although the C-peptide test is equivalent to insulin, direct measurement of insulin will still give more accurate results. Therefore, the C peptide test will reflect islet cell function more accurately, specifically in the following cases:Diabetics treated with insulin injections and people with insulin antibodies. Patients self-administering insulin (insulin overdose) causes insulin levels to rise so that the direct measurement of insulin does not accurately reflect the production capacity of beta cells when using the C peptide test will give lower results. compared with insulin. Diabetics taking insulin who want to have their C peptide levels checked to monitor remission and may not need insulin from the medication. The test will help your doctor distinguish between type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes when it is first detected. On that basis, the doctor will have the best treatment plan for the patient. When a patient is suspected of having an insulinoma, the C peptide test can also be used to show elevated levels of the C peptide. Once the diagnosis of an islet tumor is indicated for surgery, this test can be used. It can also be used to monitor the results of treatment or after surgery to remove a pancreatic tumor. The test is used to assess insulin resistance in patients on treatment. Urine C peptide is indicated for the continuous assessment of beta-cell function or when blood collection is difficult in children or the assessment of pancreatic function in gestational diabetes.
3. What to prepare before doing the C peptide test?

Với một số trường hợp thì bệnh nhân sẽ được yêu cầu nhịn đói trong 8-12 giờ trước khi xét nghiệm
Several factors can affect the test including:
Patients with renal failure cause most of the C peptide to be broken down in the kidneys or may increase the concentration. Antidiabetic drugs such as sulfonylureas. Besides, it is also important to consider the risks of C peptide testing:
Difficult sampling process that requires multiple injections. Excessive bleeding at the injection site. The patient fainted due to blood loss. The area where the procedure was performed is bruised due to the accumulation of blood under the skin. Infection of the injection site.
4. Insulin peptide C . test procedure
The sampling procedure of the peptide C test is to draw blood with the following steps:Wrap an elastic band around the upper part of the upper arm to prevent blood circulation, the vein below the cuff expands to facilitate the Inject the needle into the vein
Disinfect the blood collection site with alcohol. Insert a needle into a vein to draw blood. Take the right amount of blood into the syringe and test tube. Remove the rubber band from the upper arm when enough blood is drawn. Press gauze or cotton ball to the injection site after withdrawing the needle. Place cotton pads on the skin to stop bleeding and cover.
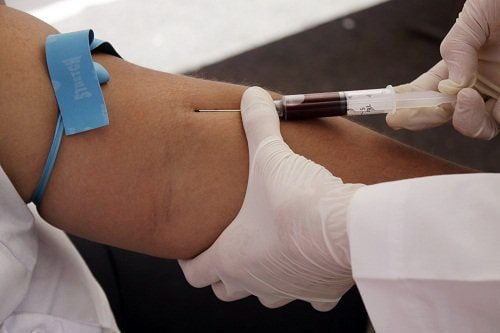
Thực chất quy trình lấy mẫu của xét nghiệm peptide C chính là lấy máu
5. How to read peptide C test results?:
Test results will be measured in nanograms/ml and are grouped into 3 result zones:Normal index range: The normal range of C peptide index is 0.51-2.72 ng/ml (0) ,17-0.9 nmol/l). Low Result Area: Below the normal range and high blood sugar is a sign of type 1 diabetes, while both low blood sugar and C peptide can be a sign of liver disease, infection or Addison's. High Results Zone: If the C-peptide is high and blood sugar is also high, it could be a sign of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, or Cushing's syndrome. If the C-peptide is high and the blood sugar is low, it may be due to a pancreatic islet tumor or a sulfonylurea-type hypoglycemic agent. Note that the C peptide test must be done in conjunction with the blood glucose test. The doctor will base on age, weight as well as duration of the disease to distinguish type 1 and type 2 diabetes according to the following steps:
The first blood sample will be taken as a standard. Then, the patient was injected with glucagon, a hormone that raises blood sugar, and drew blood for the second time and compared. With type 1 diabetes, C peptide levels will always be low because the pancreas cannot produce insulin when glucagon levels increase. People with type 2 diabetes had higher levels of C peptide in blood sample 2 than in the first sample, because the pancreas produced more insulin than usual when stimulated by glucagon. To diagnose, monitor and treat diabetes, patients can go to Vinmec International General Hospital. There is a team of well-trained, experienced and professional endocrinologists; system of modern equipment, meeting international standards; Professional service quality, high efficiency in diagnosis and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.