This is an automatically translated article.
The diuretics in which the loop diuretics have a common property is to increase the excretion of sodium and water through the kidneys. This effect is due to the drug inhibits the reabsorption of sodium ions in the renal tubules. This property of diuretics should not be used to balance water and sodium unless used to treat edema and arterial hypertension.1. What is a loop diuretic?
Loop diuretics are effective in treating high blood pressure and edema caused by heart failure or kidney failure.
2. Loop diuretics
2.1 The usual preparation is Furosemide (Lasix, Lasilix), 40 mg tablet, 20mg/2ml tube. Anti-aldosterone diuretics (Verospiron): Spiromide 50mg/20mg, 50mg/40mg. 2.2 How to use Take 20 - 80 mg / day, effective 20 minutes after taking. Intravenous injection 1-2 ampoules, effect after 3-5 minutes. The effect wears off after 4-6 hours. Maximum dose up to 1000 mg/day (intravenously via electric pump)
Lasix - thuốc lợi tiểu quai
3. Mechanism of action of loop diuretics
Most of the sodium filtered through the glomerulus (primary urine) is reabsorbed in the renal tubules: in the proximal tubule (60-65%) and in the loop of Henle (20%). NaCl migration in cells in the ascending loop of Henle is via Na-K-2Cl co-transportation. Loop diuretics directly inhibit sodium, potassium, and chloride reabsorption by competing for the chloride channel of co-transporters at the enlarged segment of the ascending loop of Henle, increasing the elimination of ions. Sodium, Chlorine and Potassium ions. Thus, it allows the excretion of up to 20-25% of the sodium filtered through the glomerulus, and can eliminate up to 30% of the urine filtered through the glomerulus. Loop diuretics also have the activity of increasing calcium and magnesium excretion by inhibiting the reabsorption of NaCl leading to inhibition of the reabsorption of divalent cations such as calcium and magnesium due to a decrease in the potential difference in membrane. In addition, loop diuretics may increase the elimination of H+ ions (weak effect). In people without edema, loop diuretics are still effective, so they are still indicated in cases of hypertension because reducing the concentration of extracellular sodium ions and the vessel wall will increase the effect of antihypertensive drugs and make the blood pressure worse. decrease the effect of vasoconstrictor hormones (such as ADH). The diuretic effect of loop diuretics is strong, thus leading to a hypotensive effect in people with pulmonary edema, furosemide causes an increase in venous volume, thereby reducing the preload pressure of the left ventricle before obvious diuretic effect.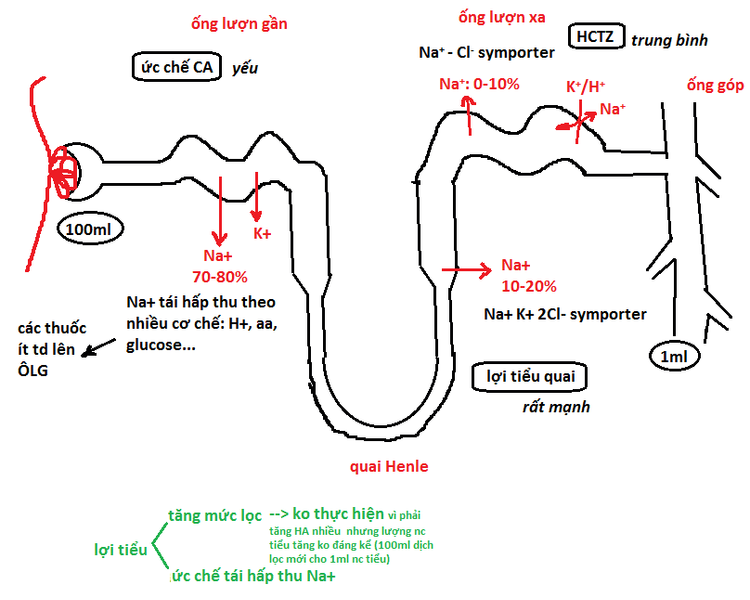
Quai Henle
4. Undesirable effects of loop diuretics
4.1 Circulation Decrease blood volume in case of high dose therapy. Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis. Orthostatic hypotension. 4.2 Metabolism Hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hyperuricemia, hypochloremic alkalosis. Temporarily increased plasma cholesterol and triglyceride concentrations. Increased blood glucose, urinary glucose. 4.3 Skin Allergic reactions, skin rash, vasculitis, paresthesia.
4.4 Ear Causes VIII nerve toxicity causing deafness, tinnitus, reversible hearing loss (at high doses).
4.5 Causes dehydration and electrolytes Fatigue, cramps, low blood pressure.
In addition, there are other undesirable effects: Increased blood sugar, digestive disorders, liver - kidney dysfunction, decreased red blood cells, decreased white blood cells, itchy papules, numbness...

Người bệnh mệt mỏi
5. Indications and contraindications of loop diuretics
5.1. Indications for loop diuretics Edema is caused by heart (heart failure), liver (cirrhosis) and kidney (renal failure, glomerulonephritis, nephrotic syndrome). Chronic renal failure: Loop diuretics are the preferred choice, the dose response depends on the degree of renal impairment (furosemide 40-500 mg/day). Hypertension: Use of loop diuretics alone or in combination with other classes of antihypertensive drugs (synergistic effect). However, loop diuretics are not recommended for the treatment of hypertension except in the presence of impaired renal function. Heart failure. Emergency indications:
Acute pulmonary edema Acute hypertensive crisis Hypercalcemia (metastatic bone cancer, multiple myeloma). Hypercalcaemia is common or accompanied by signs of dehydration, so loop diuretics should be used with fluids.
Người bệnh bị suy thận mạn tính
5.2. Contraindication of loop diuretics Complete obstruction of the urinary tract (Urinary retention due to prostate enlargement, ureteral stones causing hydronephrosis, urethral stones...): Solving the obstruction is a priority. First line before giving diuretics (insertion of urinary catheter, cystostomy, percutaneous pyelonephritis, intervention or cesarean section,...). Hemodynamic instability, hypotension or low blood pressure. Signs of dehydration, electrolyte loss (dry skin, dry mucous membranes, thirst, skin pinching): Prioritize circulating volume. Hemoconcentration status: Complete blood count test, need to compensate for circulating volume first, compensate for oncotic pressure in nephrotic syndrome. Edema and hypertension due to pregnancy can cause amniotic fluid depletion, fetal anemia and fetal atrophy. However, loop diuretics can be indicated in the treatment of edema caused by heart, liver, and kidney disease in pregnant women (relative contraindications) in cases of large edema, little urine, and risk of developing complications. Cardiovascular complications (elevated blood pressure, acute pulmonary edema) or progressive renal failure.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.