This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease affecting the colon with an unclear pathogenesis. The disease can be diagnosed and evaluated by many methods, including X-ray and CT Scan.
1. Clinical manifestations of bleeding ulcerative colitis
Hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis is characterized by diffuse and superficial inflammatory lesions of the colonic mucosa, beginning in the rectum and extending to other segments of the colon. The small intestine is usually not involved, although the terminal ileum may have superficial inflammatory lesions. Based on the extent of colonic lesions, ulcerative colitis can be classified into the following types: Proctitis (localized lesions in the rectum), sigmoid colitis - rectum or left colon. (spread to the splenic angle) or diffuse/global colitis. The extent of the lesion is not only related to severity but also affects wages and treatment options. Symptoms and course of disease are related to the extent and severity of inflammatory lesions. Symptoms are often insidious, although the disease may develop acutely after an episode of infectious colitis or travel diarrhea. Proctitis causing bloody stools is the most common symptom of patients. The degree of bloody stools can be severe, profuse or moderate, with bloody and mucusy stools. The patient may have frequent urge to defecate and strain or increase the frequency of defecation. The more widespread the colonic lesion, the more severe the diarrhea, while if the patient is simply proctitis, the symptoms may alternate between episodes of constipation with episodes of bloody stools.Abdominal pain before defecation or a feeling of abdominal distension will occur when the disease is advanced. In advanced or fulminant cases, the patient may present with systemic symptoms such as night sweats, fever, vomiting, nausea, weight loss accompanied by diarrhea. In addition, may experience extra-gastrointestinal symptoms such as in the eyes, skin, joints, liver.
Ulcerative colitis is diagnosed when the inflammatory lesion extends as far as the transverse colon or the right colon. Patients often present with diarrhea, bloody stools, painful defecation, abdominal fullness, abdominal cramps or localized pain. In addition, patients in this group often have weight loss, systemic symptoms, extra-gastrointestinal symptoms, and anemia. Toxic megacolon is the most severe complication of hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis when the inflammatory lesion spreads from the superficial mucosa to the submucosal and muscular layers. This complication often occurs in patients with disseminated colitis or severe colitis. Clinical manifestations include fever, exhaustion, severe abdominal cramps, abdominal distention, and local or total abdominal pain.
2. Abdominal barium scan
The development of endoscopic methods has replaced barium imaging in the diagnosis of bleeding ulcerative colitis. However, in some cases of severe patients, dangerous complications such as toxic colonic dilatation, colonic perforation, intestinal obstruction have not been ruled out. In addition, on unprepared radiographs, the sacroiliac joints and vertebrae can be evaluated if the patient has symptoms of back pain. On barium film, the noted features include rough mucosa, diffuse continuous ulceration, longitudinal symmetry from the rectum to the upper segments of the colon, and loss of folds in inflammatory colon segments.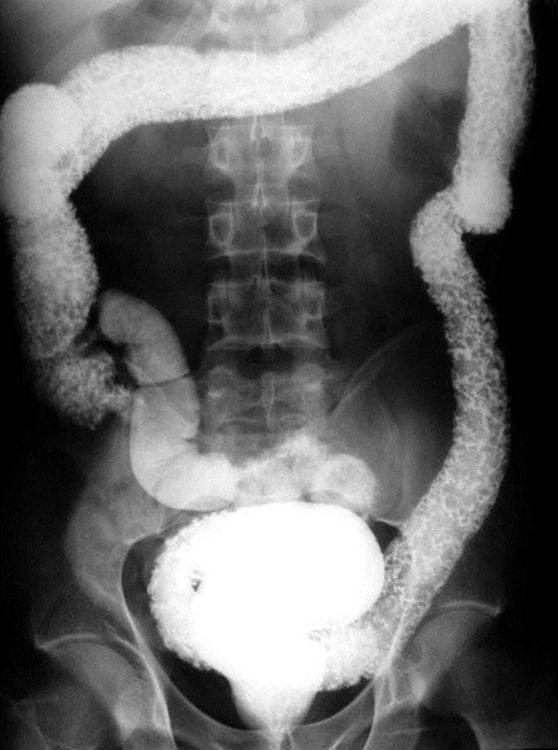
3. Computed tomography (CT Scan)/magnetic resonance imaging
To date, the ECCO guidelines as well as the consensus between ECCO and the European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Imaging (ESGAR) have not given specific recommendations on the indications and value of microscopic tomography. Abdominal properties in assessing the extent and disease activity of hemorrhagic ulcerative colitis. Colonic enema technique can be used in computed tomography with injection so that the arrowhead - thickening of the wall of the colon Sigma, small arrow - the lesion can be seen as the enhancement of the intestinal wall and tissues. fat around the colon is more obvious. However, this approach is not indicated when the patient is suspected of having toxic dilated colonic aneurysm, perforation, or peritonitis.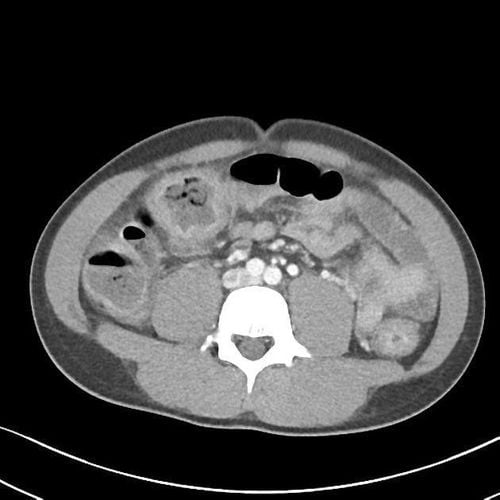
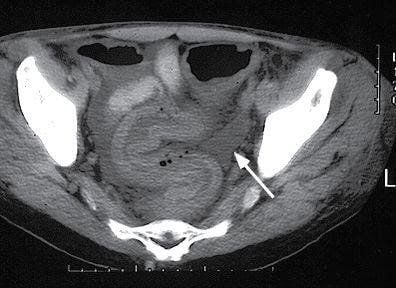
In addition, in exacerbations, perirectal or colonic edema may be seen with edema of the fatty layer surrounding the intestinal wall or with little fluid, with lymphadenitis. In practice, magnetic resonance imaging is also valuable in severe cases in acute progression and is the option to avoid the risk of complications as well as to evaluate the entire colon segment.
Both X-ray, CT Scan and MRI are highly specialized techniques. Patients who want to perform the above techniques should choose reputable centers - hospitals. Vinmec International General Hospital system across the country is invested with advanced technical facilities and a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors, which is a prestigious address for many patients to choose to visit. . X-ray, CT, and Magnetic resonance imaging techniques here will be performed according to standard procedures, giving the most accurate results. In particular, there will be necessary considerations to ensure absolute safety for the patient.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.