This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by Th.S, BS. Ton Nu Tra My, Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Contrast is often used in some imaging methods such as X-ray, CT to help improve images, distinguish between normal and pathological images, or help narrow the diagnosis based on characteristics. Contrast absorption properties of normal and pathological tissues. So, in which cases do you need to use contrast agent?
1. What is contrast agent? How is the effect?
Contrast, also known as contrast or contrast material, is a substance that is introduced into the body before an X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan (see more in X-rays and microscopic tomography). count). The purpose of contrast is to improve imaging, to help differentiate between normal and pathological images, or to help narrow the diagnosis, to exclusion from other diagnoses because of differences in enhancement properties. contrast of normal tissue and different types of pathological tissues.
Contrast is usually introduced into the body in one of three ways:
Swallowing (by drinking or pumping into the stomach); Inject directly into the rectum; Inject into a vein or artery. After entering the body, the contrast material will be absorbed or eliminated by the body through urine or bowel movements.
Tiêm vào tĩnh mạch là một cách đưa chất cản quang vào cơ thể
There are two main types of contrast agents used in X-ray and computed tomography (CT, CT) are Barium-sulfate and iodine-containing contrast agents.
Barium-sulfate is the most common contrast agent given by mouth or injected into the rectum.
Iodine contrast is often used intravenously.
2. When to use contrast agent?
2.1. Oral Contrast
Barium-sulfate contrast agent is swallowed or taken (orally) in X-ray, computed tomography (CLVT) to evaluate some diseases of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract in:
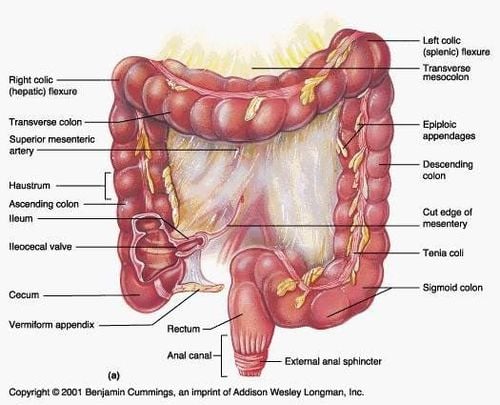
Oropharynx; Stomach; Stomach; Small intestine; Large intestine (colon). In some cases, iodinated contrast agent is substituted for oral barium-sulfate.
2.2. Contrast for the rectal route
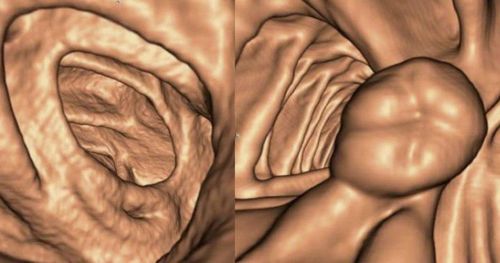
Barium-sulfate contrast agent is used in radiography, computed tomography (CT) to evaluate pathology of the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract (colon and rectum).
In some cases, iodinated contrast agent is substituted for barium-sulfate for rectal injection.
Chụp cắt lớp vi tính tiêm chất cản quang giúp chẩn đoán các bệnh lý đường trực tràng
2.3. Intravenous Contrast
Iodine contrast agents are injected intravenously to enhance X-ray and CT images in the evaluation of internal organs, including: heart, lungs, liver, adrenal glands, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, uterus and bladder; evaluate the gastrointestinal tract including the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine; Examine the arteries and veins of the body including vessels in the brain, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, upper extremities, lower extremities, evaluate the skull, neck, chest, and soft tissues of the body.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
References: ACR Manual on Contrast Media, radiologyinfo.org