This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Truong Duc - Radiographer - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Dr. Duc has more than 17 years of experience in diagnostic imaging.A diverticulum is a small pouch that forms in the wall of the colon. Diverticulitis occurs when that pouch becomes infected and/or inflamed. If left untreated, the disease can become more dangerous and lead to an abscess or bowel obstruction. To diagnose diverticulitis, doctors usually order a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis.
1. What is diverticulitis?
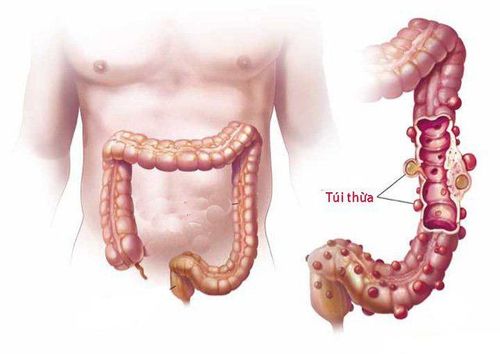
Diverticula are small, bulging pouches that can form in the lining of the digestive system. Diverticulosis is most often found in the lower part of the large intestine (colon). Diverticulosis is common, especially after age 40, and rarely causes problems.When one or more pouches become inflamed and in some cases infected, the condition is called diverticulitis. Diverticulitis can cause severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and a marked change in bowel habits.
Mild diverticulitis can be treated with rest, dietary changes, and antibiotics. Severe or recurrent diverticulitis may require surgery.

Bệnh viêm túi thừa có thể được điều trị bằng kháng sinh
2. Symptoms of diverticulitis
You can have diverticula without having the diverticulum yourself. The diverticulum is usually painless and causes few symptoms. But you may notice:Cramps on the left side of your abdomen that go away after you have a bowel movement or bowel movement Bright red blood in your stool More noticeable diverticulitis symptoms include severe abdominal pain and fever. Diverticulitis can be acute or chronic. With the acute form, you may have one or more episodes of severe infection and inflammation. In chronic diverticulitis, inflammation and infection may decrease but never completely go away. Over time, the inflammation can lead to a bowel obstruction, which can cause constipation, small stools, diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain. If the blockage continues, abdominal pain increases and you may feel uncomfortable or vomit.
3. Causes and risk factors of diverticulitis
Diverticulosis usually develops when there are naturally weak spots in the colon due to the effects of pressure. Diverticulitis occurs when the diverticulum tears, leading to inflammation and, in some cases, infection. Several factors can increase the risk of developing diverticulitis, including:Aging: The incidence of diverticulitis increases with age. Obesity: Being severely overweight increases your odds of developing diverticulitis. Smoking: Smokers are more likely to develop diverticulitis than non-smokers. Lack of exercise.: Regular exercise reduces the risk of diverticulitis. Diets high in animal fat and low in fiber: Following a low fiber diet combined with a high intake of animal fat seems to increase the risk of diverticulitis, despite the role of low intake. Fiber in the risk of diverticulitis if standing alone has not been clearly studied. Certain medications: Certain medications have been linked to an increased risk of diverticulitis, including steroids, opioids, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and naproxen sodium (Aleve).
Người bị béo phì làm tăng nguy cơ mắc bệnh viêm túi thừa
4. Diagnostic techniques in diverticulitis
To diagnose diverticulitis, your doctor will likely ask you about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you're already taking. In addition, the doctor will conduct a physical exam to check your abdomen for pain, if more information is needed, he will perform a transrectal finger exam to check for rectal bleeding. pain, tumors or other problems.To rule out other conditions that can cause symptoms similar to diverticulitis and to check for signs of diverticulitis, your doctor may order one or more imaging techniques and tests.
Imaging techniques:
CT scan of diverticulitis: CT scan of the abdomen is the best diagnostic technique to diagnose diverticulitis. The technique can also help determine disease severity and guide treatment planning. You may receive an intravenous (IV) injection of contrast material or oral contrast an hour before the scan. Contrast allows the doctor to clearly see the intestines and abdominal organs in the patient's abdomen. Colonoscopy: A small camera is inserted inside the colon to see if the pouches are inflamed, infected, or infected. chemical. However, the ultrasound images from this technique do not have the detail of the CT images and it is not possible to accurately assess the bowel with CT scans. Lower GI tract X-ray: Your doctor may use an X-ray to evaluate complications from diverticulitis. Some diagnostic techniques by testing:
Pregnancy test: If you are of childbearing age, your doctor may order you to take a pregnancy test. This will help rule out pregnancy as a cause of abdominal pain. Stool test to check for infection, such as Clostridium difficile Urine test to check for urinary tract infection

Để chẩn đoán bệnh viêm túi thừa, người bệnh có thể được chỉ định xét nghiệm nước tiểu
More than 75% of diverticulitis cases will be uncomplicated, but about 25% will develop complications. These complications may include:
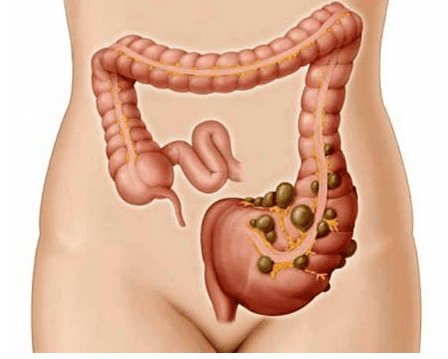
Abscess, an infected sac filled with pus Fistula, an abnormal tube that can develop between two organs or between an organ and the skin Intestinal perforation, tear or A hole in the bowel wall can lead to the contents of your colon leaking into the abdominal cavity, causing inflammation and infection Intestinal obstruction, a blockage in the intestines that can prevent stool from moving through the digestive system.
5. Prevention of diverticulitis
To help prevent diverticulitis, you need to:Exercise regularly: Exercise promotes normal bowel function and reduces pressure inside the colon. Try to exercise for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Eat more fiber: A high-fiber diet reduces the risk of diverticulitis. High-fiber foods, such as fresh fruits and vegetables and whole grains, soften stools and help them pass through the colon more quickly. Eating nuts does not cause diverticulitis. Drink plenty of water: Fiber works by absorbing water and increasing soft waste in your colon. But if you don't drink enough fluids to replace what you've absorbed, fiber can clump up and lead to constipation. No smoking. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of diverticulitis.
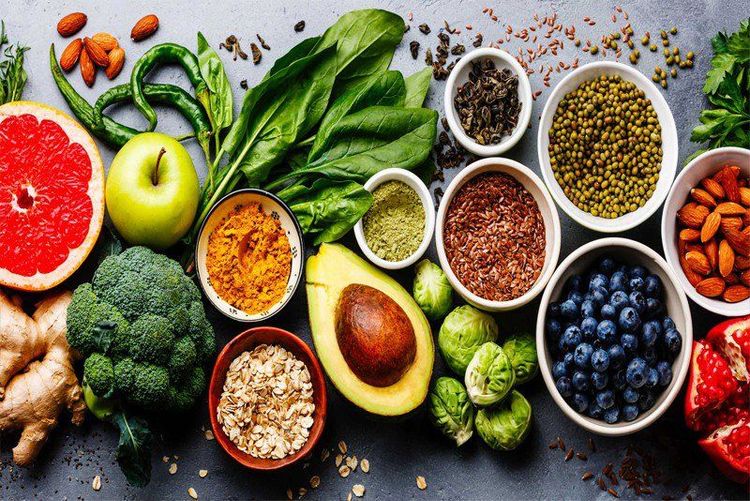

Chất xơ có lợi trong việc phòng ngừa bệnh viêm túi thừa
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has full facilities and modern techniques to examine, diagnose and evaluate diverticulitis. Especially with the performance of experienced and qualified doctors, they will give accurate results and advise on effective prevention and treatment, ensuring the health of customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: radiologyinfo.org, mayoclinic.org, webmd.com