This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Le Hong Lien - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.When you are pregnant, you will be tested to screen for birth defects, if any abnormalities are found, your doctor may recommend a chromosomal test to determine if your baby is pregnant. genetic or chromosomal problems. Especially for infertile couples, miscarriages or in families with malformations, chromosomal testing is the best option.
1. What is Chromosome?
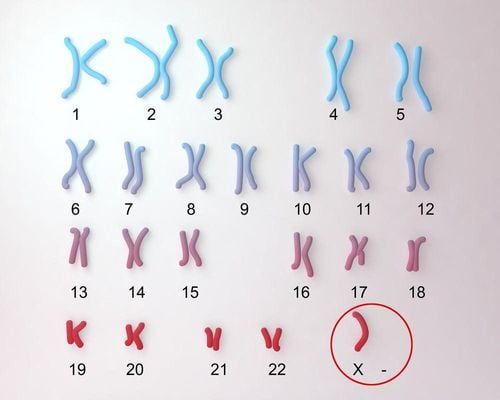
The normal human chromosome set consists of 22 pairs of autosomes and 1 pair of sex chromosomes, XX in females and XY in males. Any change in the number or structure of chromosomes can lead to abnormalities in the person's development.Chromosomes or Karyotyping is a chromosomal test on a sample of cells to identify genetic disorders that cause birth defects. This test says:
Number of chromosomes. Changes in chromosome structure. This test can be done on samples of blood, bone marrow, amniotic fluid, placenta, or other organ tissues.
To test amniotic fluid , amniocentesis is required . A bone marrow sample is obtained through a biopsy. Samples are grown in special lab dishes or tubes. After the appropriate time, cells will be harvested, smeared and stained. The size, shape, and number of chromosomes in the cell sample will be observed under the microscope and photographed arranged in a set of chromosomes. Then abnormalities in the number and structure of chromosomes will be detected.
Normal chromosome set:
Female: 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XX), symbols: 46, XX. Male: 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes (XY), symbol: 46, XY. Chromosome abnormality:
More or less 46 chromosomes. The shape and size of one or more chromosomes is abnormal. A pair of chromosomes can be broken or separated inappropriately.
2. When is chromosomal analysis necessary?
2.1. Prenatal diagnosis In prenatal diagnosis, pregnant women are indicated for amniocentesis or placental biopsy for fetal chromosomal analysis when at least one of the following factors is present:Older women (over 35 years old) age, usually 38 years or older). Pregnant women with a history of spontaneous abortions, recurrent stillbirths, or deaths at birth. Pregnant women with a history of birth defects. Pregnant couples have been identified that one of them has a heritable chromosomal structural mutation, for example carrying a chromosomal deletion, translocation, inversion,... Pregnant women who have been determined that the carrier of the X chromosome at the fragile Xq27.3 position is at risk of passing this mutated X chromosome to his or her children. Pregnant women who have confirmed fetal ultrasound with morphological abnormalities have a high risk of giving birth to a baby with birth defects (increased nuchal translucency or nuchal translucency ≥3mm, with lymphatic cysts, without nasal bone,... or other abnormalities suspected of fetal chromosomal abnormalities). Pregnant women with serological screening results (Double test, Triple test) have a high risk of having a baby with a birth defect.

Newborns with congenital malformations. People who are ambiguous about gender, genitals are not clear whether male or female. Children with psychomotor retardation of unknown cause. People with a family history of chromosomal mutations. Couples with primary or secondary infertility. Primary infertility is a condition in which a couple of childbearing age are unable to conceive after 12 months of having sex without using contraception. Secondary infertility is a couple who have been pregnant before but after 1 year of normal sexual intercourse do not get pregnant again. Girls reach puberty (>16 years) without a period (primary amenorrhea) or women who have had periods but suddenly stop menstruating (secondary amenorrhea). Couples with consecutive miscarriages or stillbirths. People with cancer such as acute myeloid or lymphocytic leukemia, neuroblastoma,... need to have a chromosomal test of bone marrow or tumor cells which is very valuable in disease classification, prognosis and treatment.
3. The role of chromosomal testing
Chromosome testing in prenatal and postnatal diagnosis helps to identify quantitative and structural chromosomal mutations. The results of the chromosomal test will be consulted by genetic specialists and depending on the type of mutation, the person with the chromosomal mutation and the family will be consulted and have a specific prognosis about the causes and possibilities. could happen to them as well as to future generations.4. Common chromosomal abnormalities
4.1. Down syndrome 47, XX (XY), +21 or trisomy 21: This is an extra chromosome 21 disorder (trisomy 21 or Trisomy 21), most common in children live with a frequency of 1/700 - 1/1000. People with Down syndrome often show mental retardation, low intelligence, low IQ and almost no learning ability. More than 50% of people are sick with congenital malformations such as: Cardiovascular, digestive,...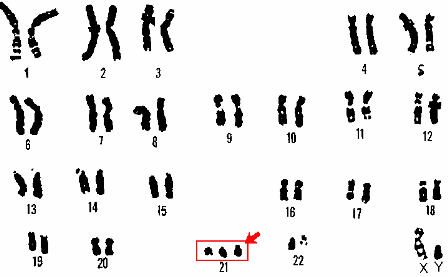
Trisomy 8: Long face, thick lower lip, scoliosis,... Can live to adulthood, mostly in mosaic form. Trisomy 9: Bone and joint malformations, cardiovascular malformations. Trisomy 22: Small head, most die within the first year. 5p syndrome (Missing short arm of chromosome 5): cat meow syndrome. 4.2. Sex Chromosome Disorders Turner syndrome (45, XO or 46,XO/46,XX): A chromosomal abnormality caused by a lack of an X sex chromosome with a frequency of 1/2500 females. Common manifestations include dwarfism, large neck, low hair growth, low closed ears, small uterus and ovaries, amenorrhea, infertility,... Klinefelter syndrome 47, XXY: This is a disorder affecting infection. sex chromosomes, X and Y. Normally, people only have two sex chromosomes. If it's female, it's XX, if it's male, it's XY. With Klinefelter syndrome, the person has an XXY sex chromosome, with an extra X sex chromosome in males. This is the most common sex chromosome disorder with a frequency of 1/1000 males. Patients often have small testicles and are infertile. Chromosomal abnormalities are one of the genetic diseases and can now be screened as early as 9 weeks with the outstanding advantage of being non-invasive, completely harmless to the fetus. NIPT is recommended. Indicated for high-risk subjects and may even be the first choice for pregnant women in screening for aneuploidy in the first trimester.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, prenatal screening techniques Non-invasive NIPT is fully compliant with ILLUMINA's strict recommended standards and is considered the "key" to deciphering fetal malformations, resulting in a remarkable improvement in the results of prenatal screening for abnormalities. multiple. Analytical results will be available in about 1-2 weeks and will be evaluated by genetic experts at the Institute of Stem Cell and Gene Technology. Customers will be consulted specifically about the risks by Fetal Medicine doctors with many years of experience about problems that may be encountered when performing NIPT test, especially for negative cases/ false positives for appropriate intervention.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.