This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Phan Dinh Thuy Tien - General Internal Medicine - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalAmong venous diseases, venous thrombosis is one of the most dangerous diseases. The disease, if not treated promptly, can lead to pulmonary embolism, which is a dangerous and life-threatening complication.
1. What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is an inflammatory condition that is associated with blood clots. Blood clots can be present in one or more veins deep in the body, usually in the upper or lower extremities, where blood flow in the vein is completely or partially blocked.Deep vein thrombosis is a common disease, common today with a high mortality rate. The disease causes many serious complications with great treatment costs. In Vietnam, according to the INCIMEDI study, deep vein thrombosis is not uncommon in our country, although there are no exact data. The study found that, based on Duplex ultrasound, up to 22% of hospitalized medical patients with deep vein thrombosis were asymptomatic. The elderly are often missed at diagnosis, or patients are diagnosed only after death.
If patients with deep vein thrombosis are diagnosed and treated early, it will help increase survival rates and limit potentially dangerous complications.
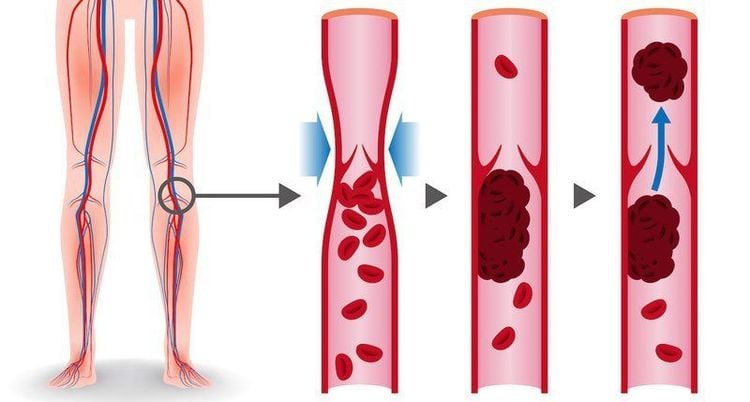
Cục máu đông làm tắc nghẽn dòng máu trong lòng tĩnh mạch
2. Signs and causes of deep vein thrombosis
Manifestations of deep vein thrombosis are often nonspecific, so it is not noticed by many people. In the area where the thrombosis occurs, there may be some symptoms such as redness, swelling, pain, often in the leg area.The appearance of blood clots leads to increased production of elastic fibers in the endothelial layer of blood vessels, causing blood vessels to swell, causing the endothelium to thicken at the site of thrombosis, leading to narrowing of the lumen, the risk of occlusion. veins increase over time. In addition, patients with deep vein thrombosis were 6 times more likely to develop varicose veins than those without the disease. Therefore, clinically, symptoms of venous insufficiency may appear in patients with venous thrombosis.
There are many causes of deep vein thrombosis, such as surgery, trauma or an immune system reaction that can all cause the disease. Besides, the formation of blood clots can stem from other major causes, including genetic disorders, hormonal changes in the body, sitting for a long time,...

Chấn thương cũng có thể dẫn đến hình thành cục máu đông
Coagulation helps stop bleeding after a wound, which is a normal body process, such as a cut in the skin. Blood clots can form in a vein with the following conditions:
Blood flows too slowly The lining of the vein is damaged Disturbances in the blood lead to easier clotting. The formation of blood clots in the deep veins causes blood circulation to slow down, the volume of blood in the veins increases. It is very dangerous if a piece of the blood clot breaks off and travels through the blood vessels to the lungs. This condition, called pulmonary embolism, carries a high risk of death. Nearly one-third of people with deep vein thrombosis are at risk of developing a pulmonary embolism. Therefore, in order to prevent pulmonary embolism, it is imperative to screen, detect and treat deep vein thrombosis in time.
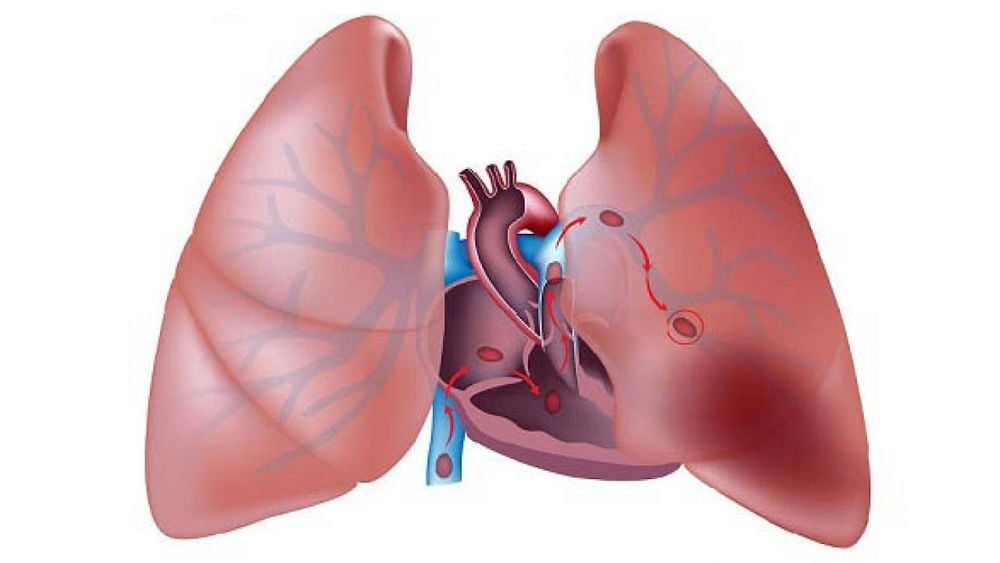
Nếu không điều trị kịp thời cục máu đông có thể di chuyển gây tắc mạch phổi
3. The relationship between deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism refers to a thrombus that has ruptured and is free-floating in a blood vessel. The blood clot can travel to another area of the body and cause a blockage in a blood vessel. There may be multiple blood clots (emboli). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is blood clots that don't move and stay in a vein. The majority of blood clots that become pulmonary emboli are formed in veins in the legs. The severity of the disease depends on the blood flow not reaching the lungs.Blood clots can be detected through venous blood flow studies (Doppler ultrasound). Early treatment of DVT can help relieve symptoms and prevent pulmonary embolism.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.