This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by a General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.The endocrine system affects the functioning of the heart, bones, growing tissues and even the ability to have children. It plays an important role in the development of diabetes, thyroid disease, growth disorders, sexual dysfunction and a variety of other hormone-related disorders.
1. Glands of the endocrine system
Each gland of the endocrine system secretes specific hormones and enters the bloodstream. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to cells and help control or coordinate many processes in the body.Endocrine glands include
Adrenal glands: Two glands located on top of the kidneys that release the hormone cortisol. Hypothalamus: The part of the lower midbrain that signals the pituitary gland when to release hormones. Ovaries: Female reproductive organs that release eggs and produce sex hormones Cells in the pancreas: These cells control the release of the hormones insulin and glucagon. Parathyroid glands: Consists of four small glands in the neck that play a role in bone growth. Pineal gland: A gland found near the center of the brain that may be associated with sleep patterns. Pituitary: Gland found at the base of the brain behind the sinuses. It is often called the master gland because it affects many other glands, especially the thyroid gland. Problems related to the pituitary gland can affect bone growth, a woman's menstrual cycle, and milk production during breastfeeding. Testicular Glands: The male reproductive glands that produce sperm and sex hormones. Thymus: Gland in the upper chest that helps develop the body's immune system. Thyroid: A butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck that controls metabolism.
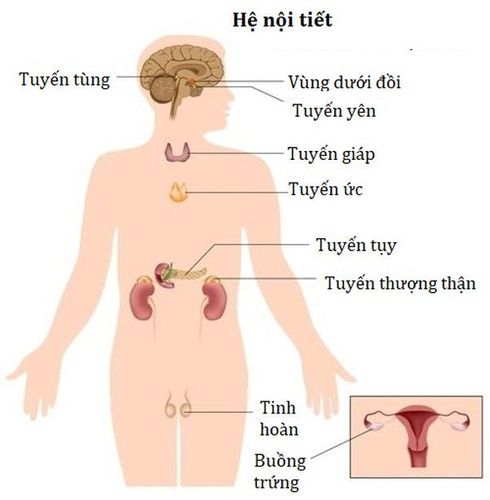
Các tuyến của hệ thống nội tiết con người
2. Causes of endocrine disorders
Types of endocrine disorders are generally grouped into two categories:Endocrine diseases caused when a gland produces too much or too little endocrine hormone is called a hormone imbalance. Endocrine disease is caused by the growth of lesions (such as lumps, cysts or tumors) in the endocrine system. It may or may not affect hormone levels. The endocrine feedback system helps control the balance of hormones in the blood. If the body has too much or too little of a certain hormone, the feedback system signals the appropriate gland to correct the problem. Hormonal imbalances can occur if this feedback system has trouble keeping the right levels of hormones in the blood. Or if the body can't properly remove them from the bloodstream.
Increased or decreased levels of endocrine hormones can be caused by factors such as:
Certain problems related to the endocrine feedback system Diseases Failure of one gland to stimulate another gland to release hormones ( for example, a problem with the hypothalamus can disrupt hormone production in the pituitary gland). Genetic disorders, such as multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) or congenital hypothyroidism Infections Injury to the endocrine glands Tumors of the endocrine glands Most endocrine tumors are noncancerous. They usually do not spread to other parts of the body. However, a tumor or a nodule on an endocrine gland can also interfere with the glands' hormone production.

Mất cân bằng nội tiết có thể gây ra một số bệnh
3. Classification of endocrine disorders
There are many different types of endocrine disorders. Diabetes is the most common endocrine disorder diagnosed in the United States. Types of endocrine disorders include:Adrenal insufficiency: The adrenal glands secrete too little of the hormone cortisol and sometimes aldosterone. Symptoms of this disorder include fatigue, upset stomach, dehydration, and changes in skin color. Addison's disease is a type of adrenal insufficiency. Cushing's disease: The overproduction of pituitary hormones leads to overactive adrenal glands. This condition, also known as Cushing's disease, can occur in young people, especially children, or in people who often take high doses of corticosteroid medications. Acromegaly (giant disease) and other growth hormone problems. If the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, a child's bones and organs may grow abnormally fast. Conversely, if growth hormone levels are too low, the child may stop growing in height. Hyperthyroidism: The thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone leading to weight loss, irregular heartbeat, sweating, and nervousness. The most common cause is an overactive thyroid causing an autoimmune disorder called Grave's disease. Hypothyroidism: The thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone leading to fatigue, constipation, dry skin, and depression. An underactive thyroid can cause growth retardation in children. Some types of hypothyroidism can be present at birth.
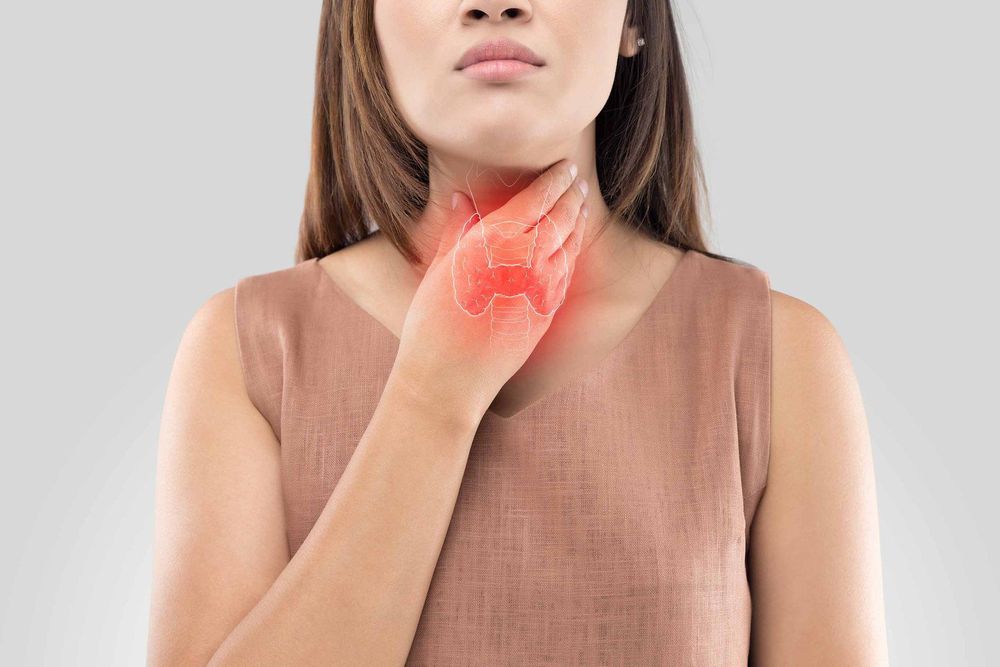
Bệnh suy giáp do hormone tuyến giáp không sản xuất đủ

Hormone giới tính gây ra tình trạng dầy thì sớm
4. Test for endocrine disorders
If you have an endocrine disorder, you may need to consult an endocrinologist to understand the cause of the disease and make a definite diagnosis of the disease.Symptoms of endocrine disorders vary widely and depend on the specific gland involved. However, most endocrinologists complain of fatigue and weakness.
Blood and urine tests to check hormone levels can help your doctor determine if you have an endocrine disorder. In addition, imaging tests can be used to locate or locate nodules or tumors.
Treatment of endocrine disorders can be complicated because a change in one hormone level can eliminate another. Your doctor or specialist may order periodic blood tests to check for disease-related problems or to determine medication use and adjustments in your treatment plan.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Reference source: webmd.com
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
Signs of female hormone disorders Melasma due to hormonal disorders Hormonal disorders: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment