This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has over 18 years of experience in the field of ultrasound - diagnostic imaging.Computed tomography of the abdomen and subframe with contrast injection is a technique that uses a multi-segment computed tomography machine to reconstruct images of the entire structure of the abdomen and sub-frame to search for and detect lesions. injury, abnormality, pathology in the image area if any.
1. Overview of CT scan of abdomen and pelvis with contrast injection
Computed tomography of the abdomen and subframe with contrast injection is the use of a low-end CT scanner with the application of X-rays and algorithms to capture and reconstruct the abdominal and urinary organs. The frame from the diaphragm to the pubic joint includes: Liver, biliary tract, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, gastrointestinal tract, .... In computed tomography, the use of iodinated contrast agents has the effect of lightening these areas. structures, lesions, resulting in clearer images, thereby helping doctors easily distinguish and make diagnoses.In addition to evaluating the visceral parenchyma, computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis using intravenous iodine contrast also allows the morphological and pathological evaluation of the vessels supplying blood to the viscera, as well as the stalks blood vessels and drainage of malformed blood vessels, lesions in tumor cases, if any.
2. Indications for computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast injection
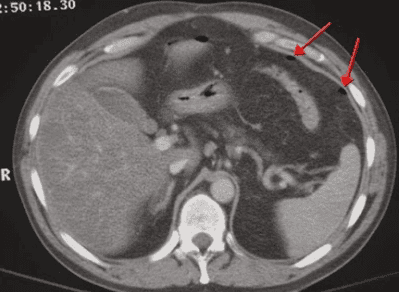
Computed tomography of the upper abdomen with contrast injection is indicated in cases of examination to help detect abnormalities in internal organs such as:Liver: Damage to the liver such as trauma, liver abscess, hepatitis, tumor. Biliary tract, gallbladder: Diseases of the biliary tract - gallbladder such as, gallstones, tumors. Pancreas: Pancreatic diseases such as acute and chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic tumor. Spleen: Damage to the spleen such as trauma, tumor. Gastrointestinal tract: Injury to the digestive tract such as inflammation, trauma, gastrointestinal bleeding, tumor. Other lesions: Abdominal abscess, pelvis, mesenteric fatty mane, mesenteric tumor, omental necrosis, ... Note, pregnant women in the first weeks should be considered for indications for micro tomography. Calculation of the upper abdominal cavity with contrast injection.
3. Why should contrast injection be used in computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis?
The procedure of computed tomography of the abdomen/subframe with contrast injection is safe with very low risk of radiation exposure. The abdomen is large, so it is relatively difficult to observe. Contrast injection will help to show and distinguish structures more clearly. Contrast has the effect of making the structure and surface of the tumor more prominent. Helps to accurately diagnose in cases of infection, inflammation, internal abscess. Helps to thoroughly diagnose and detect vascular diseases such as aneurysms, vascular dissection, vascular dissection of unknown cause. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast injection is a highly sensitive method to diagnose, evaluate the degree of calcification, the perfusion area or determine the tumor vascular source.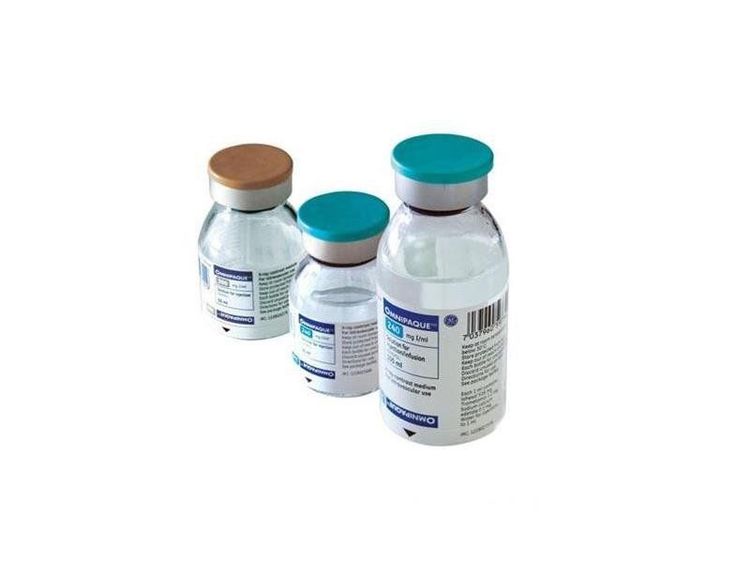
4. Abdominal/subframe computed tomography with contrast injection
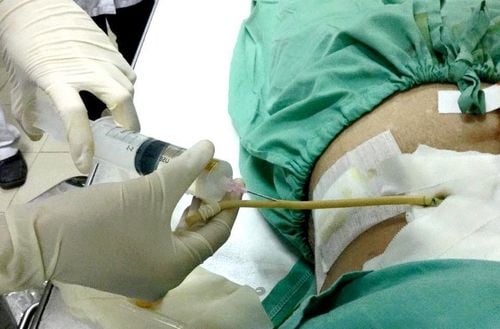
The procedure of computed tomography of the abdomen/subframe with contrast injection consists of the following steps:Step 1: The patient is placed supine on the scanning table, arms raised above the head to limit image noise. The technician instructs and asks the patient to hold their breath during the scan to avoid image noise. Step 2: Set up an intravenous line to inject contrast. The dose of iodinated contrast media is from 1.5 to 2 ml/kg body weight. Use a syringe pump for rapid injection with a minimum required velocity of 3ml/s. After injection, the injection velocity in the arterial and venous phases should reach 4 - 5ml/s. Step 3: Computed tomography of the abdomen, subframe from the diaphragm to the pubic joint, the thickness of the cut is 5-8mm, the small lesions are taken with a thin layer of about 3mm. Depending on the size of each individual and to evaluate the entire skeletal system, fat, air, soft tissue, the technician will change the appropriate field of view and the corresponding window width. Conduct imaging with cross-sectional layers before contrast injection to locate the lesion. Assess the lesion composition including fat, bleeding, or calcification by measuring the density of the suspected lesion. Compare the density of the lesion area after contrast injection to assess the extent of drug permeability of the viscera, more or less damaged blood vessels. Consider the possibility of infection and bleeding by measuring the density of the fluid structure inside the abdomen, and at the same time assessing the status of the contrast agent escaping from the gastrointestinal tract lumen into the peritoneal and retroperitoneal cavity.

5. Complications in computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast injection
Computed tomography of the abdomen and subframe with contrast injection is a modern technique, the risk of radiation is very low, contrast is used only to temporarily change the color of internal organs for imaging purposes. . However, in very rare cases, reactions to contrast may occur with the following degrees:Mild: Headache, nausea and vomiting, itching, heat, hives or rash light. Moderate: Low or high blood pressure, shortness of breath, wheezing, arrhythmia, severe hives or rash. Severe: Swollen throat, difficulty breathing, convulsions, drop in blood pressure, cardiac arrest, swelling in other parts of the body. The cases of patients who are allergic to contrast are contraindicated to have computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis, therefore, in most cases, it is indicated to perform, if an allergic condition is present, it is usually only in mild and severe cases will be treated according to the allergy protocol.
Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis with contrast injection is a modern imaging technique to help find and detect pathological abnormalities or injuries in viscera such as liver, pancreas, spleen, etc. ..
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.