This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Cong Hien - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging.The anal canal is a short tube surrounded by muscle at the end of the body's rectum. The rectum is the bottom part of the colon. Anal cancer begins when cells in the body divide without stopping. What imaging techniques are used to evaluate anal cancer?
1. What is anal cancer?
Cancer is a condition in which cells overproduce and form tumors that compress the surrounding organs. Because cancer involves cell abnormalities, nearly every part of the body is at risk for cancer. When cancer cells spread to other organs, the disease also enters the final stage, called metastasis. Most patients who enter this stage have no chance of being cured.Anal cancer originates in the anus. An opening at the lower end of the intestine and the end, which connects to the environment outside the body. When food is digested, they move from the stomach to the small intestine and then from the small intestine to the main part of the large intestine (also known as the colon). The colon absorbs water and salt left over from digested food. The final part of these substances, called feces, is eliminated from the body through the anus. The process of excreting stool outside the body through the anus is controlled by the anal sphincter. These are the ring-shaped muscles surrounding the anus that keep stools inside the body until a person has a need to defecate. The anal opening is connected to the rectum by the anal canal. The normal human anal canal is about 1.5-2 cm long. This is also the channel connecting the anus with the outer skin.
The inner lining of the anal canal is called the anal mucosa. Most cancer cells are formed and grow here. Beneath the mucosa is a system of glands and ducts responsible for secreting mucus to lubricate the mucosa. Cancer cells that form from these glands are called adenocarcinomas. Anal cancer is divided into 2 groups and has different treatments. They include:
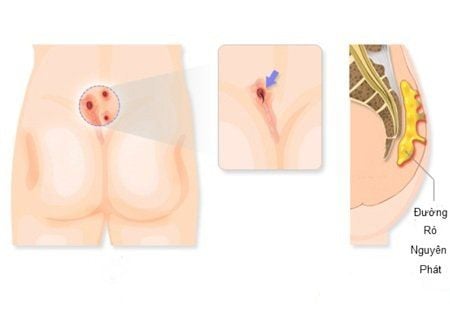
Anal cancer Cancer of the anal margin Sometimes anal cancer extends from one area to another, so It is difficult to pinpoint where they begin.
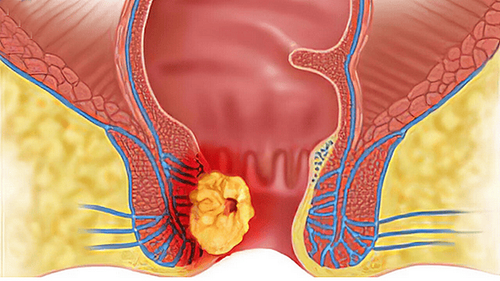
Ung thư hậu môn gây ảnh hưởng đến sinh hoạt của người bệnh
2. Classification of anal cancer
Anal cancer is divided into several types as follows:Outer tissue cancer: Sometimes abnormal cells on the inner surface layer of the anus look like cancer cells but do not grow into masses u really. This is called carcinoma in situ, otherwise known as Bowen's disease. Some scientists consider this a pre-cancer of the anus, not an actual cancer. Invasive anal cancer: This is the collective name for several different types of cancer that start in the anal area including: squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma. squamous cells of the anal margin. Adenocarcinoma: A small number of anal cancers are called adenocarcinomas. They start in the cells that line the upper part of the anus near the rectum. They can also start in the submucous glands of the anus that release secretions into the anal canal. Most anal adenocarcinomas are treated in the same way as rectal carcinoma. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Cancers involving the gastrointestinal tract commonly occur in the stomach or intestines and rarely arise from the anus. When these tumors are detected at an early stage, the most common indication for treatment is surgical resection. If it has spread to the anus, chemotherapy may be used to treat it.
3. Anal cancer symptoms
The symptoms of anal cancer can be similar to those of hemorrhoids, irritable bowel syndrome, and many other gastrointestinal diseases. These include:Disorders of defecation Loose, mucoid stools Rectal bleeding Pain The appearance of lumps near the anus In many cases anal itching and bowel incontinence may occur.

Rối loạn đại tiện là một trong các triệu chứng ung thư hậu môn
4. Causes and risk factors for anal cancer
Anal cancer is thought to be partly caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. However, anal cancer can be caused by cancer cells in other organs in the body and metastasize to the anal canal.Anal cancer can happen to anyone, but in fact, there are certain groups of people who have a higher risk of anal cancer than others, including some of the following cases:
HPV infection: HPV is a group of viruses that are sexually transmitted and remain in the body after infection. HPV is present in most anal cancers. It is also the leading cause of cervical cancer. HIV infection : People with HIV have a higher risk of anal cancer due to an already weakened immune system Sexual activity: Having multiple sex partners and having anal sex can increase the risk have anal cancer. Not using safe sex methods such as condoms also increases the risk of anal cancer by increasing the risk of HPV infection. Smoking: Smokers are more likely to get anal cancer, even if they have quit. Weakened Immune System: A weakened immune system can make the body more susceptible to anal cancer in particular and other types of infections in general. Weakened immune system occurs most commonly in people with HIV and those taking immunosuppressive drugs or those who have undergone organ transplant surgery. Age: Most anal cancers occur in people over the age of 50.
5. Imaging techniques used in the evaluation of anal cancer
One of the typical symptoms of anal cancer is rectal bleeding. This can also be the basis for doctors to initially diagnose anal cancer. In some other cases, anal cancer is diagnosed through a routine physical exam.Surgical Pap smears can also be used to check for anal cancer. Your doctor will use a large cotton swab to remove cells from the lining of the anus. These cells are then tested to identify possible abnormalities.
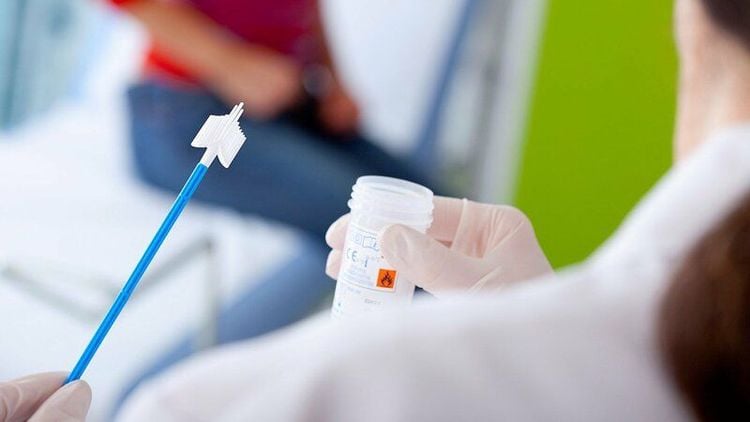
Tế bào niêm mạc của hậu môn được lấy làm xét nghiệm
However, in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis of anal cancer, doctors will order a number of imaging tests, including:
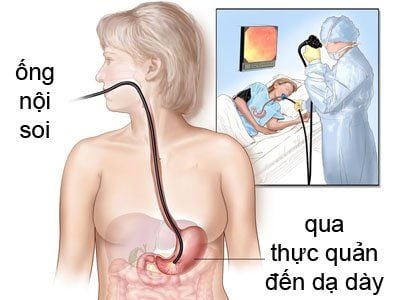
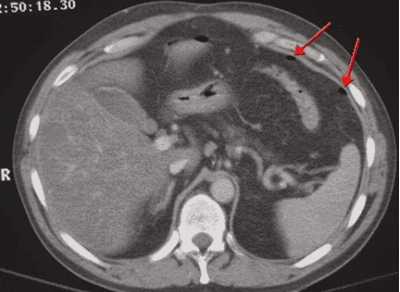
Laparoscopy : This method uses an endoscope with Attaching a small camera at the tip of the tube allows doctors to see the inside of the anus and rectum as well as perform a biopsy of the lining of the anus to identify cancer. Magnetic resonance imaging: Magnetic resonance imaging is used to determine tumor size, lymph node involvement, and invasion of nearby organs. Magnetic resonance imaging does not use harmful radiation, so it is completely safe for the patient's health. Endoanal ultrasound: Endoanal ultrasound helps doctors evaluate the structure of the sphincter and the thickness of the muscle fibers around the anal canal. This technique is also used to identify sphincter tears and assess the size and invasion of tumors. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis: This method uses X-rays to determine the spread of cancer cells and can create images of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis. Emission tomography. Emission tomography is a nuclear medicine scan that uses a small amount of radioactive material to describe several body functions. Emission tomography can detect and determine the location of cancer and the extent of anal tumours. Like other types of cancer, anal cancer is a dangerous disease for health. However, many people can live long and healthy lives after anal cancer because it is detected early. The 5-year survival rate of patients with anal cancer is 66.9%, in addition, cases with localized anal cancer have a 5-year survival rate of up to 81.3%. It is important to detect and screen for cancers early before they metastasize.
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of all types of cancer. Vinmec International General Hospital currently has a high-tech cancer screening and screening package, including genetic testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. A single gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer) Bowel cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,....)
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: cancer.org, fascrs.org, radiologyinfo.org