This is an automatically translated article.
Mitral stenosis is one of the heart diseases that will get worse over time, when the heart valves are attacked and deformed by immune complexes. Unfortunately, mild mitral stenosis often causes few symptoms. Therefore, when patients come to the hospital for examination, it is often late, the heart valve is very narrow, leading to heart failure.1. What is mitral stenosis?
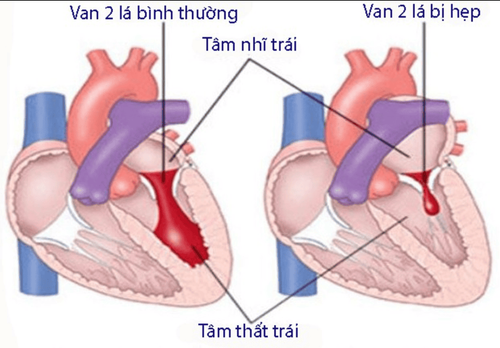
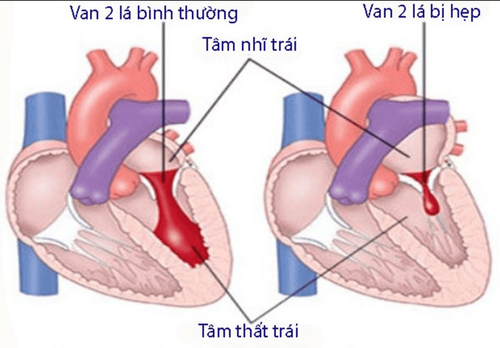
Mitral valve is a heart valve located between the left atrium and the left ventricle. It allows blood to flow in only one direction from the left atrium to the left ventricle. Blood flows into the left ventricle when the left atrium contracts, when the left ventricle contracts, the heart valve closes and blood flows through the aortic valve. A healthy mitral valve allows blood to pass through but prevents it from flowing back.
Mitral stenosis is a disease that occurs when the damaged mitral valve cannot fully open. This condition makes it difficult for the left atrium to pump blood into the left ventricle, causing blood to pool in the pulmonary circulation and in the right heart. Mitral stenosis is the main cause of congestive heart failure and leads to a number of other serious health problems such as shortness of breath and fatigue. Along with mitral regurgitation and mitral valve prolapse, mitral stenosis is also one of the three most common mitral valve diseases.
2. Causes of mitral stenosis
The most common cause of mitral stenosis is a sequelae of rheumatic fever - posterior rheumatic heart valve disease.
Rheumatic fever is a serious complication of strep throat or scarlet fever. Children are the most susceptible to this condition, as the immune system reacts to the streptococcal infection. The disease can progress for 5-10 years before it affects the mitral valve or other heart valves.
There are also a number of other causes that also cause mitral stenosis, namely:
Calcification of the mitral valve leaflet. Mitral valve ring. Complications of malignant carcinoids. Lupus erythematosus. Rheumatoid arthritis. Treatment with methysergide (rare condition). Accumulation of amyloid on the posterior rheumatic valve can cause obstruction of blood flow through the mitral valve. Genetic metabolic defects, eg Fabry disease, Hunter-Hurler disease, Whipple disease.
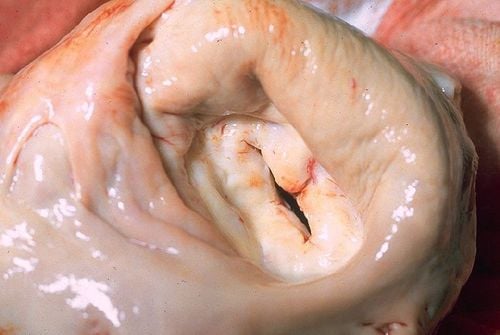
Hình ảnh hẹp van hai lá ở tim
3. Symptoms of mitral stenosis
Common symptoms of mitral stenosis include:
Shortness of breath: When mitral stenosis, the patient often has the most noticeable symptoms of shortness of breath and fatigue. Shortness of breath when lying down, on exertion, or with pulmonary edema. This is the result of a decrease in the elasticity of the lungs. Coughing up blood due to increased left atrial pressure dilates the small veins of the bronchi. Palpitations, palpitations due to arrhythmia. Chest pain. Embolism: About 80% of patients with embolism have atrial fibrillation, about 50% of patients with clinical embolism are in the cerebral blood vessels. In addition, patients can have coronary artery occlusion causing angina attacks, myocardial infarction, renal embolism causing high blood pressure. The large left atrium presses on the esophagus causing difficulty swallowing. Hoarseness due to enlarged left atrium pressing on left recurrent vocal cord. Right heart failure: Leg edema, hepatomegaly, distended jugular veins. If you feel that your body shows the above signs and symptoms, especially shortness of breath, fatigue, heart palpitations and chest pain, you should see your doctor immediately for examination and treatment. time.
4. Factors that increase the risk of mitral stenosis
Several key factors can increase the risk of mitral stenosis, including:
A history of rheumatic fever as a child. Untreated streptococcal infection. Someone in the family had mitral stenosis.
5. Complications of mitral stenosis
One of the most common complications of mitral stenosis is atrial fibrillation. The frequency of atrial fibrillation will depend on the severity of the obstruction and the age of the patient.
Patients with severe mitral stenosis and under the age of 30 usually have only 10% atrial fibrillation, if over 50 years old, 50% of atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation causes thrombosis in the left atrium and causes systemic embolism. Patients with mitral stenosis and atrial fibrillation generally have a worse systemic prognosis than those with atrial fibrillation but without mitral stenosis.
Coughing up blood and lung infection, acute pulmonary edema is also one of the serious complications of mitral stenosis. In addition, patients may also have liver dysfunction and cardiac cirrhosis. Some other complications such as: progressive rheumatic heart disease, arterial occlusion due to thrombus forming in the left atrium running out of the colon completely, endocarditis.
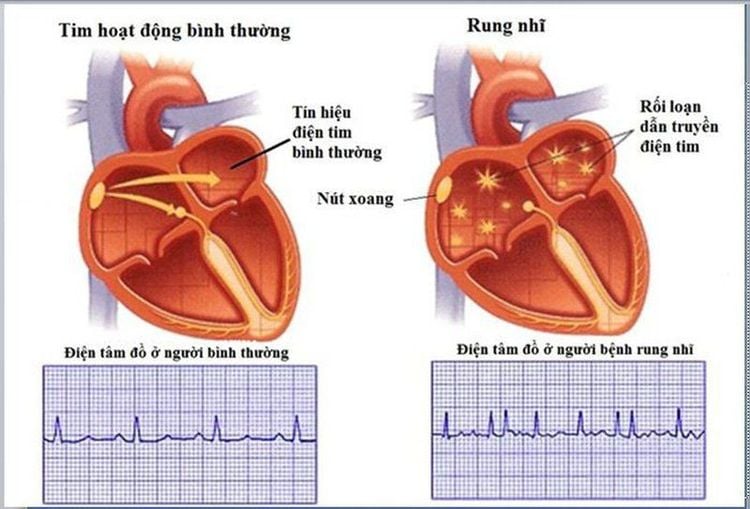
Rung nhĩ là một trong những biến chứng của hẹp van hai lá gây ra
6. Diagnosis and treatment of mitral stenosis
6.1 Diagnosing Mitral stenosis The doctor can diagnose mitral stenosis through a physical examination and performing a number of tests such as echocardiography, chest X-ray, cardiac catheterization, transmural echocardiography esophagus to identify the disease and find the root cause of the problem. In addition, the doctor can also evaluate the abnormal heart rhythm through tests such as electrocardiogram and Holter electrocardiogram, stress test to assess the heart's tolerance to physical activity.
6.2 Treatment of mitral stenosis In case the patient is diagnosed with mild mitral stenosis, the doctor may recommend that the patient visit the patient periodically to monitor the progress of the disease.
If the body shows obvious symptoms of mitral valve stenosis, you may be prescribed medication to treat.
If the patient's mitral stenosis becomes severe and medication is not effective, surgery will be the appropriate option. Surgery for mitral stenosis includes:
Valve repair Plastic surgery or balloon dilation Mitral valve replacement surgery: biological valves (from carcasses or pigs or cows), or chemical valves. 6.3 Lifestyle changes Although mitral stenosis cannot be cured through changes in daily habits and lifestyle, it plays an important part in reducing the symptoms and progression of the disease. You can make adjustments to old, unhealthy habits in the following ways:
Schedule regular check-ups to monitor your medical condition Do not arbitrarily use drugs without a doctor's prescription or do not voluntarily quit smoking prescribed by prescription Take good care of your teeth and gums Limit salt intake Maintain a healthy weight Limit alcohol, beer, caffeine Don't smoke Eat healthy, lots of green vegetables, supplements heart-healthy foods Regular exercise to improve fitness Heart valve replacement surgery is necessary when the heart valves are severely damaged, unable to be repaired or treatment with drugs does not respond. New valve replacement is intended to relieve symptoms and prevent future heart failure, arrhythmias, and other complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: patient.info