This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat - Interventional Cardiologist - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Mitral valve stenosis is a common disease in underdeveloped countries such as Vietnam, the disease is more common in women than in men. When the disease is new, there are few symptoms, so it is missed and only diagnosed at a late stage, so it has serious consequences.
1. Learn about mitral stenosis
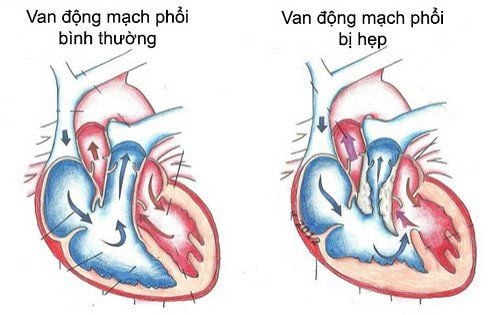
Mitral stenosis is when the damaged mitral valve cannot fully open. Normally, the area of the mitral orifice is 4‒6 cm2. When the mitral valve fat area is ≤ 2cm2 (≤1.18 cm2/m2 body charge), blood flow through the mitral valve is obstructed, forming a pressure gradient (between the left atrium and the left ventricle) diagnosed as valve stenosis 2. leaves . As a result, it is difficult for the left atrium to pump blood into the left ventricle, blood will stagnate in the pulmonary circulation and right heart. This is the main cause of congestive heart failure.Lesions in mitral stenosis are mainly infiltrates, fibrosis, thickening of the leaflets, adhesions of the valve margins, contracture of ligaments, and muscle columns that contribute to mitral stenosis. The presence of calcified deposits on the valve, ligaments, and annulus, continues to limit the normal function of the valve.
Mitral valve stenosis is a progressive disease that causes many complications such as heart failure, arrhythmia, thromboembolism or infective endocarditis ...
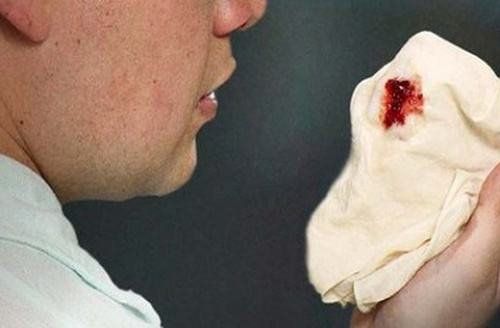
Người bệnh ho ra máu do bị hẹp van 2 lá lâu ngày
2. Causes of mitral stenosis
Congenital rheumatic heart disease Atherosclerotic lesions Congenital such as parachute mitral valve or supramitral sphincter Systemic disease that can cause mitral fibrosis: Carcinoid tumor. Systemic lupus erythematosus Rheumatoid arthritis Mucopolysaccharide deposition Infective endocarditis3. Symptoms of mitral stenosis
3.1 Physical symptoms The most common symptom is dyspnea: Dyspnea on exertion, possibly paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea and dyspnea when lying down. In the later stages, it manifests as an asthma attack and acute pulmonary edema. Coughing up blood Hoarseness Swallowing Palpitations due to atrial fibrillation Chest pain due to increased right ventricular oxygen demand with high pulmonary artery pressure Fatigue due to low cardiac output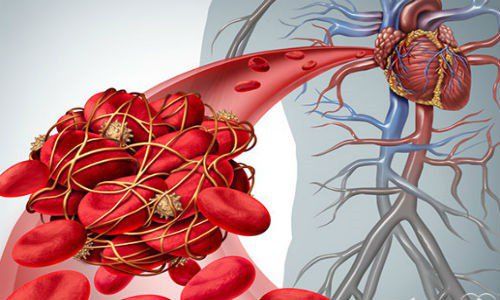
Huyết khối hình thành gây tắc đại mạch tuần hoàn
4. Subclinical tests to diagnose mitral stenosis
4.1. Electrocardiogram The first stage of the disease is still mildly narrow, not affected, so the electrocardiogram is normal.Later stage, there is a picture of left atrial dilatation with: P wide, P 2 peaks > 0.12 seconds in lead II; P2 phase, negative phase > positive phase in V1, V2 (if sinus rhythm is still present), or right axis of the heart, right ventricular thickening: high R wave in V1, V2; deep S waves in V5, V6; Sokolow - Lyon right ventricle (+).
There are also patients without sinus rhythm but atrial fibrillation causing complete arrhythmia.
4.2. Chest X-ray Image of a prominent pulmonary artery, a typical 4-arc image on the left border of the heart The lower right side of the heart has a 2-arc image due to left atrial stasis. In addition, valve calcification can be seen 2 leaves, right ventricle dilated,... 4.3. Ultrasound diagnosis of mitral stenosis Echocardiography is an important exploratory measure to confirm the pathology. In addition, ultrasound also helps to evaluate the severity of valve stenosis, the cause or mechanism, evaluate the pathological effects (cardiac function, dilated heart chambers, pulmonary hypertension), other valve lesions, thereby helping to evaluate prognosis and treatment direction

Siêu âm tim chẩn đoán hẹp van hai lá
Transthoracic echocardiography: allows detection of: thickened leaflets, reduced mobility, poor mitral valve opening amplitude, parallel mitral mobility, decreased diastolic gradient EF (EF < 15 mm/s is constriction) and helps assess the size of the chambers of the heart. 2D ultrasound: allows image detection of mitral valve with limited mobility, arch opening, thickness and calcification of the leaflets, degree of ligament adhesions, retraction of subvalve tissue as well as assessment of thickness. , sticky, calcified valve edges. 2D ultrasound also allows direct measurement of mitral orifice area, assessment of left ventricular function and other possible associated valve lesions. Doppler ultrasound: especially important to evaluate the degree of stenosis based on parameters such as: Method PHT (half-time pressure reduction) Mean pressure difference across the mitral valve, which allows to estimate the severity of the stenosis valve Estimation of pulmonary artery pressure by measuring the spectrum of associated tricuspid regurgitation or associated pulmonary regurgitation Allows assessment of comorbid lesions such as mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation, and aortic regurgitation. This is very important to help decide on the appropriate mitral valve intervention method. Transesophageal echocardiography:
A solid echocardiogram in the esophagus helps to see clearer images, more accurately assess the degree of valve stenosis as well as valve morphology and subvalve organization, helping to detect thrombosis Left atrium or left atrial appendage when transthoracic echocardiography is not identified, thereby helping to indicate the treatment modality of mitral valve dilation.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Master, Doctor Tran Hong Nhat has more than 10 years of experience in examining and treating interventional cardiovascular diseases. The doctor has participated in training courses at home and abroad. The doctor used to be an interventional cardiologist at Hue Central Hospital before working at the Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park Hospital as it is now.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support
LEARN MORE
Learn about valve replacement techniques in people with mitral valve disease How many types of heart valve disease are there? Treatment methods for mitral valve regurgitation