This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II, Senior Doctor Doan Du Dat - General Internal Medicine Doctor - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.According to statistics in Vietnam, the number of patients with mitral stenosis is quite large. This is a narrowing of the mitral valve that restricts blood flow. Although it is a cardiovascular disease, some patients have additional bleeding. So why does valvular stenosis lead to this phenomenon?
1. Where is the mitral valve located?
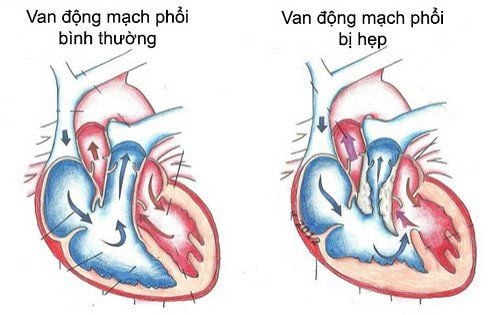
The mitral valve is a heart valve located in the left heart, separating the two chambers of the heart: the left atrium above and the left ventricle below. Normally, blood flows from the left atrium through the mitral valve, down the left ventricle and into the aorta. A healthy mitral valve will help blood flow through and prevent blood from flowing back when the heart contracts.2. What is mitral stenosis?
Mitral stenosis is a condition in which the heart valve between the left ventricle and the left atrium narrows and cannot fully open. This disease will reduce blood flow from the upper left chamber of the heart to the lower left chamber, in other words, not enough blood flow.Mitral stenosis can lead to many other problems such as fatigue, shortness of breath, blood clots, and possibly even heart failure. Possible causes of mitral stenosis include: thrombosis, radiation therapy, calcium deposition in the heart valves, congenital heart defects (abnormal heart valves have appeared since infancy).
Hẹp van 2 lá có thể dẫn đến suy tim
3. Why is he coughing up blood in mitral stenosis?
Normally, blood flows from the left atrium through the mitral valve and into the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is narrowed, blood will pool in the left atrium because it cannot drain completely into the ventricle. This leads to increased pressure in the pulmonary veins and capillaries (the system of blood vessels that supply blood to the left atrium) known as microcirculatory hypertension.Due to increased pressure in the microcirculation, the alveolar capillaries and capillaries in the lungs become enlarged and dilated, and the blood vessel walls become thinner. Under the great blood pressure created by the heart's contraction, at the same time, the slow flow through the heart will push the red blood cells and plasma into the alveolar lumen.
The bronchial artery receives blood from two main sources, the aorta and the intercostal arteries, to nourish the lungs. The bronchial vein drains blood to a single vein and then to the right heart. From the tertiary bronchi, the blood of the bronchial veins will be collected by the pulmonary veins, which are physiological left and right shunts.
Because of that connection, when the pressure in the small circulation increases, it will increase the opening of the shunts, creating collateral vessels connecting the bronchial veins to the pulmonary veins. The small blood vessels located between these two systems will have high pressure, are very fragile, when blood rushes into the bronchioles causing coughing up blood.
4. What are the characteristics of hemoptysis in mitral stenosis?
Hemoptysis in mitral stenosis is usually a sporadic cough, rarely fatal. If mitral stenosis is severe, you can feel your heart beating very fast.As valvular disease progresses, the mitral stenosis becomes worse, which will lead to increased resistance to the pulmonary circulatory system, causing right heart failure or the appearance of tricuspid regurgitation/stenosis.
Ho ra máu trong hẹp van 2 lá thường ho ra 1 ít
5. It is necessary to distinguish hemoptysis due to valvular stenosis from other diseases
Pulmonary infarction: the patient spits up dark red sputum (because it is accompanied by a necrotic part of the lung parenchyma). This is a consequence of pulmonary embolism: acute disease causes severe chest pain, shortness of breath, blocked blood vessels causing endothelial damage and vasodilatation reaction, extravasation, easy inflammation, parenchymal necrosis, making patients sick. gob. Acute pulmonary edema: common in left heart failure due to sudden decrease in blood flow from the left heart, but the right heart is still normal, or due to external factors such as infusion of large amounts of fluid causing fluid to flood the alveoli, the patient spits up pink foam. Vomiting blood in digestive diseases: the patient has no or coughs up little foam, dark brown or reddish brown, coffee grounds color. Gastrointestinal vomiting is often mixed with food, feeling nauseous, often acidic pH.
Ho ra máu do hẹp van tim với các bệnh phù phổi cấp
6. Some drugs to treat mitral valve stenosis
The use of drugs may not be able to completely treat a narrowed heart valve, but drugs can contribute to reducing the symptoms of the disease. Some drugs that can be used in the treatment of mitral stenosis are:Anticoagulants: repel, dissolve blood clots. Antihypertensives: beta blockers or calcium channel blockers. Antibiotics: treatment and prevention of group A streptococcus. Antiarrhythmic drugs: help stabilize the heart rhythm. Diuretics: When edema is present, taking diuretics will prevent the accumulation of fluid in the lungs and related organs. (Medical treatment is only a temporary treatment of symptoms, while the treatment of radical mitral stenosis requires intervention with percutaneous valve dilation, or surgical separation, valve repair or artificial valve replacement. prevent rheumatic heart disease causing mitral stenosis).
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.