This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Le Thi Thu Hang - Dermatologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Sweat ducts are yellow, translucent or skin-colored nodules that often appear on the face, especially around the eyes. Skin lesions of this type are often asymptomatic. However, sweat glands can be extremely itchy, especially when sweating, and are sometimes cosmetically invasive. When indicated, sweat glands can be treated with surgery, electrocautery, or laser.
1. How to diagnose a sweat gland tumor
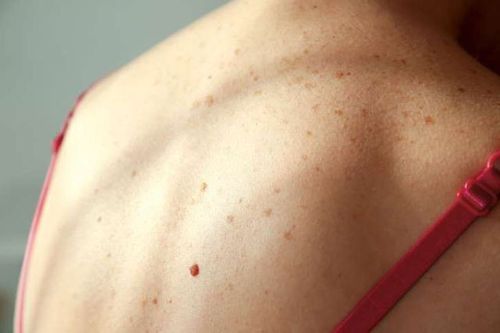
Sweat ducts are benign tumors of the sweat ducts in the skin. These tumors are located in the layers of cells from the dermis to the deep part of the dermis, and are more common in Asians and people with darker skin types.Skin lesions appear as many small, skin-colored papules, 1 to 3 mm in diameter. In people with colored skin (depigmented or darkened skin), they may appear as yellow or pale bumps. Sweat duct tumors are more common in women and most commonly appear during or after adolescence. The most common site is the skin around the eye area, sometimes on the trunk, chest, and abdomen.
The majority of ductal tumors are asymptomatic. However, some people may experience itching accompanied by excessive sweating. The diagnosis of sweat duct tumor often cannot be based on clinical signs alone, because it is difficult to distinguish it from acne vulgaris, hemangiomas, basal cell carcinomas, hair cysts, and cysts. fibrous papillae, molluscum contagiosum, sebaceous hyperplasia or eyelid yellowing.
Accordingly, when it is necessary to treat sweat gland tumors by invasive measures, it is extremely important to diagnose the nature of the skin lesion as a sweat duct tumor. At this time, a high-grade skin biopsy is indicated, as a basis for the diagnosis of sweat duct tumors as well as to rule out microcystic adnexal carcinoma or for monitoring purposes in persistent or severe lesions. Occur again periodically.
The histology of sweat duct tumors is usually located mostly in the superficial dermis and consists of many small ducts embedded in a sclerosing tissue. The duct wall is usually lined by two rows of cuboidal to flattened epithelial cells and has a lumen containing eosinophilic acid-Schiff-positive amorphous debris. Some ducts have long "tails" of epithelial cells, giving them the characteristic comma or tadpole appearance. In rare cases there has been an accumulation of glycogen in tumor cells.
In the setting of sweat duct tumor studies, skin biopsies will be performed with enzyme immunohistochemistry tests, to demonstrate the presence of sweat duct-related enzymes.

2. How is sweat duct tumor treated?
Treatment of sweat glands is aimed at reducing the appearance of the tumor rather than removing it completely, which will reduce the risk of scarring. Conversely, if attempts to remove tissue are made deeply, the intervention can lead to scarring, which compromises aesthetics. Furthermore, people with darker skin types have a higher risk of scarring. So dermatologists often recommend doing small treatments before going on to larger areas.There are two options for the treatment of sweat ducts , including medication or surgery.
2.1 Medication For this treatment, the patient can do it at home by applying drops of trichloroacetic acid to the affected area. The medicine will make the tumor shrink and fall off after a few days.
In some necessary situations, the doctor also prescribes isotretinoin for oral administration in addition. At the same time, common creams and ointments can also be used to reduce the side effects of skin irritation.
On the other hand, there is evidence that topical acitretin and tretinoin are effective when used to treat sweat duct tumors, and topical atropin has been used to relieve itching. In addition, topical application of adelmidrol, a semi-synthetic cannabinoid, was also beneficial in a case of giant sweat ducts through a mechanism of upregulation of mast cell activation. However, these topical methods are often ineffective, especially when applying these substances to the skin around the eyes, which can cause irritation.
2.2 Surgery The primary reason for choosing surgical intervention for a sweat duct tumor is for cosmetic purposes, especially if the tumor is located on the eyelids and cheeks, where it can be easily seen. The goal of tumor intervention therapy should be to destroy the tumor with minimal scarring and no recurrence. However, because sweat duct tumors are located deep in the dermis, complete removal is often unsuccessful and recurrence is common.
Here are some different surgical methods to treat sweat duct tumors :
Laser treatment : This is the most common treatment preferred by many doctors because it can reduce the risk of muscle scarring. This method uses either complete abrasion or fractional ablation laser devices including CO2 lasers and erbium lasers. For people with darker skin types, a doctor may recommend an erbium laser. The healing time is from 5 to 14 days. On darker skin types, hypopigmentation may occur and persist for several months. Electrical surgery. By using electrical energy but a knife to burn sweat glands, treatment can be successful for very small lesions or areas with milia. Cryotherapy method. The principle of treatment is to freeze the tumor. The most commonly used liquid nitrogen treatment process. Cut u. Excision is a suitable method for septal tumors that are localized to a small area. However, this treatment is not recommended for people with darker skin, as pigmentation changes will occur and take months to improve. While in Caucasians, excision works well for proliferative lesions.
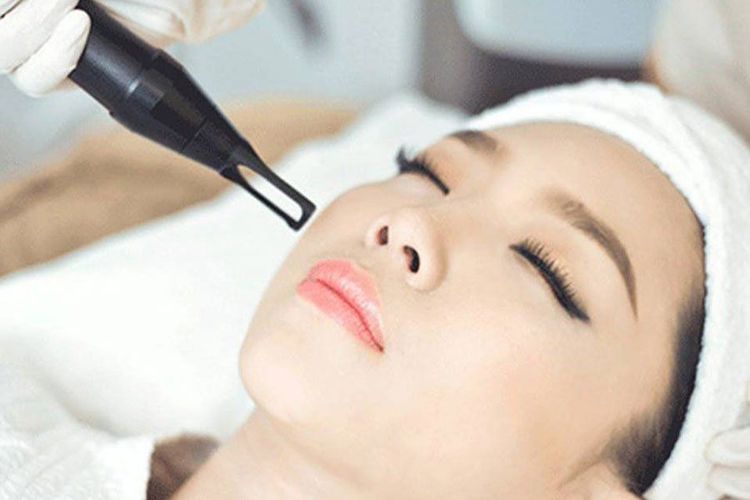

3. Complications can be encountered when treating sweat duct tumors
Recurrence, hypertrophic or atrophic scar formation, concave appearance, and excessive dyschromia (looks too dark or too pale) are common complications of ductal adenomas treatment.Accordingly, although treatment is often successful, sweat duct tumors always have the potential for recurrence and maintenance treatment may be necessary.
In summary, most cases of sweat duct tumors are diagnosed by physical appearance. However, a skin biopsy may be necessary to rule out other similar tumor types as well as before more intensive intervention. Because of the high recurrence rate as well as the risk associated with the procedure, before proceeding to cure sweat gland tumor, the patient should be consulted on methods as well as guided on subsequent skin care steps to limit healing. unsightly scars.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases, including Dermatology. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used modern facilities and machinery along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of doctors. well-trained doctors, both at home and abroad.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.