This is an automatically translated article.
Skin cancer usually begins with changes in the skin. They can be new growths or precancerous lesions. Skin cancer can be cured if detected and treated early.1. Conditions that have the potential to develop into skin cancer
1.1. Actinic keratosis Actinic keratosis is caused by overexposure of the skin to the sun. It usually occurs on the head, neck, or hands, but can also be found in other locations. Actinic keratosis can be an early warning sign of skin cancer, but it can be difficult to tell if these patches change over time and become truly cancerous. You should get early treatment to prevent it from progressing to squamous cell skin cancer. People with fair skin, blonde hair, or red hair with blue or green eyes are most at risk.1.2. Actinic cheilitis Related to actinic cheilitis, actinic cheilitis is a precancerous condition that usually occurs on the lower lip. The disease is manifested by the appearance of persistent scaly patches on the surface of the lips. Some less common symptoms include:
Swollen lips; Loss of sharp line between lips with lines separating skin from lips. Light cheilitis can progress to invasive squamous cell carcinoma if left untreated.
1.3. Cutaneous Horns Cutaneous horns develop a funnel-shaped growth that extends from the surface of the skin and then rises upward. The composition includes compressed keratin (the same type of protein in nails). It is a specialized type of photochemical keratosis. Size and shape can vary considerably, but most are several millimeters long. Squamous cell carcinoma can be found in keratosis pilaris. It usually occurs in fair-skinned elderly people with a history of significant sun exposure.
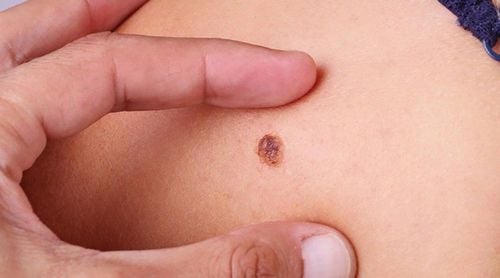
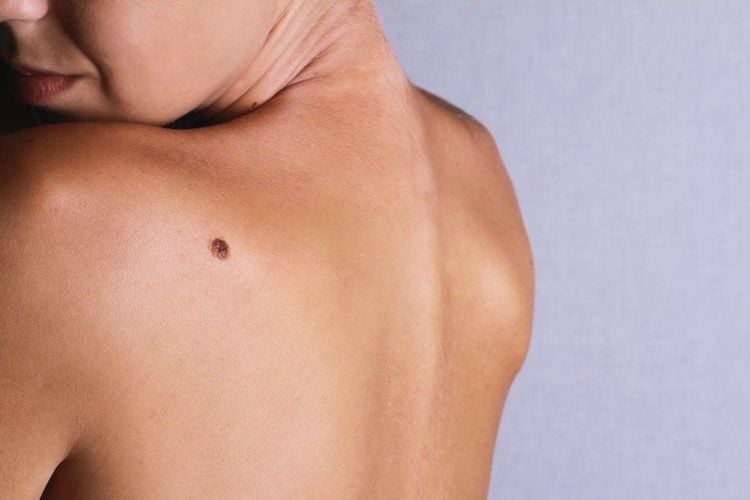
1.4. Unusual mole
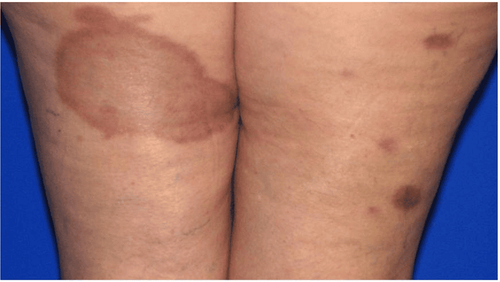
1.5. Dysplastic Nevi Dysplastic Nevi is not cancerous but has the potential to develop into malignancy. These moles can be found on areas of the skin that are exposed to the sun a lot. Dysplastic nevi are approximately 1⁄4 inches or larger, irregularly shaped with marked or faded borders. They can be flat or raised, smooth or rough in surface, often mixed in color, including pink, red, and brown.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. ABCDE sign in skin cancer detection
Most body moles look the same. Moles or freckles that look different from others or have any features of ABCDE should be checked by a dermatologist. The ABCDEs are important features to consider when examining your moles.2.1. The symbol 'A' is asymmetry Asymmetry means that one half of the mole does not match the other half. Normal moles are symmetrical. When examining moles or freckles, draw a line that divides the mole in half and compares the two halves. If they don't look the same on both sides, have them checked by a dermatologist.
2.2. The 'B' sign is the boundary If the border or edge of the mole is torn, blurred, or irregular, get it checked out by a dermatologist because melanomas often have an irregular border.
2.3. The symbol 'C' stands for color Moles that are not the same color, are transparent or have shades of brown, black, blue, white, red are suspicious. Benign moles are usually a single color. Moles that come in different colors or light and dark should be checked by a doctor.
2.4. The symbol 'D' is the diameter of the suspicious Mole if the diameter is larger than the pencil eraser.
2.5. The 'E' symbol is the degree of progression A mole that is growing, shrinking, increasing in size, changing color, starting to itch or bleed should be checked. If part or all of the mole is above the skin's surface, have it checked by your doctor. Melanoma usually grows in size or changes height rapidly.
3. Mole Screening Tips for Skin Cancer
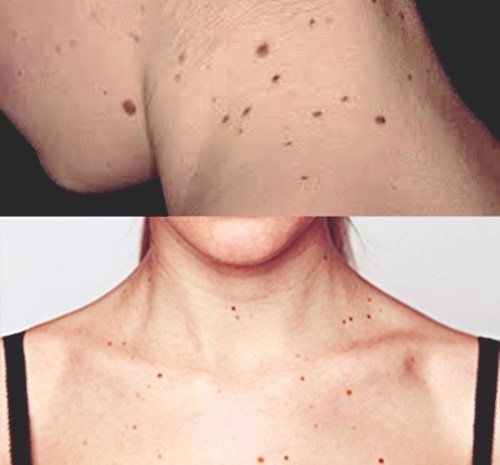
You can check for moles using a hand mirror or have a family member look at it for you. For new abnormal moles, you should take a picture of the mole and get it checked out. You should pay attention to moles if you are a teenager, pregnant or going through menopause.
4. How are moles assessed?
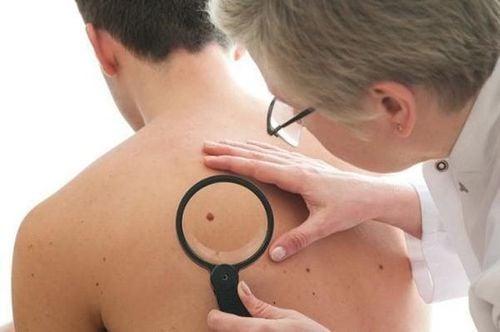
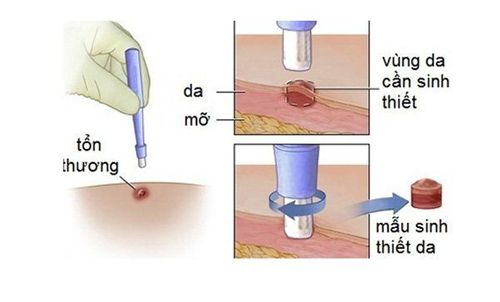
If you find a mole with abnormal ABCDE signs, soft, itchy, watery, scaly, not healing, or red, swollen outside the mole, you should see your doctor. Your doctor will perform the test by taking a small tissue sample from the mole and taking a biopsy. If cancer is found, the entire mole and surrounding skin will be removed and the wound closed. Your doctor will also perform additional treatment for you.See More: Learn skin biopsy technique
5. Early diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer
Melanoma, especially in the later stages, is very serious and difficult to treat. Early diagnosis and treatment can increase survival rates. Nonmelanoma skin cancer includes basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Both are common forms of cancer and are almost always curable when caught early. People who have had skin cancer once have an increased risk of recurrence, so they should be screened at least once a year.6. Certain types of skin cancer
6.2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma can appear as a red nodule, a scaly growth, bleeding, or a sore that won't heal. It usually occurs on the nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other sun-exposed areas of the body. The disease is curable if detected and treated early. If skin cancer is more advanced, treatment will depend on the stage of the cancer.
6.3. Bowen's disease Bowen's disease is also known as "in situ" squamous cell carcinoma. It is a type of cancer that spreads on the outer surface of the skin. In contrast, "invasive" squamous cell carcinoma can grow inside the body. The red patches may break and be mistaken for rashes, eczema, thrush, or psoriasis.
6.4. Basal Cell Carcinoma Basal cell carcinoma is the easiest type to treat. Because basal cell carcinoma spreads slowly, it occurs mainly in adults. Basal cell tumors take many forms, including a white or waxy bump, often with visible blood vessels, on the ear, neck, or face. Tumors may also appear as a flat, scaly, flesh-colored or brown patch on the back or chest, and more rarely as a white, waxy scar.
6.5. Some less common cancers Some less common types of skin cancer include Kaposi, which is mainly seen in people with weakened immune systems; sebaceous adenocarcinoma, an invasive cancer that originates in the oil glands in the skin; Merkel cell carcinoma, which is usually found on sun-exposed areas of the head, neck, arms, and legs, has the potential to spread to other parts of the body.
7. Factors that increase the risk of skin cancer
Sun exposure is the biggest cause of skin cancer. However, skin cancer also occurs in people with little sun exposure. Therefore, some other causes such as exposure to toxic environments, radiation or genetics can also be factors in causing skin cancer. Although anyone can get skin cancer, the risk is higher in people with:Light skin or light-colored eyes; Having many large and irregularly shaped moles on the body; Family history of skin cancer; Have a history of excessive sun exposure or sunburn; Live in highlands and get sun exposure year round; Have received radiation treatment.
8. Measures to reduce the risk of skin cancer

Limit your exposure to the sun's ultraviolet rays, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., when the sun's rays are strongest. When outdoors, wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher (cover both lips and ears), wear a hat, sunglasses, and sun-protective clothing. If you notice changes in your skin like new growths, the appearance of a mole, or a sore that won't heal, see your doctor right away.
Early diagnosis to have timely treatment to increase the chance of recovery for skin cancer patients. A skin biopsy is one of the methods used to diagnose skin cancer. At Vinmec International General Hospital, the skin biopsy technique is currently being applied in a sterile environment. The doctor performing the procedure is experienced and highly qualified, professional medical examination and treatment services.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Webmd.com and Cancer.orgSEE ALSO:
Measures to diagnose skin cancer The role of biopsy in diagnosing skin cancer "Miracle" returns the face to a person who has had 10 years of skin cancer