This is an automatically translated article.
Hemangioma is a benign tumor caused by the growth (excessive proliferation) of blood vessels. Hemangiomas can appear anywhere on the body, most commonly hemangiomas are seen at birth or appear in the first 6 months of a child's life.
1. Location of hemangioma
Hemangiomas can appear in any location, can be in the skin or internal organs (gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, central nervous system, larynx, thyroid, lungs, spleen) lymph nodes, bladder, kidneys, adrenal glands, etc.). In addition, hemangiomas can also be found in rare locations (bone hemangiomas, intramuscular hemangiomas, skin - visceral hemangiomas, cluster hemangiomas)...
2. When to surgically remove hemangioma
Indications for surgical removal of hemangiomas depend on the location, size and effects of the hemangioma on health. Most hemangiomas are benign tumors that do not cause complications. In this case, surgical treatment of hemangiomas may not be necessary or should be considered very carefully on the part of the physician, the patient and the patient's family.
In some cases where hemangiomas can have negative effects on certain bodily functions, patient comfort, or even be life-threatening, surgery is indicated. . For example, in the case of a large hemangioma in the skin for both children and adults, in the head and neck positions, it can cause cosmetic loss, loss of confidence or affect the functions of parts of the face such as: Hemangiomas in the eyelid folds can interfere or cause pain when the child blinks the eyelids. Not only causing discomfort, children can also feel guilty, low self-esteem and be shunned when they go to school later. Similarly, for hemangiomas in the head, nose, lips or ears, which can cause facial deformities, structural deformities of facial parts, and affect the child's aesthetics and confidence, surgery should be performed. is an option worth considering. For hemangioma surgery, the decision to have surgery should be carefully considered by the family, the tumor removal surgeon and the plastic surgeon.
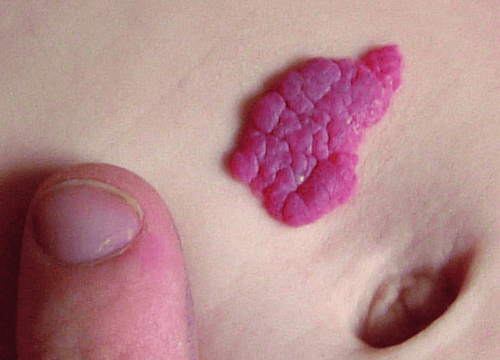
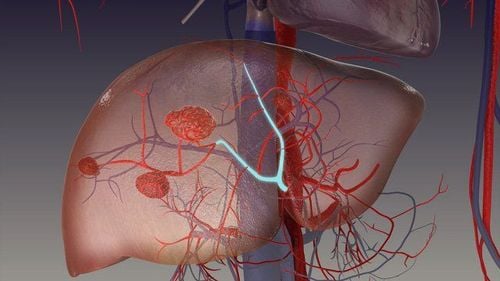
Hình ảnh u máu
3. Liver hemangioma and surgery
For hemangiomas in the liver, when diagnosed, patients are often very worried and seek treatment. However, most liver hemangiomas are small in size, if not capable of causing dangerous complications, do not need to be treated because these tumors are usually benign and rarely progress to malignancy. symptom. There is no evidence that if left untreated, liver hemangiomas will lead to cancer. Current medicine has not discovered drugs to reduce the size of tumors in the liver, only applied in some specific cases when the tumor causes typical symptoms and causes discomfort to the patient.
Large hemangiomas with a diameter of ≥ 10 cm are the most common hemangiomas in the liver. The consequences of hemangiomas in the liver can cause heart failure by increasing blood flow. Hemangiomas of the liver can occur at any age, but are usually detected in young people between 30 and 50 years old and are more common in women than in men. So depending on the size, location, and number of hemangiomas in the liver, the doctor will recommend surgery for the patient.
Surgery includes removal of the liver tumor, removal of part of the liver including the tumor and blood vessels, blocking blood flow to the liver tumor, liver transplant surgery or radiation therapy
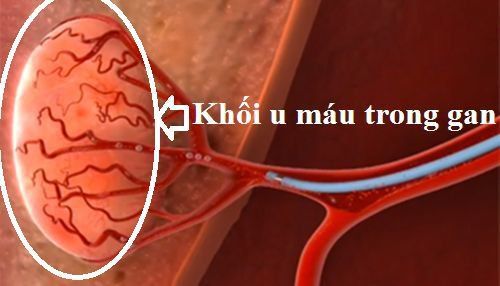
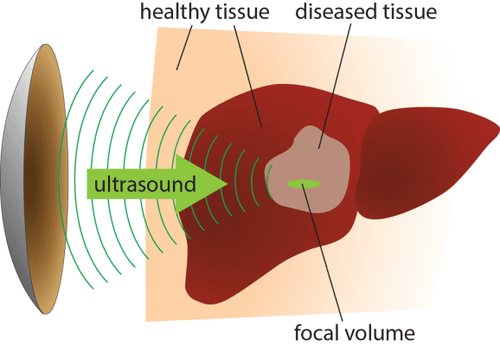
Vị trí khối u máu trong gan
4. Follow-up after surgery for liver hemangioma
After surgery, about 6 months to 1 year, the patient will be monitored for clinical examination, monitoring and examination of laboratory tests. Postoperative symptom relief was also monitored and evaluated. Treatment results will be evaluated on the scale
Totally cured There is improvement Aggravated to Counterproductive (surgery gives the opposite result than expected)

Sau một thời gian phẫu thuật, người bệnh cần tái khám
5. Common complications after surgery to remove large hemangiomas in the liver
Study by Wei Zhang et al showed that complications after resection of large liver tumors were observed in patients undergoing surgery for large hemangiomas of the liver. Of which, 32.6% had complications after surgery but no patient died. Common complications are pleural effusion (25.6%). Other less common complications included diaphragmatic injury (1 patient), hemorrhage (1 patient), pneumonia (1 patient), and bile leak (1 patient).
Care after surgery to remove large hemangiomas in the liver: After surgery, the patient should rest, do light labor, avoid stress and agitation. In addition, it is necessary to have a reasonable diet: eat easily digestible, full of nutrients, divide into many meals a day, eat lots of green vegetables and fruits. Do not drink alcohol, use stimulants and tobacco.
The most common large hemangioma surgery today is a hemangioma in the liver. After surgery, the patient should have a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition to maintain good health.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
MORE:
Benign and malignant liver tumors: What you need to know Liver hemangiomas: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Liver cancer is treated by “blocking” the blood vessels that feed the malignant tumor.