This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by resident Doctor Nguyen Quynh Giang - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. Dr. Giang has many years of experience in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially in the field of multi-segment computed tomography, magnetic resonance.Cirrhosis is caused by conditions such as chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, or fatty liver disease. It can be diagnosed by testing using X-rays such as computed tomography (CT), ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or through a liver biopsy. The results of these tests help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and predict an effective treatment.
1. What is cirrhosis of the liver?
Cirrhosis is a late stage of scarring of the liver as many liver diseases and conditions such as hepatitis and chronic alcoholism can damage the liver and lead to cirrhosis.Every time the liver is damaged, whether due to illness, drinking too much alcohol or another cause, the liver tries to repair itself. As cirrhosis progresses, more and more scar tissue forms, making it difficult for the liver to function (decompensated cirrhosis) which can be life-threatening. Some causes of cirrhosis include:
Chronic alcohol abuse Chronic hepatitis (hepatitis B, C and D) Fat accumulation in the liver (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) Iron accumulation in the liver body (hemochromatosis) Cystic fibrosis Copper accumulation in the liver (Wilson's disease) Poorly formed bile ducts (bile duct atresia) Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency Inherited disorders of sugar metabolism (galactosemia or glycogen storage disease) Disorders hereditary digestive tract disease (Alagille syndrome) Liver disease caused by your body's immune system (autoimmune hepatitis) Damage to the bile ducts (primary biliary cirrhosis) Hardening and scarring of the bile ducts (cholangitis) primary sclerosis) Infection, such as syphilis or brucellosis Using medicines, including methotrexate or isoniazid.

Fatigue Easy bleeding or bruising Loss of appetite Nausea Swelling in the legs, feet or ankles (edema) Weight loss Itchy skin Discoloration yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice) A buildup of fluid in your abdomen (ascites) Spider blood vessels in your skin Redness in the palms of your hands For women, amenorrhea or irregular periods. For men, decreased sex drive, enlarged breasts (gynecomastia), or testicular atrophy Confusion, drowsiness, and slurred speech (hepatic encephalopathy) Liver damage from cirrhosis often cannot be undone. But if cirrhosis is diagnosed early and the cause is treated, further damage can be limited and rarely reversed. In addition, it is recognized that cirrhosis can be caused by risk factors such as:
Drinking too much alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption is a risk factor for cirrhosis. Being overweight: Obesity increases the risk of diseases that can lead to cirrhosis, such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatitis: Not everyone with chronic hepatitis will develop cirrhosis, but it is one of the causes of liver disease.
2. Diagnosis of cirrhosis of the liver
People with cirrhosis in the early stages often have no obvious symptoms. Usually, cirrhosis is first detected through a blood test or routine checkup. If your doctor suspects you have cirrhosis, one or more of the following imaging tests may be ordered to diagnose cirrhosis:Computed tomography (CT): This procedure incorporates a device. Special X-ray with sophisticated computers to create multiple digital images or pictures of the liver. You may be given a contrast dye before the test to help your doctor see your liver better. This test helps determine the severity of cirrhosis as well as other liver diseases. Liver ultrasound: An ultrasound is a type of imaging test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the inside of the abdomen and/or pelvis, including images of the liver. Doppler ultrasound allows the assessment of blood flow to and from the liver. Elastography: This test evaluates the stiffness of the liver and can help diagnose the severity of scarring in the liver (known as cirrhosis). If left untreated, cirrhosis of the liver can eventually lead to cirrhosis that cannot regenerate. Elastography can detect liver stiffness due to cirrhosis earlier than other imaging tests. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): This imaging test uses a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of the liver that allow damage from various liver diseases to be assessed. cause. With this test, you may be given a contrast medicine to help your doctor see your liver better. Magnetic resonance cholangiography (MRCP): MRCP is a special type of MRI protocol designed to evaluate a part of the liver and gallbladder, called the biliary system, which is part of the liver. Magnetic Resonance Elasticity (MRE). This advanced non-invasive imaging test detects hardened liver or hardened liver fluid. Endoscopy: uses a flexible tube that attaches a light head and a camera. It can be used to look for abnormal blood vessels called varicose veins. These images show cirrhosis of the liver blocking blood flow in the portal vein that carries blood to the liver, or, over time, pressure building up in this vein, or backflow of blood into the blood vessels in the stomach. , intestines or esophagus.
Blood tests : If you have symptoms of cirrhosis or are at risk for the disease, your doctor will take a blood sample for testing. These help detect signs of liver damage, cirrhosis. What's more, it can help your doctor find out what's causing the disease. Complete blood count (CBC) test. This test checks red and white blood cells to get a picture of the body's overall health.
Viral hepatitis blood test: Viral hepatitis is caused by a virus that damages the liver and can lead to cirrhosis. These tests check the blood for hepatitis A, B, and C.
The test measures the level of enzymes and proteins the liver makes: Alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) are components that help the body break down destroy proteins and amino acids. The levels of both ALT and AST in the blood are usually low. In some cases, this level becoming high could mean that the liver is leaking enzymes, due to it being damaged by cirrhosis or another medical condition. However, levels may still be normal if you have cirrhosis. Albumin test: Albumin is a protein that the liver makes by the liver. When the liver is damaged, the level of albumin in the blood drops. Bilirubin level test: This is the yellow pigment left over when old blood cells are broken down. The liver normally removes bilirubin from the blood and removes it in the stool. But when the liver is not working properly, bilirubin builds up in the blood and can cause yellow skin and eyes. Creatinine test: This is a waste product made by the body's muscles. The kidneys will have the role of filtering this substance out of the blood. High creatinine levels are a sign of kidney damage, which can occur in the late stages of cirrhosis. Sodium blood test: If the sodium level in the blood is low, it could be one of the signs of cirrhosis of the liver. Low blood sodium levels are called hyponatremia. Biopsy: A part of liver tissue is sampled and studied by a pathologist, analyzing the extent of liver damage. Liver biopsies are usually performed by a radiologist using ultrasound guidance and are minimally invasive. If you have cirrhosis, your doctor may recommend regular diagnostic tests to monitor for signs of disease progression or complications, especially esophageal varices and liver cancer. Noninvasive tests are becoming more widely available for follow-up.
3. Treatment of cirrhosis
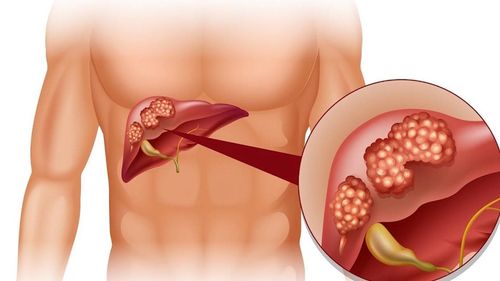
Although there is no cure for cirrhosis, your doctor can recommend different treatments to help slow scarring of the liver and reduce symptoms of the disease. First, your doctor may try to treat the underlying disease that is causing your cirrhosis through medication, weight loss, or alcohol treatment programs. To treat symptoms of cirrhosis, your doctor may recommend:Lifestyle changes including dietary changes with low sodium diets and cessation of alcohol use. Medications, such as antibiotics, may be prescribed to prevent infection, as well as vaccinations for viral hepatitis, pneumonia, and flu to help you avoid illnesses that can cause infection. Your doctor may also prescribe medication to help reduce toxins in the blood. Intra-hepatic porto-intrahepatic access (TIPS), a procedure for the treatment of portal hypertension caused by cirrhosis. An interventional radiologist places a small tube (stent) into the liver to help reduce the pressure on blood flow to the liver by returning it to the heart. Surgery in severe cases, possibly a liver transplant. This method applies a liver transplant to replace the damaged liver with a healthy liver from an organ donor. Cirrhosis is a dangerous disease that can progress to liver cancer. Therefore, early detection and treatment of cirrhosis is essential, especially in subjects at high risk of cirrhosis. Periodic health examination, liver and biliary screening at least every 6 months, screening for liver and biliary diseases is a way to protect health, early detection of diseases and signs of disease to conduct treatment, timely intervention.

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: radiologyinfo.org, mayoclinic.org, webmd.com