This is an automatically translated article.
Surgery of nerve tumors in general and surgery of anterior cranial tumors in particular by the method of opening the skull cap is an operation that requires a high level of expertise and should be carried out according to the correct procedure.
1. Introduction to the method
Anterior cranial basal tumors are prone to many types of lesions, especially cranial basal nerve tumors are difficult to surgical intervention. Giving the right indications will bring good results for the treatment of the disease.
Surgery to open the skull cap on both sides of the forehead to cut tumors in the anterior floor of the skull can be applied to lesions in the following locations: basal forehead, pituitary fossa region, around the orbital ceiling.
The goal of treatment is surgical removal of the tumor as much as possible, preserving vital functions and minimizing complication rates.
Indicated cases
Brain tumor in frontal position. Neuroma around the orbital ceiling. Neuroma in the pituitary region. Cases of contraindications (There are no absolute contraindications)
Should be avoided in cases where the tumor arises and expands at the base of the skull, it is necessary to apply another craniotomy.
Tumor invades bilateral orbit, second nerve, optic interference due to malignancy (may be contraindicated for general surgery). Tumor is responding well to endocrine therapy or radiation therapy. Cases where the patient's physical condition does not meet the requirements for surgery, severe systemic disease in combination.
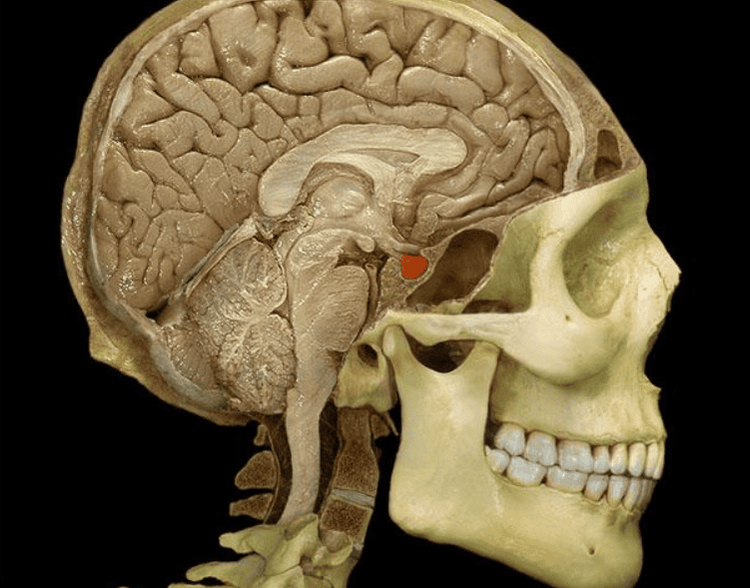
Trường hợp u thần kinh vùng hố yên cần được chỉ định phẫu thuật mở nắp hộp sọ
2. Preparation for surgery
Before surgery, the patient will be carefully examined clinically, evaluated by specialists in ophthalmology, endocrinology, otolaryngology, brain magnetic resonance imaging, CT scan to evaluate the structure of the skull base, status. tumor anterior to the base of the skull.
After that, the patient is given a shampoo, a urinary catheter (to drain the urine out) or a gastric tube (to provide food, monitor the patient's condition and aspirate fluids). When entering the operating room, the patient is instructed to keep his head 30 degrees, straight, without tilting or flexing his neck.
The composition of the operating team includes 7-8 people including anesthesiologists, neurosurgeons, surgical assistant doctors, anesthesiologists, nurses serving surgical instruments, Nursing.
Surgical instruments include skull cap opener, microsurgery instruments, Sonopet ultrasonic scalpel, hemostatic device, hemostatic glue, epidural closure supplies: artificial dura, biological glue , fat, thigh muscle scales... consumables such as cotton, gauze, skull wax, Surgicel, Prolene 4.0 thread, Vicryl 0...
3. Surgical procedure for anterior stratum corneum
At the beginning of surgery, the patient is placed in a supine position of 15 degrees and anesthetized with a mixture of adrenaline 1/1000 solution and Lidocaine; followed by endotracheal anesthesia.
Then the surgeon makes a skin incision just in front of the patient's external ear canal about 1cm, going from the upper border of the zygomatic arch upward along the hairline of the forehead on both sides (to open the craniofacial lids on both sides).
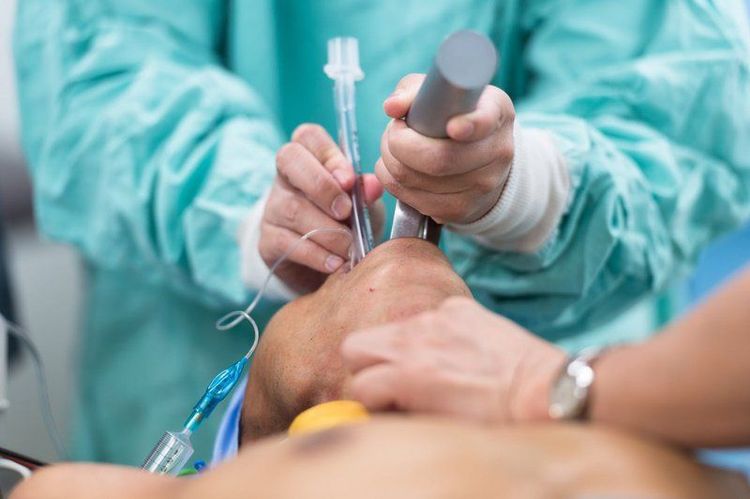
Người bệnh được gây mê nội khí quản trước khi tiến hành phẫu thuật
Perform dissection of the muscle fascia, prevent the dura mater. Open the bone close to the base of the skull, use a high-speed drill to grind the base of the forehead. (Limit cutting through the frontal sinus. Except for large frontal sinuses, it must be cut through and treated by burning the frontal sinus mucosa. Seal the frontal sinus window with thick Betadine-impregnated skull wax and seal the dura to avoid cerebrospinal fluid leakage. posteriorly through the frontal sinus). If the lesion is approached from the medial base of the skull anteriorly, resection can be performed after ligation of the anterior third of the superior sagittal sinus. Open the U-drum with a small surgical knife of size 11 with the base returning to the superior sagittal sinus. Stage 2: Carrying out tumor removal
The operation of aspirating cerebrospinal fluid at the base of the skull is at risk of brain collapse, so it is necessary to limit the use of fixed valve for too long, to avoid contusion and cerebral edema after surgery. . Using a suction tube has the effect of replacing the valve and helping to expose the lesion more clearly. The surgeon dissects the lesion (anterior stratum corneum) from important components of the anterior skull base such as: carotid artery, anterior and middle cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery and nerves (wires). I, II cord, III cord, visual interference). For large-volume neuromas, a partial tumor removal technique should be used to reduce the volume gradually. Preserve the arachnoid layer around the tumor if possible to minimize impact on normal structures around the tumor.
Stage 3: Epidural closure
By using scale, thigh fat, Bioglue, Tisseel to create adhesion.
Stage 4: Replacing the bones
Fix the bones with skull pins.
Stage 5: Close the skin and separate the nasal muscle
Use vicryl 0/0 with the muscle scale, vicryl 3/0 with the subcutaneous tissues and dafilon 3/0 with the skin layer.
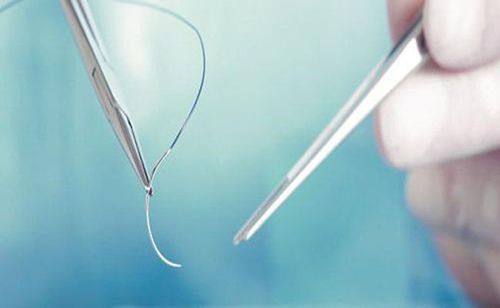
Giai đoạn cuối cùng được bác sĩ sử dụng chỉ khâu y tế đóng các tổ chức da
4. Monitoring and treatment after surgery
Monitor vital signs: Monitor the patient's respiratory, circulatory, endocrine, electrolyte, liver and kidney function... to assess vital signs. Nerve signal monitoring: Assess the patient's nerve signals based on the following criteria: Assessment of consciousness: based on the Glasgow coma scale Assessment of arm and leg mobility Observe pupil size , round or distorted shape, reflexes to light Function assessment of other cranial nerves: VIII nerve palsy (hearing loss, tinnitus, deafness), peripheral VII nerve palsy (face distortion), aspiration swallowing , choking, hoarse speech (IX cord paralysis) Monitor for infection at the surgical site such as: red, swollen incision, pus, cerebrospinal fluid leak, meningitis, encephalitis, brain fungus... and other infections other infections such as pneumonia, ulcers, malnutrition, urinary tract infections. Assess drainage status at incision: If epidural drainage (for patients with closed dura) and drainage under the scalp, perform continuous suction. If subdural drainage is found, continue to monitor and take care as ventricular drainage. Drainage is usually withdrawn after 48 hours.
Caring for patients after surgery for anterior cranial fossa tumor:
Note on patient's head position: keep neck straight, head 30 degrees, adjust position every 2 hours when patient is comatose. Caring for the patient's hair: gently wash your hair after 24-48 hours. Avoid sores by changing the head position every 2 hours, taking care of pressure points by applying medicine or physical therapy... Suture removal is performed after 7 days after surgery, for children, the time to remove sutures. later.
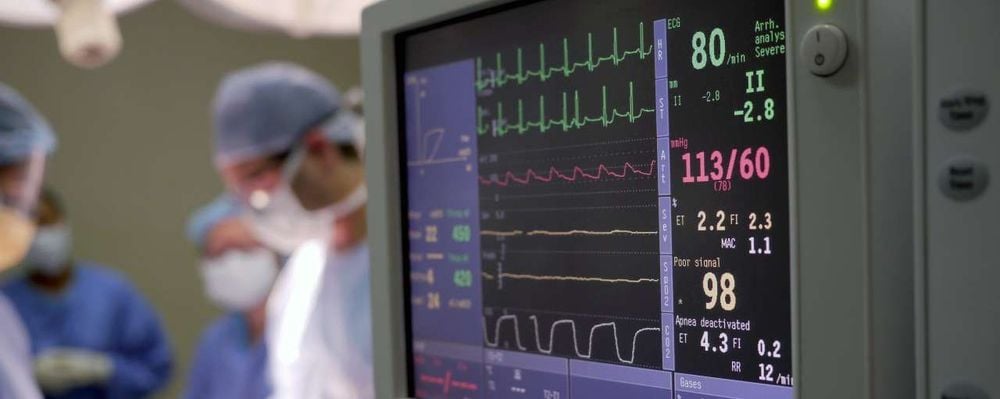
Người bệnh được theo dõi các chỉ số sinh tồn sau mổ u tầng trước nền sọ
5. Complications and post-operative treatment
After surgery for anterior stratum corneum, some risks may still occur, leading to complications. Some common postoperative complications may include:
Postoperative cerebral hemorrhage: the surgical procedure may inadvertently affect large arteries such as the carotid artery, superior sagittal sinus, and venous sinuses. cavernous vessels or small blood vessels... leading to postoperative bleeding. In this case, it is possible to manage according to the bleeding lesion and consider surgical removal of the hematoma if necessary. Cerebrospinal fluid leak: is a complication that occurs when cerebrospinal fluid flows from the skull to the outside through the patient's nostrils or ears. To manage, it is necessary to drain the lumbar spinal fluid for 4-5 days until the leak is gone; Indicated for patients using diuretics Diamox 250mg dose of 4 tablets/day in combination with soft diet, bed rest, avoid strong cough or sneeze. More severe cases may require surgery to patch the fistula. Infection, brain abscess, meningitis: For this infection, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics according to the antibiotic chart if blood cultures and cerebrospinal fluid show bacteria. In the case of the test, there is no bacteria but there is evidence of bacteria using the 3rd or 4th generation in combination with Vancomycin or Glycoside groups. Other complications such as decreased vision, smell, hemolysis, epilepsy... are treated according to the respective forms. Customers who need medical examination and treatment can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or contact to book an appointment online HERE.
Recommended video
Notes on cancer radiotherapy
MORE:
Brain abscess: When to operate? How is traumatic brain injury surgery? Treatment in patients with cerebral hematoma due to traumatic brain injury