This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Vu Van Quan - Department of General Surgery & Anesthesia, Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 10 years of experience working in the field of General Gastroenterology.Mediastinal tumor is a pathological condition in which the body's mediastinum has the appearance of benign or malignant tumors, which can be anterior mediastinal or posterior mediastinal tumors. To treat this condition, mediastinal tumor resection is considered a reasonable and effective method of treatment, but there are still some dangerous complications that should be kept in mind when operating on mediastinal tumors.
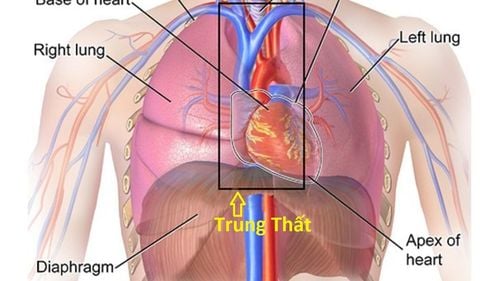
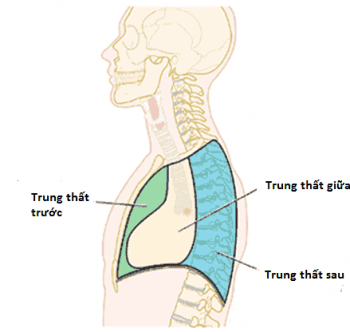
1. Anterior mediastinal tumor
Anterior mediastinal tumor is a tumor that can be either benign or malignant mediastinum occurring in the anterior region of the mediastinum, the clinical manifestation of which may be posterior pain. Besides, there can also be tumors in the posterior mediastinum and some other locations. Pre-mediastinal tumors often develop very silently, with few symptoms, so patients often discover this pathological condition at a late stage. In the later stages of mediastinal tumor appearance, the patient has serious health effects on organs such as the heart, lungs, large blood vessels in the body that do respiratory and circulatory activities. obstructed. At this time, the patient may have serious signs such as chest pain, shortness of breath, cough with blood, weight loss, weakness...If the anterior mediastinal tumor metastasizes to the pericardium, there is a can affect the body's circulatory function and cause death. Therefore, patients need to be detected at the earliest, or regularly screened for cancer to be able to successfully treat this dangerous disease.
With malignant mediastinal tumor, there may be facial edema, eye edema, cyanosis, dizziness, tinnitus... After a while, there may be edema in the hands and forearms, dilated superficial veins in front of the chest, distended neck veins, pits above the collar fullness... are signs of superior vena cava compression Shortness of breath, wheezing, dry cough Middle mediastinal tumor may have hoarseness, difficulty pronouncing, when bronchoscopy shows left vocal cord paralysis. X-ray showed compression of phrenic nerve Difficulty swallowing due to tumor pressing on esophagus. Some other symptoms such as drooping eyelids, narrowing of the eyes, constricted pupils, hot half of the face, pain in the sternum, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, and collarbones. In particular, mediastinal neuroma can lead to hiccups in patients. The dangerous complications that can be mentioned when having a mediastinal tumor are:
Obstructive pneumonia Bloody cough Upper vena cava syndrome Pleural effusion syndrome Paraplegia of lower extremities, paralysis of the diaphragm Pain in different locations innervation of sensory nerves.
2. Mediastinal tumor resection
After doing necessary tests such as blood tests, X-rays, computed tomography scans, biopsies to diagnose mediastinal tumors as well as identify benign or malignant mediastinal tumors, in most cases, In some cases, the patient will be indicated to remove the mediastinal tumor if it has reached the stage where the tumor presses on other organs and causes dangerous complications in the patient's breathing and circulation. In addition, patients can also be combined with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for the highest treatment effectiveness.To prepare for the surgery to take place most smoothly, the patient needs to do the following steps to assess the patient's general condition before performing mediastinectomy:
Assess the status of bronchitis , pneumonia in the patient and stable treatment if any before surgery. Assess tracheal stenosis, dyspnea, hypoxia in patients. Blood count test Arterial blood gas test to assess the extent of lung and mediastinal disease of the patient. Measurement of respiratory function Check the patient's cardiovascular status, possibly echocardiography. Chest X-ray, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging to investigate tracheal deviation, pulmonary infiltrates, and syndromes. pleural effusion, pneumothorax, and adjacent lung lesions. A transthoracic or endoscopic biopsy, a percutaneous biopsy to check for a tumor.
2.1 Laparoscopic mediastinal surgery Endoscopic surgery Mediastinoscopy is a method to probe the invasion of tumors in the lung, outside the lung into the mediastinum to diagnose mediastinal tumors as well as to treat mediastinal tumors. The method is performed by the doctor making a small incision on the top of the sternum and inserting the endoscope into the lower sternum, anterior to the trachea. This procedure still requires anesthesia and can stimulate the patient's trachea as well as the carina and the main bronchus of the patient intermittently.
Some complications of laparoscopic surgery for mediastinal tumors are pneumothorax, large blood vessel tear, respiratory tract injury, tracheal compression...
2.2 Chamberlain maneuver Performed by making an incision near the sternum, biopsy of the lung and anterior mediastinal mass to diagnose or drain the abscess. During this procedure, the patient needs to be bedridden and under general anesthesia. After the procedure, the patient's pneumothorax should be closely monitored.
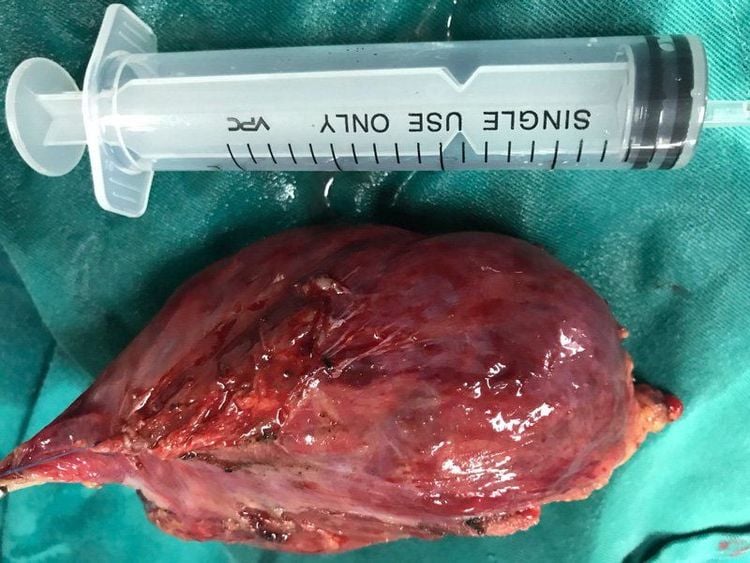
2.3 Mediastinal tumor resection Mediastinectomy is one of the most optimal methods in the treatment of mediastinal tumors. The surgical techniques for mediastinal tumors are performed as follows:
Incision between the 2 ribs to open the thorax makes it easier to remove the tumor. Open the sternum to expose the heart, blood vessels, and lungs so that large tumors can be removed. During the mediastinectomy, the patient needs general anesthesia as well as the use of other drugs. adjuvant drugs such as muscle relaxants. Some dangerous complications of this method are right ventricular tear, atrial tear, large blood vessel tear. After surgery, the patient should be supported with analgesia, which can be non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or epidural analgesia.
Video-assisted thoracic surgery or VATS: using modern video technology to increase recovery. Quickly restore the patient by setting up a camera between the ribs to make mediastinal resection techniques easier. Robotic surgery: this is a very modern method, using a robot in surgery to help see the image inside the chest and can operate through a robot arm to help minimize injuries and complications. Mediastinectomy surgery is currently being invested and developed. Depending on different pathological conditions, appropriate treatment methods can be selected, which can be open mediastinal tumor surgery as before, surgery to remove mediastinal tumors. Mediastinoscopy or other minimally invasive methods.
Recommended video:
Cancer screening: Methods for early detection of disease, reducing treatment costs and cancer mortality
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.