This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor of General Surgery & Anesthesiology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Awakening craniotomy is performed to operate on the part of the brain affected by a lesion or tumor that involves or is located near areas that control vital bodily functions or sensory and language abilities. of the patient.
1. What is craniotomy?
Arousal craniotomy is a technique performed on the brain while the patient is still awake and aware. This technique is used to treat certain brain (neurological) diseases, such as: Brain tumors or epilepsy.The most important thing in craniocerebral surgery is that the patient remains awake during the entire operation so that the doctor can monitor vital functions during surgery.
Although awake, the patient will not feel pain or any discomfort. Since the patient is anesthetized for complete analgesia of the surgical site, intravenous analgesia and target concentration controlled intravenous anesthesia (TCI).
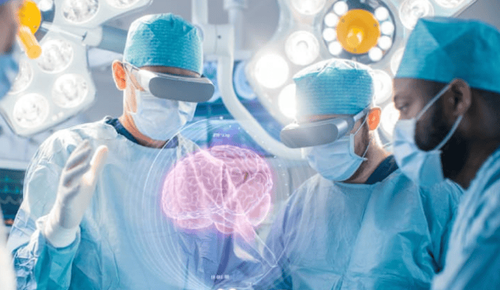
Phẫu thuật sọ não thức tỉnh là một kỹ thuật được thực hiện trên não khi người bệnh vẫn trong trạng thái tỉnh táo và có nhận thức
2. When does the patient need to perform awake brain surgery?
If the tumor needs dissection or the seizure-causing area of the brain is near parts of the brain that control motor skills, language, and vision, you may want to consider awake brain surgery.The surgeon will precisely locate important areas in the patient's brain to minimize the risk of damage to these important areas. Then, the surgical team will separate part of the patient's skull to access the brain organization. During this phase, the patient may be asked to follow a series of instructions or answer questions.
Communicating with the doctors during surgery is important for the team to evaluate the effectiveness of the surgery while the surgery is in progress and to ensure that vital functions are not compromised.
The neurologist will ask questions for the patient to answer, thereby monitoring the activity in the brain. This technique helps the surgeon to manipulate more accurately, avoiding affecting other brain areas, thereby leaving no postoperative sequelae such as dumbness or paralysis for the patient.
This surgery is especially beneficial in cases such as: Parkinson's disease or epilepsy, in which cases the surgical team can check for improvement in motor function or control of seizures during the procedure. surgery.
Arousal cranial surgery can also be used to accurately diagnose the type of brain tumor a patient has, and to remove or treat tumors located in important brain regions that may otherwise be considered non-invasive. surgery due to the risk of brain damage.
Awakening brain surgery can safely reduce the size of a growing brain tumor, prolong life, and improve quality of life. Patients who were once diagnosed as incapable of conventional brain surgery now have an additional option to consider.
Phẫu thuật sọ não thức tỉnh đặc biệt có lợi trong các trường hợp như bệnh Parkinson hoặc động kinh
3. What is the procedure for brain surgery?
3.1 Before surgery In addition to considering whether the awake brain surgery technique is the right choice for the patient, the doctor will also explain the expected results and risks. The doctor or speech-language pathologist may ask the patient to identify pictures and words on cards or on a computer so that the patient's answers can be compared during surgery.It is important for the patient to be courageous and able to remain calm during the procedure and to respond to the doctor. Because the surgery is not completely anesthetic, hearing the sound of the drill is also more or less uncomfortable for the patient. Panic and uncooperative will make surgery more difficult.
3.2 During surgery The neurosurgeon and neurologist will work closely together to determine the most appropriate type of anesthesia for each patient. These could be:
Awake during surgery: The patient will be given a targeted pain reliever (Sufentanil-TCI) and a local anesthetic on the scalp and sedation to ensure comfort. during the skin incision phase (Propofol TCI). Anesthesia at the beginning and the end, awake during surgery: The patient is given a little sedative at the beginning of the procedure. The anesthesiologist will stop the anesthesia when the surgeon is ready to begin removing the brain tumor. Once the surgeon is done, the anesthesiologist gives the patient a deeper sedation. During the procedure, the doctors keep the patient's head in a fixed position to ensure the accuracy of the surgery. The patient's hair will be shaved. The surgeon then drills a portion of the skull to access the patient's brain area. The doctor will also stimulate the area around the tumor with small electrodes.
If the tumor is in close proximity to areas of the brain that govern vision, language or movement, the surgeon will use CT images of the brain taken before and during surgery, along with human feedback disease to create a map of the functional areas of the brain. The doctor will use this brain map and 3D images from the computer to avoid affecting those areas, focusing on thoroughly eliminating brain tumors and reducing the risk of damaging important body functions. . The neurosurgeon will ask the patient to perform tasks such as talking, counting numbers, recognizing images, or raising a finger. The patient's response helps the surgeon determine the correct area to be treated as well as avoid contact with the functional brain area.
The anesthesiologist will make sure the patient does not feel pain during the surgery in addition to monitoring the vital signs (heart rate, breathing rate and blood pressure). This doctor will also talk to the patient to help the patient stay calm.
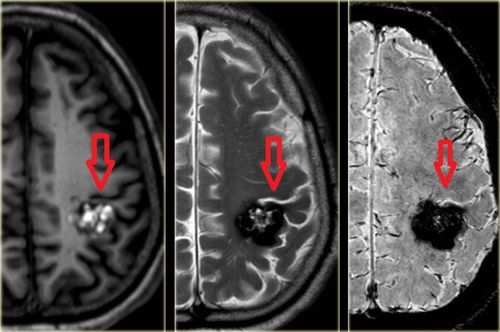
3.3 After surgery Your doctor may order a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan to make sure the tumor has been completely removed. The patient will be transferred to the intensive care unit and stay under observation for 2-3 days. Patients can usually return to work and normal activities 6 weeks to 3 months after surgery. After three months, the patient needs to be re-examined.
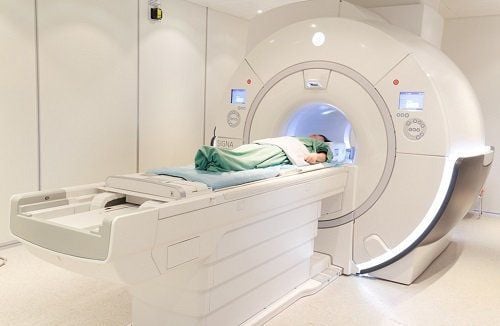
Bác sĩ có thể yêu cầu chụp cộng hưởng từ (MRI) sau phẫu thuật để đảm bảo đã loại bỏ triệt để khối u
4. Is awake brain surgery dangerous?
Since awakening brain surgery is major surgery involving the cranial nerves, some risks exist as follows:Vision changes Seizures Difficulty speaking or learning Amnesia Coordination and poor balance Stroke Cerebral edema or accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid Meningitis Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid Muscle weakness.
5. Results of brain surgery awakening
If the patient has had brain surgery to control epilepsy, significant improvements are usually confirmed. Some people no longer have seizures, while others have fewer seizures than they did before surgery.If the patient uses this technique in a brain tumor, the surgeon will attempt to remove all of the tumor. You may still need other treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy, to destroy the rest of the tumor that surgery can't reach.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests and treat diseases here can be completely assured of the accuracy and high efficiency in the treatment process.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE MORESurgery for cranial nerve tumors below the base of the skull Common warning signs of brain tumors Signs and features of brain tumors