This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Ngo Dac Thanh Huy - Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has experience and strengths in the field of diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, echocardiography, coronary angiography and intervention.Superficial vein thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot in a superficial vein. The patient will feel a dull pain, redness and swelling in the corresponding superficial vein. It is important to detect and treat the disease early before it causes other dangerous complications.
1. General information about superficial vein thrombosis
Superficial venous thrombosis occurs quite unusually, either spontaneously or from certain causes.
Subjects susceptible to superficial thrombophlebitis include:
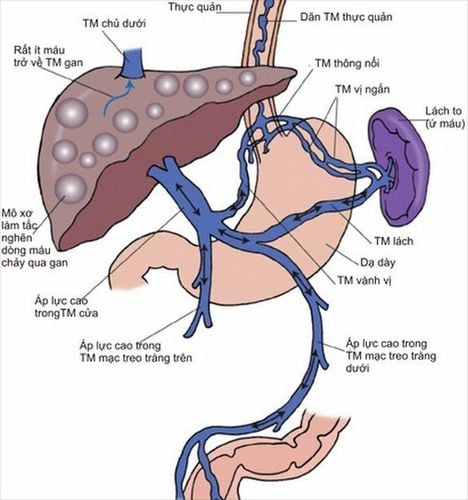
People with thromboembolic vasculitis. People with varicose veins. Pregnant. Women in the perinatal period. People with injuries. People with cancer. If superficial vein thrombosis combined with deep vein thrombosis will be very dangerous. When having a venous thrombosis, the patient will have a venous catheterization using a specialized catheter made from plastic. The catheter should be checked regularly to avoid local infection. If there is a local reaction in the vein, it should be discarded, otherwise complications can cause the thrombosis to become worse.

2. Clinical symptoms of superficial vein thrombosis
When having superficial vein thrombosis, the patient will have symptoms such as:
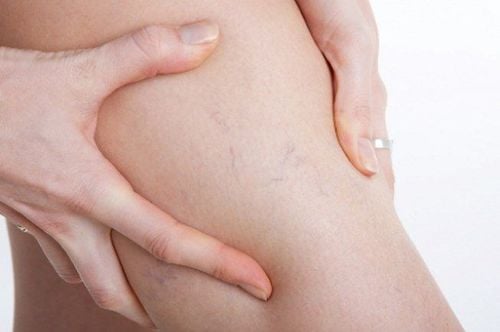
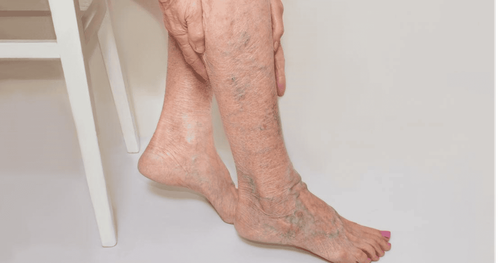
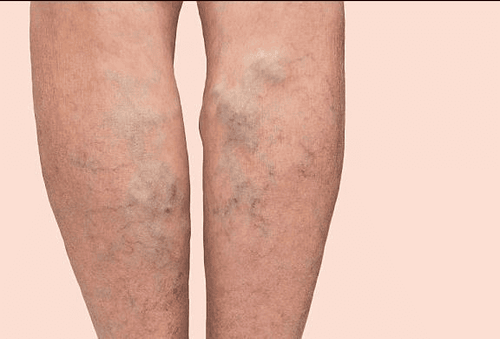
Dull pain in the corresponding vein area. Varicose veins. Redness. Pain sensitivity along the veins. These symptoms may be local or extend most of the long saphenous vein and its branches. Signs of inflammation last about 1-2 weeks, but pathogens can stay for a long time. Patients may experience swelling in the legs and tenderness in the back of the calf. If the patient has a high fever, chills, it may be septic phlebitis.
3. Differential diagnosis of superficial vein thrombosis
In superficial vein thrombosis, the contours are more prominent in the lesions and appear along the superficial veins, thereby distinguishing superficial phlebitis from cellulitis, fibrositis, erythema nodosum nodes, erythema harden or inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue.
4. Treatment of superficial vein thrombosis
To relieve the symptoms of superficial vein thrombosis, the patient may be prescribed steroid anti-inflammatory drugs. If the site of thrombus formation is not near the femoral-sigmoid junction, the thrombosis can be reduced by bed rest in combination with leg elevation and local heating.In case of dangerous superficial vein thrombosis such as a tendency to the femoral-seminal junction or widespread thrombosis, ligation and separation of the saphenous vein can be performed. If you want to recover faster, you can remove the vein. However, this method should be considered because it is quite complicated.
In case of rapid progression, anticoagulants can be used. If the disease has spread to the deep veins, possibly due to staphylococci, antistaphylococcal antibiotics should be given. If the blood culture is positive, it should be continued for more than a week, or if complications of endocarditis have not been ruled out, it can be continued for more than 6 weeks.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.