Vietnam Oncology Journal – Issue 5/2017, pp. 230-235.
Authors: Đoàn Trung Hiệp, Trần Bá Bách, Nguyễn Đình Long, Nguyễn Ngọc Tuệ, Hà Ngọc Sơn, Nguyễn Trung Hiếu, Nguyễn Văn Nam, Nguyễn Văn Hân
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the outcomes and initial experiences with using SBRT (Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy) for the treatment of lung and liver cancer at Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
Subjects and Methods: Three patients (PTs) were included: two patients with advanced liver cancer (BCLC-B, C Child A stage) ineligible for surgery, and one patient with stage IB lung cancer who was medically contraindicated for surgery.
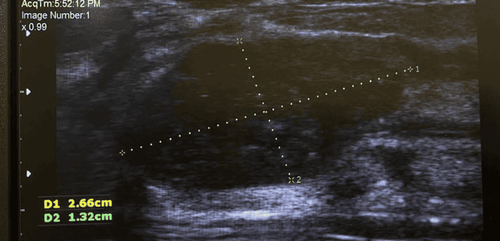
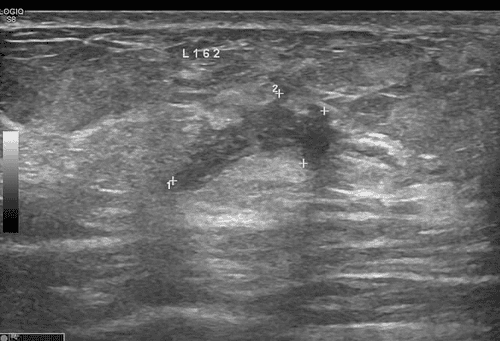
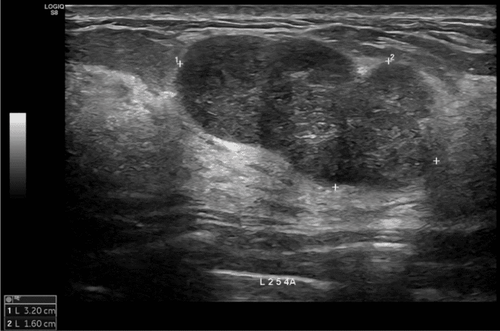
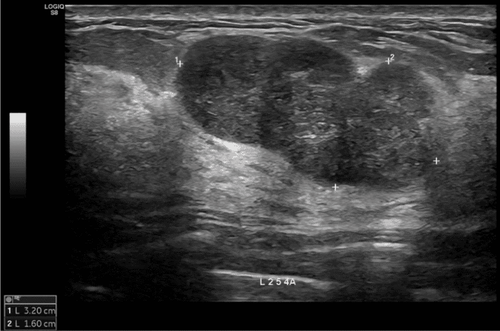
Results: All patients achieved very good partial responses: ECOG performance status scores improved significantly compared to pre-treatment levels, and both liver cancer patients experienced complete pain relief 4 weeks after completing SBRT. Tumor volumes decreased by 57% and 41% in the liver cancer patients and by 42% in the lung cancer patients. Tumor markers declined rapidly and significantly in the two liver cancer patients (81% and 98%). Side effects were observed in the two liver cancer patients receiving sorafenib, but no side effects from radiation therapy were detected. Setup errors and exposure doses related to the use of CBCT and kV-OBI were within safe limits.
Conclusion: Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) using a linear accelerator is effective for managing early-stage lung cancer with surgical contraindications and advanced-stage liver cancer ineligible for surgery. It offers rapid clinical and subclinical responses with minimal side effects. Long-term monitoring with a larger patient cohort is required for definitive conclusions.
Keywords: Liver cancer, lung cancer, Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy.