This is an automatically translated article.
Child growth retardation is currently a problem that many parents are concerned about because the rate of children suffering from this condition is increasing. However, knowing the specific causes and symptoms of growth retardation in your child will help you determine an effective treatment for your child.
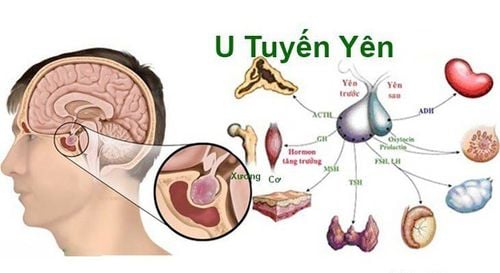
1. What is slow growth in children?
Growth retardation is a condition that occurs when a child's growth rate does not reach the normal weight and height milestones for their age. This problem can be caused by certain health conditions in the child, such as hypothyroidism or a deficiency of growth hormone in the body.
To help children grow in height normally and healthy, it is best for parents to take their children to a pediatrician periodically if their children have abnormal growth symptoms. Growth retardation can be linked to other worrisome health problems, so talking to your doctor early will help you and your child overcome this concern.
2. Common symptoms of growth retardation in children
If a child looks shorter than other children their age, there is a high chance that they are having a growth problem. On the other hand, the condition becomes more serious if the child looks 95% shorter than other children of the same age, and the child's growth rate also seems to be very slow.

Tăng trưởng chậm ở trẻ thường biểu hiện ở chiều cao của đứa bé so với bạn bè đồng trang lứa
In fact, even children of normal height can be diagnosed with growth retardation if their growth rate shows signs of slowing down. In general, each group of causes of growth retardation in children will have different symptoms. Specifically:
Children with a certain form of dwarfism: Often have symptoms such as disproportionate or disproportionate size of limbs or body. Children with low levels of the hormone thyroxine in the body: It often causes symptoms such as constipation, loss of energy, difficulty keeping warm, dry hair or dry skin. Children with low growth hormone (GH) levels in the body: It may cause a child's face to look more immature than it should be for their age because facial development is significantly affected by a lack of the hormone GH. Children with growth retardation due to bowel or stomach problems: often cause symptoms such as diarrhea, blood in the stools, constipation, nausea or vomiting.
3. What causes slow growth in children?
Studies have shown that growth retardation in children can be due to many different causes. Below are the most common causes of growth retardation in children, including:*Family history: A child may have a slower growth rate than other children of the same age if in their family have a parent or relative who is short in stature. However, if the cause of slow growth in a child is rooted in a family history, this is not a sign of concern for health. The reason that children are shorter than the average growth rate is simply due to genetic factors.
*Physical growth delay: Children with this condition usually grow at a normal rate, but their height is shorter than average. Delayed physical growth can cause bone maturation, or bone age, to be slower than a child's age. This also makes children more likely to go through puberty later than other children of the same age. Therefore, during the early years of adolescence, children's height seems to be below average, but they can still catch up with other children as adults.

Trẻ bị trì hoãn tăng trưởng thể chất vẫn có thể bắt kịp tốc độ phát triển chiều cao khi trưởng thành
*Children's body has a deficiency of growth hormone (GH): In a normal body, GH hormone plays an important role in stimulating and promoting the growth of tissues in the body. However, when a child has a partial or complete deficiency of this hormone, it can seriously affect the child's growth rate.
*Hypothyroidism : This is a health problem in children that is related to an underactive thyroid gland. Normally, the thyroid is the organ responsible for releasing hormones that promote and maintain a normal rate of growth in children. Therefore, slow growth can be a sign that your child's thyroid functions are underactive.
*Children with growth retardation due to Turner syndrome (TS): This is an inherited condition that occurs mostly in women with a partial or complete loss of the X chromosome. Children with TS can still produce growth hormones as normal, but their bodies cannot use them effectively.
*Some other causes of growth retardation in children: These are less commonly mentioned causes, including:
Anemia in children, especially sickle cell anemia Children with syndromes Down : This is a genetic condition, children often have up to 47 chromosomes instead of 46 as in normal people. Digestive, heart or lung problems Bone dysplasia, which often severely affects bone growth Poor nutrition Pregnant women taking certain medications Excessive stress
4. Diagnosis of growth retardation in children
In order to diagnose growth retardation in a child, the pediatrician will first gather some detailed information about the child's medical history as well as the patient's family history, including:Your child's birth history What is the baby's weight and height at birth? Height measurements of other family members Does any family member have a developmental delay?

Bác sĩ nhi khoa sẽ thu thập thông tin để chẩn đoán tình trạng chậm tăng trưởng ở trẻ
Sometimes, a child's slow growth and small stature can be a sign of serious syndromes, such as Turner or Down syndrome.
5. Treatments for growth retardation in children
Choosing the right treatment for your child will depend a lot on the underlying cause of the growth retardation.If the main cause of growth retardation in a child is related to genetic problems or to a delay in physical growth, the physician will not recommend any use or intervention to the patient. any treatment. On the other hand, if growth retardation is due to other underlying causes, some of the following treatments may be recommended:
*Growth hormone (GH) injections: This is commonly used. for children with growth retardation due to a deficiency of growth hormone (GH) in the body. Children can be given GH injections at home and are usually given once a day. In general, this treatment can be continued for several years while the child is growing. During treatment, the child will be monitored by a specialist to evaluate the effectiveness of the GH injection and the dose can be adjusted as needed.
In addition, the doctor may also order GH injections for children with growth retardation caused by Turner syndrome (TS). Although the body of a child with TS is still able to produce growth hormones naturally, they are not used effectively. Therefore, doctors often recommend parents to give children from 4-6 years old GH injections every day to increase the ability to develop normal height for children when they are adults.
*Use of thyroid hormone replacement medicine: If your child's growth retardation is caused by hypothyroidism, the doctor may prescribe thyroid hormone replacement medicine for the child. During the use of the drug, the doctor will regularly monitor the child's thyroid hormone levels to assess the effectiveness of the treatment. Some children may be able to correct their thyroid hormone disturbances on medication for several years, but others may need to continue on treatment for the rest of their lives.
Tùy thuộc vào nguyên nhân khiến trẻ chậm tăng trưởng để có phương án điều trị phù hợp
6. Are there prospects for children with growth retardation?
The outlook for treatment for children with growth retardation will depend on its underlying cause, as well as when to begin treatment for the child. If growth retardation in children is diagnosed and treated early, the child can completely reach a height close to normal or even develop normally like other children of the same age.Late diagnosis and treatment can increase the risk of physical retardation and a number of other dangerous complications for the child's health. Because, when reaching adulthood, it will cause the child's bone growth cartilage to close and the ability to grow more height seems to be an impossible thing.
To prevent and improve slow growth in children, parents should supplement with supporting products containing lysine, essential micro-minerals and vitamins such as zinc, chromium, selenium, B vitamins to help meet the needs of children. meet the nutritional needs of children. At the same time, these essential vitamins also support digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, help improve anorexia, and help children eat well. Parents can also apply dietary supplements and functional foods derived from nature for easy absorption by the baby. The most important thing is that the improvement of the baby's symptoms must take place over the long term. Combining many types of functional foods at the same time or changing many types in a short time can make the baby's digestive system unable to adapt and completely not good. Therefore, parents must be really persistent with their children and regularly visit the website vimec.com to update useful baby care information.
Reference source: healthline.com