This is an automatically translated article.
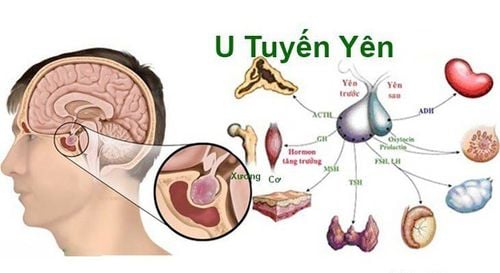
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Do Thi Hoang Ha - Doctor of Biochemistry - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.The pituitary gland is an extremely important endocrine gland in the body, directing the activities of most other endocrine glands. Although it is only the size of a pea and weighs about 0.5g, it is a place where a lot of hormones are secreted.
1. What is IGF-1?
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1, abbreviated "insulin-like growth factor-1"), also known as Somatomedin-C, has an insulin-like structure, encoded by the IGF-1 gene - together with growth hormone (GH) secreted by the pituitary gland, helps promote the growth of the whole body and the growth of bones and normal tissues in particular. The main role of IGF-1 is to promote cell division (mitosis) and differentiation (differentiation) of cells in different tissues. IGF-1 is produced by the liver, skeletal muscle, and many other tissues in the body under the stimulation and regulation of the hormone GH. Therefore, IGF-1 plays a central role for all GH activities, stimulating the growth of the whole body, especially the growth of the skeletal system and the production of lean muscle mass.Since GH is released into the bloodstream by the pituitary gland throughout the day, it is difficult to interpret results from a single GH test. Unlike GH, which is characterized by stable levels at all times of the day, IGF-1 is a reflection of GH excess and deficiency. This makes IGF-1 a useful indicator of average GH levels. Therefore, the IGF-1 test is often used to help diagnose the cause of growth abnormalities, evaluate GH deficiency or GH excess.
IGF-1 is produced throughout life; The highest rates of IGF-1 production occur during the growth spurt of puberty. Levels of IGF-1, like GH, are usually low at birth, increase gradually as the child grows, peak at puberty and then decline gradually throughout adult life. Deficiency of GH and IGF-1 can occur when the pituitary gland is dysfunctional, causing the total depletion of pituitary hormones (hypopituitarism) or by a pituitary tumor, which damages the cells that synthesize GH. . Besides, IGF-1 deficiency also occurs when the body is insensitive to GH, which can be primary (inherited) or secondary to conditions such as malnutrition, hypothyroidism, sex hormone deficiency or have severe chronic diseases and severe malnutrition.
If IGF-1 deficiency occurs early in life, usually as a result of GH deficiency, bone growth as well as overall body growth is inhibited, resulting in a child with short stature. small, shorter than other children of the same age, late puberty. In adults, decreased IGF-1 production can lead to low bone density, less muscle mass, and dyslipidemia.
Conversely, excess GH and IGF-1 can cause skeletal abnormalities and signs and symptoms of gigantism and acromegaly. In children, the bones will grow longer, becoming a very tall person with large feet and hands. In adults, acromegaly causes thick bones and soft tissues, such as the nose and ears, to swell, painful joints, erectile dysfunction or menstrual disorders. Both of these conditions can lead to disorders of other organs such as the heart, liver, and kidneys, increased risk of cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, osteoarthritis, and reduced life expectancy.
IGF-1 là một loại hormone do tuyến yên tiết ra
2. What is the role of the IGF-1 test?
An IGF -1 test may be used for one of the following purposes:Determination of growth hormone (GH) deficiency. Although this is not a diagnostic test for GH deficiency, IGF-1 may be ordered along with GH stimulation tests to provide additional information. Monitor for abnormal results on other hormone tests Assess pituitary function (eg, co-administer adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), administer with prolactin or FSH and LH to help diagnose dysfunction pituitary function and hypopituitarism (hypopituitarism) Detects excess GH and helps diagnose and monitor acromegaly and gigantism. with tests of other hormones in GH stimulation testing, when:
Child has symptoms of GH deficiency, such as slow growth rate, short stature Child has symptoms of delayed puberty Adults with symptoms that suggest a GH deficiency, such as decreased bone density, fatigue, reduced exercise capacity, and dyslipidemia Suspect hypopituitarism Periodic follow-up patients being treated with exogenous GH Periodic follow-up of patients after treatment of pituitary tumors by surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy to Evaluation of pituitary tumor recurrence. More rarely, the IGF-1 test may be ordered, along with the GH suppression test, when examining a child with symptoms of gigantism or an adult with signs of acromegaly.
3. How is the IGF-1 test done?
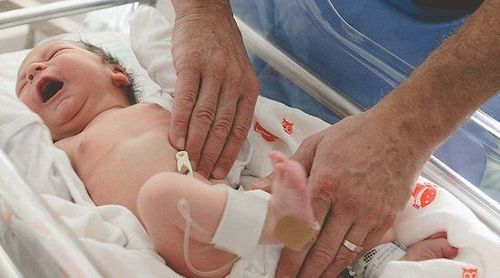
The IGF-1 test measures the level of the hormone IGF-1 in the blood. A blood sample will be collected by inserting a needle into a vein in your arm, similar to regular blood tests.
In general, the patient does not need to prepare anything before taking this test. Where it can be done at the same time as other tests, you may need to fast for at least 12 hours before the sample is taken.
The test tubes containing the patient will be inserted into the machine and the whole process will be done automatically, until the test is printed. Therefore, after taking blood, the patient can return to normal activities, go home and schedule a date to return for results.
Xét nghiệm IGF-1 là đo lường nồng độ của IGF-1 trong máu
4. How are IGF-1 test results analyzed?
Any one result of the IGF-1 test must be considered in a particular context. Some people can be GH deficient but still have normal IGF-1 levels.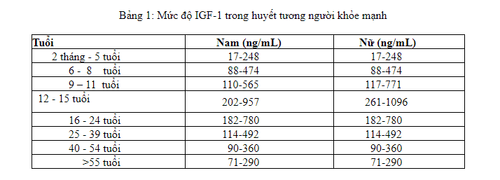
Mức độ IGF-1 trong huyết tương người khỏe mạnh phụ thuộc vào tuổi và giới
4.1 Lower-than-normal IGF-1 Levels A decreased IGF-1 level is likely due to GH deficiency or GH insensitivity.
If occurs in children, GH deficiency will cause short stature and growth retardation, At this time, children should be treated with GH supplements from outside. However, in adults, IGF-1 levels tend to decrease with age. Even so, if IGF-1 is below physiological levels in the general population of the same age group, this should also be considered due to GH deficiency or GH insensitivity.
If low IGF-1 is suspected to be due to decreased pituitary function (hypopituitarism), several other endocrine glands and pituitary-regulating hormones will need further evaluation to determine the appropriate treatment. Impaired pituitary function may be due to genetic defects or may result from damage to the pituitary gland following conditions such as trauma, infection, or autoimmune conditions.
In addition, decreased IGF-1 levels can also be found in malnourished patients such as anorexia nervosa, chronic kidney disease or chronic liver disease,...
4.2 High IGF-1 levels Higher than normal IGF-1 levels higher than normal are associated with increased GH production. Because GH levels vary throughout the day, the IGF-1 test should be viewed as a reflection of average GH levels, not actual GH levels in the blood at the time of IGF-1 sampling. Accordingly, if GH is produced abundantly, the level of IGF-1 will stabilize at a high maximum level in the blood. Elevated levels of GH and IGF-1 are physiologically normal during puberty and pregnancy but are most commonly caused by pituitary tumors (usually benign).
If measured IGF-1 is still elevated after surgical removal of the pituitary tumor, the intervention being considered may not be completely effective. Other therapies such as additional medications and/or radiation therapy will need to be considered. In case the IGF-1 levels have returned to the "normal direction" indicating that the treatment is effective, the patient's pituitary gland is no longer producing excess GH, long-term monitoring is also necessary. detect increased levels of IGF-1 to know early the possibility of recurrence of pituitary tumor.
In summary, even though the pituitary gland is tiny and located deep in the brain, its function can still be detected by measuring IGF-1 levels in a simple, easy-to-implement blood test. At this point, the results will be a valid answer to the patient's condition and help guide the correct active intervention.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE
MORE:
Symptoms of cancer Pituitary gland Consequences of pituitary dysfunction Hypopituitarism: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment