This is an automatically translated article.
Biopsy of skin moles is an important procedure, helping doctors accurately diagnose skin cancers, especially melanoma. However, what should be kept in mind when performing this biopsy method?1. What is melanoma?
Melanoma is the deadliest type of skin cancer, which develops from melanin-producing cells. Most skin melanomas appear as moles on the skin that can then spread to nearby areas. More dangerous, they will invade the retina, veins, lymph nodes and eventually metastasize to the brain, liver, lungs or bones.
According to research, people under the age of 40 will have a high risk of this disease, especially for women (accounting for a higher rate than men).
2. Causes of skin cancer
The main causes of skin cancer include:
UV (ultraviolet) rays from sunlight or ultraviolet lamps are the leading factor in causing the disease, because it messes with the skin too much. melanin production in the skin. Inherited genetic mutations There are also a number of factors that increase the risk of skin cancer, including:
Severely sunburned skin Caucasian skin Living near the equator: often exposed to direct sunlight The sun has a higher amount of radiation, so it is more susceptible to UV exposure. Freckled skin Having many moles or unusual moles on the skin Using skin dyes Having a family history of melanoma Immunodeficiency
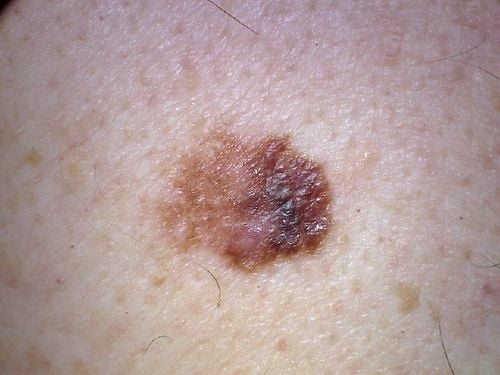
Ung thư hắc tố da là một loại ung thư da nguy hiểm nhất, phát triển từ các tế bào sản xuất melanin
3. Signs and symptoms of skin cancer
When people have melanoma, the patient may experience the following symptoms:
Uneven mole contours Asymmetrical shape The size of the moles grows over time Change in color Enlarged lymph nodes Moles that itch, ulcerate, burst, or bleed Difficulty breathing Bone pain when the tumor has spread to the bone Convulsions, headaches Vision problems when the tumor has spread to the brain You should see your doctor if you notice The following conditions occur:
The mole spreads and grows back The color of the mole or dark spot on the skin turns red, or the skin around the mole reddens, turns brown. The mole is sore, oozing pus or bleeding
4. Things to keep in mind when biopsiing a mole on the skin
Skin mole biopsy is the only way to accurately diagnose skin melanoma. This is a procedure in which part or all of a bowel nodule or suspicious growth is removed from the skin, and then a sample is sent to a laboratory to be checked to see if it is cancerous.
Some moles can be sampled through the use of a non-invasive patch that requires no anesthesia and is completely painless. However, by far the traditional skin biopsy is still the most widely used way to diagnose skin cancer.
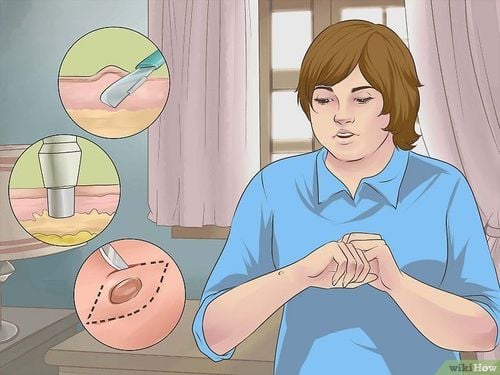
5. Types of skin mole biopsies
Types of skin mole biopsies include:
5.1 Click biopsy Using a pen-shaped needle about 2-4mm in size, the doctor will then take a biopsy sample on the skin and sew it up with a stitch. sew. However, the biopsy wound is quite small, so sometimes without stitches, the wound will heal on its own.
5.2 Shaving biopsy The doctor will use a razor-like tool to remove a small portion of the top layers of skin (the epidermis and part of the dermis).
5.3 Excisional biopsy The doctor will use a small knife to remove the entire mole or growth along with an area of normal skin.
5.4 Surgical Biopsy Only the most abnormal part of a mole or growth is performed surgically for laboratory analysis.
The type of skin biopsy procedure you undergo will depend on your medical condition. Doctors may opt for a press biopsy or excisional biopsy to remove the entire growth of abnormal moles, based on the patient's medical condition. Surgical biopsies may be used for moles that are large and difficult to remove with other techniques.

Hình ảnh minh họa các loại sinh thiết nốt ruồi trên da
6. Determining the stage of skin melanoma
After diagnosing melanoma with a mole biopsy, the next step is to determine the stage (extent) of the cancer. To determine the stage of the disease, the doctor will:
6.1 Determine the thickness The thickness of the melanoma is determined by carefully examining the melanoma under a microscope and measuring it with an instrument dedicated (micrometer). The thickness of the melanoma helps doctors decide on the right treatment plan for the patient. The thicker the tumor, the more severe the disease.
6.2 Determine how far the tumor has spread For this type of biopsy, a dye is injected into the area where the melanoma was removed.
After the injection, the dye will need some time to flow from the tumor to the nearby lymph nodes. The first lymph nodes that take the dye will be removed and checked for cancer cells. If the first lymph nodes are free of cancer, it is very likely that the melanoma has not spread beyond the area where it was first discovered. Your doctor may also consider a number of other factors to determine how aggressive a melanoma is, such as whether a mole on the skin has an ulcer, or how many dividing cancer cells are found. seen under a microscope.
The stage of melanoma is usually arranged in Roman numerals I through IV. Stage I is usually not dangerous and has a high success rate of treatment. The higher you go, the lower the chance of a full recovery. By stage IV, the cancer has spread beyond the skin and to other organs of your body, such as your lungs or liver.
Currently, at Vinmec International General Hospital, which is one of the leading hospitals in Vietnam, it is synchronously invested in facilities and the world's leading modern equipment, effectively supporting the treatment of patients. diagnosis and treatment, serving medical examination and treatment.
Here, one of the services provided is histopathology. Patients who suspect skin cancer can make an appointment to visit the doctor. Based on the clinical signs, the doctor can assign the patient to perform a skin biopsy to verify and assess the extent and condition of the disease, thereby having appropriate and timely treatment.
For detailed advice on skin biopsy techniques at Vinmec, you can go directly to Vinmec medical system nationwide or contact to book an online examination HERE.
MORE:
Role of biopsy in the diagnosis of skin cancer Skin cancer diagnostic measures Skin cancer pictures