This is an automatically translated article.
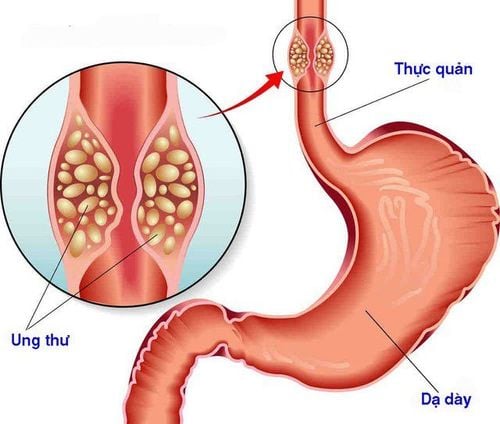
Esophageal cancer is the sixth leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Esophageal cancer usually begins in the cells that line the inside of the esophagus, but it can occur anywhere along the esophagus. So who is most susceptible to esophageal cancer?1. Esophageal cancer risk factors
AgeThe risk of esophageal cancer increases with age. Less than 15% of esophageal cancer cases occur in people under 55 years of age.
Gender
Men have a higher risk of esophageal cancer than women.
Tobacco and alcohol
The use of tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, pipe tobacco and chewing tobacco, is a major risk factor for esophageal cancer. The more tobacco a person uses and the longer a person uses tobacco, the higher the risk of cancer.
A person who smokes a pack of cigarettes a day or more has at least twice the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma compared with a nonsmoker, and the risk does not disappear or decrease as the person does not stop using the drug leaves.
Drinking alcohol also increases the risk of esophageal cancer. The more alcohol you drink, the higher your chances of getting esophageal cancer. Alcohol increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma more than the risk of adenocarcinoma.
Smoking combined with alcohol consumption increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma more than using either tobacco or alcohol alone.
Hút thuốc lá và uống rượu làm tăng nguy cơ ung thư thực quản
The stomach normally produces acid and enzymes to help digest food. In some people, acid can escape from the stomach up to the lower part of the esophagus. The medical term for this pathology is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or just reflux. In many people, reflux causes symptoms such as heartburn or pain in the center of the chest. However, in some cases, reflux does not cause any symptoms.
People with GERD have a higher risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma than the general population. This risk seems to be higher in people with more frequent symptoms. But GERD is very common, and most people with it do not go on to develop esophageal cancer. GERD can also cause Barrett's esophagus, which is associated with a higher risk.
Barrett's esophagus
If the reflux of stomach acid into the lower esophagus goes on for a long time, it can damage the inner lining of the esophagus. This causes the esophageal squamous cells to be replaced by glandular cells. These glandular cells often look like the cells lining the stomach and small intestine, and are more resistant to stomach acid. This condition is called Barrett's (or Barrett's) esophagus.
The longer people have reflux, the more likely they are to develop Barrett's esophagus. Most people with Barrett's esophagus have symptoms of heartburn, but many have no symptoms at all. People with Barrett's esophagus have a much higher risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the esophagus than people without the condition. However, most people with Barrett's esophagus do not develop esophageal cancer.
The glandular cells in Barrett's esophagus can become more abnormal over time. This can lead to dysplasia, which is a precancerous condition. Dysplasia is classified by having these abnormal cells under a microscope. Low-grade dysplasia looks like normal cells, while high-grade dysplasia is even more abnormal. High-grade dysplasia is associated with the highest risk of cancer.
Obesity
People who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. This is partly explained by the fact that people with obesity are more likely to have GERD.

Những người thừa cân hoặc béo phì có nguy cơ mắc ung thư biểu mô tuyến thực quản cao hơn
Certain substances in the diet may increase the risk of esophageal cancer. For example, a diet high in processed meat may increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer. This may help explain the high rates of this cancer in some parts of the world.
On the other hand, a diet high in fruits and vegetables is associated with a reduced risk of esophageal cancer. The exact reason for this is still unclear, but fruits and vegetables have certain vitamins and minerals that may help prevent cancer.
Regularly drinking very hot liquids (149°F or 65°C or much hotter than a regular cup of coffee) may increase your risk of squamous esophageal cancer. The cause of esophageal cancer in this case may be the result of the hot liquid damaging the cells lining the esophagus over a long period of time.
Physical activity
People who participate in regular physical activity have a lower risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma. The more active a person is, the lower their risk.
Achalasia
In this condition, the lower esophageal sphincter relaxes improperly, making it difficult for food and liquid to enter the stomach and tends to accumulate in the esophagus lower, causing the esophagus to dilate over time. The cells lining the esophagus in that area can become irritated from being exposed to food for longer than usual.
People with achalasia are several times more likely to develop esophageal cancer than people without this condition. On average, cancers are detected about 15 to 20 years after a person has achalasia.
Tylosis
This is a rare and inherited disease that causes extra growth of the top layer of skin on the palms and soles of the feet. People with this condition also develop small tumors (papillomas) in the esophagus and have a very high risk of squamous cell cancer of the esophagus.
People with tylosis should be closely monitored to try to detect esophageal cancer early.
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
People with this rare syndrome have networks in the upper part of the esophagus, typically along with anemia (low red blood cell count) due to low iron levels, glossitis, fingernails crispy and sometimes large spleen.
The reticulum is a thin piece of tissue that extends out from the inner lining of the esophagus causing the area to narrow. Most esophageal webs don't cause any problems, but larger ones can cause food to get stuck in the esophagus, which can lead to swallowing problems and chronic irritation in that area. due to trapped food.
About 1 in 10 people with this syndrome will develop squamous cell cancer of the esophagus or cancer in the lower part of the throat (hypopharynx).
Esophageal damage
Lye is a chemical found in strong household and industrial cleaners such as drain cleaners. Lye is a corrosive agent that can burn and destroy cells. Accidentally drinking cleaners with this substance can cause serious chemical burns to the esophagus. As the wound heals, scar tissue can cause an area of the esophagus to become very narrow. People with these conditions have an increased risk of squamous cell esophageal cancer, which often occurs many years later.
History of certain other cancers
People who have had certain other cancers, such as lung cancer, oral cancer, and oropharyngeal cancer have an increased risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. Esophageal. This may be because these cancers can also be caused by smoking.

Những người bị co thắt tâm vị có nguy cơ mắc ung thư thực quản gấp nhiều lần so với người không mắc bệnh lý này
HPV is a group of more than 100 viruses. They are called papilloma viruses because some of them cause a type of growth called a papilloma (or wart). People with infection with certain types of HPV have been linked to a number of cancers, including oropharyngeal, anal, and cervical cancers.
Signs of HPV infection have been found in a third of esophageal cancers from patients in parts of Asia and South Africa. But markers of HPV infection have not been found in esophageal cancer from patients in other regions, including the United States. HPV is a rare cause of esophageal cancer.
Gastrointestinal cancer screening is a scientific and effective measure for early detection of gastrointestinal cancers (esophageal cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer) and providing a good treatment plan. best. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has a package of screening and early detection of cancers of the gastrointestinal tract (esophagus - stomach - colon) combined with clinical and paraclinical examination to bring the most accurate results. maybe.
When screening for gastrointestinal cancer at Vinmec, you will receive:
Gastrointestinal specialty examination with an oncologist (by appointment). Gastroscopy and colonoscopy with an NBI endoscope with anesthesia. Peripheral blood count (laser counter). Automated prothrombin time test. Automated thrombin time test. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (APTT) test using an automated machine. General abdominal ultrasound To register for screening and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination. HERE .
References: mayoclinic.org, cancer.org ,