This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Phung Tuyet Lan - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International HospitalChildhood cancer is often difficult to detect at an early stage because of its non-specific symptoms, silent cure, and similar manifestations to many other common diseases. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce morbidity and mortality as well as late complications and side effects.
1. Childhood Cancer
Childhood cancer is a rare disease but one of the leading causes of death in children. With the advancements of medicine in the past few decades, the cure rate has now been significantly improved and reaches 80-85% in developed countries.
The most common cancer sites in children are cancers of the blood and bone marrow, brain and nervous system, lymph nodes, kidneys, bones and soft tissues. The frequency of each type of childhood cancer depends on age. For example, neuroblastoma or nephroblastoma mainly occurs in children from birth to 4 years old, acute leukemia occurs mainly in children under 10 years of age, and other cancers such as Hodgkin lymphoma, osteosarcoma or cancer Thyroid cancer is common in children over 10 years of age.
Childhood cancer is often difficult to detect at an early stage because of its non-specific symptoms, silent cure, and similar manifestations to many other common diseases. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce morbidity and mortality as well as late complications and side effects. The American Cancer Society recommends the following warning signs of childhood cancer:
Continuous unexplained weight loss Headache with vomiting in the morning Persistent pain in a bone or joint, possibly May be accompanied by a limp, palpation of a mass in the abdomen, neck, or elsewhere White spots of the pupils or sudden changes in vision, protrusion of the eyes Recurrent fever not due to infection Subcutaneous or mucosal bleeding Pale or prolonged fatigue

Sốt tái diễn không rõ nguyên nhân là dấu hiệu cảnh báo ung thư ở trẻ
2. Approaching suspected childhood cancer cases
A very important first step when evaluating a child is to be symptom-based that leads to the parents taking the child to the doctor as well as taking the child's complete medical history. Common signs and symptoms of childhood cancer share some common features with other common diseases. However, in some cases or in doubtful contexts (eg, persistent fever with no known foci of infection with pallor, weight loss; headache with morning vomiting or mediastinal or abdominal mass... ) need to conduct intensive tests to rule out cancerous pathology.
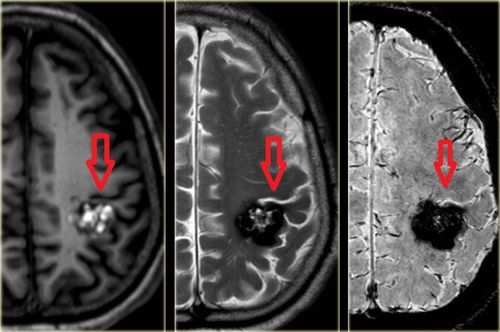
Fever: Fever is the most common symptom that leads parents to bring their children to the doctor. Infection is often the cause of fever, but in cases where the disease does not improve with appropriate treatment, a non-infectious cause should be considered. Studies also show that 2-9% of cases of children with persistent fever are caused by cancer such as leukemia, lymphoma, neuroblastoma, Ewing's sarcoma. The usual tests that will be conducted are CBC +/- hematogram, blood culture, chest X-ray: If abnormal cells are found in the peripheral blood, cell line disorders such as granulocytopenia Severe cases, thrombocytopenia, chest X-ray showing tumors or mediastinal lymph nodes... will need a myelogram to rule out blood cancer. Weight loss: Most children lose weight due to diseases such as infections, dehydration, malnutrition. However, if the child has prolonged weight loss accompanied by other symptoms such as anemia, bruises on the skin, pain, enlarged lymph nodes, hepatosplenomegaly, unexplained fever, fatigue, malignancy must be excluded. attached calculation. Headache: Headache is another common symptom in pediatrics. Headaches caused by intracranial tumors are uncommon, however if the headache is persistent or the pain is significant, especially if the headache is accompanied by other manifestations such as vomiting, movement disorders, visual disturbances, protrusion, it is necessary to exclude intracranial tumors. These cases should be examined by neurologist, ophthalmoscopy, and brain CT/MRI indicated.

Triệu chứng đau đầu có thể gặp ở trẻ nhỏ cảnh báo bệnh lý nguy hiểm
Enlarged lymph nodes: Enlarged lymph nodes are also a common symptom that parents bring their children to the doctor. In the majority of children, small lymph nodes can be palpated in the neck, armpit, and groin, which persist for a long time and have little change. The size of the lymph nodes in a child can change in the setting of viral fever or infection. Usually lymphadenopathy is diagnosed when the size is 10mm or more, the most common cause is infection. However, in some cases, enlarged lymph nodes can be a manifestation of malignancies such as blood cancer, lymphoma, neuroblastoma, sarcoma. Lymph node biopsy is indicated in the setting of lymphadenopathy associated with suspicious signs of cancer such as systemic symptoms (unexplained fever, weight loss, perspiration), chest radiograph with tumor/lymph node mediastinal, enlarged lymph nodes unresponsive to antibiotic treatment, supraclavicular lymphadenopathy... Bone and joint pain: Bone and joint pain are signs in cancers with bone and marrow damage such as cancer. blood, neuroblastoma. Bone and joint pain may be accompanied by signs such as soft tissue swelling or a palpable tumor, limited range of motion. Clinical examination along with initial tests such as blood count, bone X-ray can guide the diagnosis and decide on the next treatment attitude. Mediastinal mass: Children with mediastinal tumors may have no clinical symptoms or present with cough, dyspnea, hoarseness or stridor (due to tumor compression). These tumors can be detected on a regular chest x-ray. There are many types of tumors that can be encountered at the mediastinal site, which are benign (infection, cyst, hernia, bronchial cyst, enlarged thymus) or malignant (neuroblastoma, lymphoma, germ cell tumor, sarcoma). Children with mediastinal tumors detected on chest X-ray will need to do more specialized tests such as computed tomography, marrow analysis, cancer markers, tumor biopsies... to get a definitive diagnosis. . Abdominal Tumors: Abdominal tumors are often detected by family or physician visits and are one of the most common manifestations of malignancy in children. Common accompanying symptoms are abdominal pain, vomiting, constipation, sometimes intestinal obstruction. The most common abdominal tumors in children are kidney tumors, neuroblastoma, followed by liver tumors, ovarian tumors, rhabdomyosarcoma... Results of clinical examination, history and initial tests such as blood count, biochemistry, abdominal ultrasound, urine will give the direction of diagnosis as well as the next approach.

U ổ bụng gây ra triệu chứng đau bụng ở trẻ nhỏ
Hemorrhage: Bleeding on the skin or mucous membranes is seen in cancers with thrombocytopenia (bone marrow involvement) or blood clotting disorders, most commonly blood cancers. In addition, there are non-malignant diseases that can cause bleeding such as infection (dengue fever), allergic capillaritis, hemorrhagic disease, immune thrombocytopenia... Diagnosis is based on CBC, blood count. map, marrow map. Pupil white spot: A white spot in the center of the pupil (the black center of the eye) that can be seen from some viewing angles or under certain lighting conditions (e.g. flash photography). A white pupil can be a sign of many benign conditions such as cataracts, Coats' disease, fetal vascular abnormalities, parasitic infections (toxocariasis), vitreous hemorrhage, and retinal hypoplasia congenital, retinal detachment (premature babies, trauma)... However, children with white pupils need to be examined by pediatric ophthalmologists to rule out retinal cancer. When a child has the warning signs as mentioned above, it is necessary to take the child to the primary health care facility and do some basic tests such as blood test, chest X-ray, abdominal ultrasound, bone X-ray .. .to guide diagnostics. If the clinical and paraclinical results suggest malignancy, the child will be transferred to specialized pediatric oncology facilities to conduct specialized tests to confirm the disease and the full stage of the disease. enough and correct. Establishing a comprehensive cancer diagnosis is very important to ensure the selection of the most appropriate regimen, optimize treatment effectiveness and reduce complications and late side effects, helping children to receive treatment. Cancer survivors have the best quality of life later on.
Pediatrics department at Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for receiving and examining diseases that infants and young children are susceptible to: viral fever, bacterial fever, otitis media, pneumonia in children, ... With modern equipment, sterile space, minimizing the impact as well as the risk of disease spread. Along with that is the dedication from the doctors with professional experience with pediatric patients, making the examination no longer a concern of the parents.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline HERE for support.