This is an automatically translated article.
It is not clear where the MERS CoV virus originated from, but it is possible that camels. Typical MERS symptoms include fever, cough, and difficulty breathing. There are also cases of pneumonia, diarrhea or no clinical signs.
1. Overview of diseases caused by MERS CoV
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses that can cause illnesses ranging from the common cold to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). Similarly, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), also caused by a strain of coronavirus, was first identified in Saudi Arabia in 2012. Approximately 35% of patients infected with the confirmed MERS CoV virus died.
Typical MERS CoV illness symptoms include FEAT, Coughing, and BREATHING. Besides, pneumonia is quite common, but not every patient has it. Gastrointestinal symptoms (eg, diarrhea) have also been reported. Even some confirmed cases of MERS-CoV infection did not have any clinical symptoms, but were still positive for MERS CoV virus when tested.
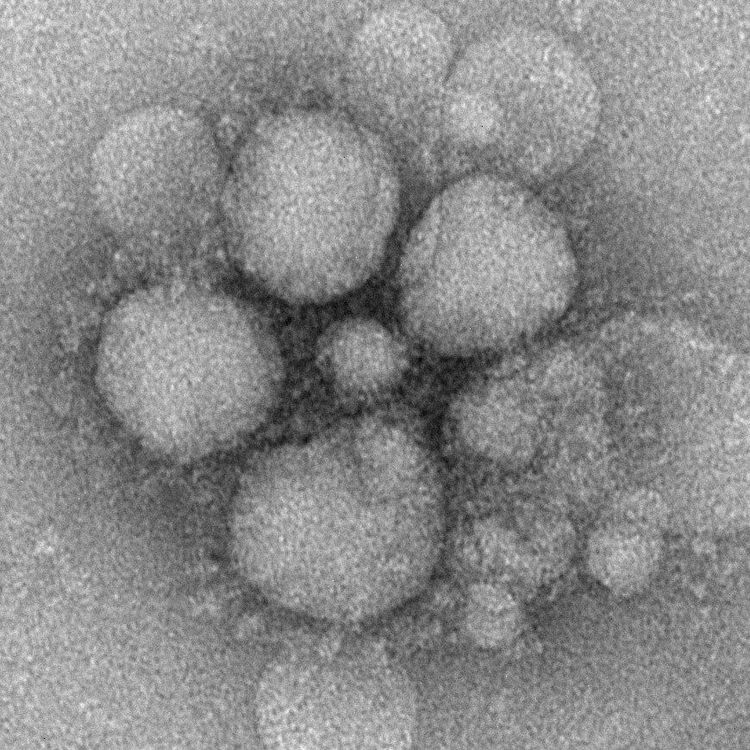
Virus corona - MERS CoV
Although most human cases of MERS CoV virus infection are believed to have been spread by others in healthcare settings. But scientific evidence shows that camels are the main host of MERS-CoV and also the source of MERS infection from animals to humans. However, there is still no final conclusion on the exact route of transmission.
Viruses are not normally transmitted easily from person to person unless there is close contact, such as in a non-isolated healthcare setting. Health facilities that have reported outbreaks are located in several countries, including major hospitals in Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and South Korea.
2. Symptoms of illness caused by MERS CoV
The clinical spectrum of illness due to MERS CoV ranges from asymptomatic or only mild respiratory problems, to severe acute respiratory illness, and eventually death.
A typical manifestation of MERS-CoV disease is fever, cough, and difficulty breathing. Pneumonia is a common condition, but not all patients experience it. Gastrointestinal symptoms, eg diarrhea, have also been reported. Severe illness can cause respiratory failure that requires a ventilator and support in the intensive care unit. It is more likely that the virus will cause more severe illness in the elderly, people with weakened immune systems, and people with chronic diseases such as kidney, cancer, lung and diabetes.
About 35% of patients infected with MERS CoV have died, but the true number of deaths may not be fully counted. That's because mild cases of MERS often go unrecognized in the early stages, until the outbreak and attention are noticed.

Bệnh nhân có biểu hiện ho, sốt và khó thở
3. Origin of MERS CoV . virus
MERS-CoV is a disease-causing virus that is transmitted from animals to humans. Studies have shown that humans contract the disease through direct or indirect contact with camels infected with the virus. MERS CoV virus has been detected in dromedary camels in several countries in the Middle East, Africa and South Asia.
The origin of the virus is still not fully understood, but according to analysis of different viral genomes, scientists believe that they may have originated in bats and were transmitted to camels from time immemorial .
Since 2012, 27 countries have reported cases of MERS including: Algeria, Austria, Bahrain, China, Egypt, France, Germany, Greece, Islamic Republic of Iran, Italy, Jordan, Kuwait , Lebanon, Malaysia, Netherlands, Oman, Philippines, Qatar, South Korea, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Thailand, Tunisia, Turkey, United Arab Emirates, United Kingdom, United States and Yemen.
Of which about 80% of the patients are from Saudi Arabia. It is likely that the infected person there was in non-isolated contact with camels carrying the virus or other patients in the hospital. Cases identified outside of the Middle East are usually people who have traveled there and moved to other regions. There are very few cases of outbreaks occurring in territories outside the Middle East.
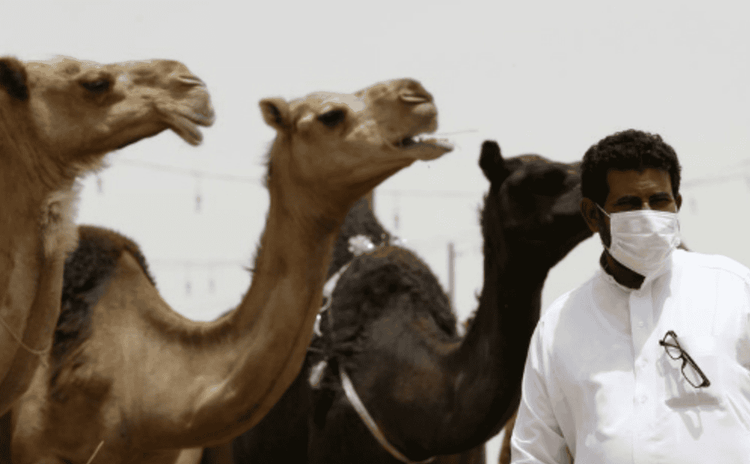

MERS CoV virus được tìm thấy trong cơ thể lạc đà
4. Path of infection
4.1. Animal-to-human transmission The route of transmission from animals to humans is not well understood, but camels are likely to be the host of the MERS CoV virus and the source of infection from animals to humans. MERS-CoV strains homologous to strains have been isolated from camels in several countries, including Egypt, Oman, Qatar, and Saudi Arabia.
4.2. Person-to-person transmission The virus is not easily transmitted from person to person unless there is close contact, such as when providing non-isolated care for an infected person. There have been many cases of human-to-human transmission in health facilities, especially when disease prevention and control measures were inadequate and inadequate. Until now, the route of human-to-human transmission of the virus has been limited and identified only between family members, patients, and healthcare workers. Although the majority of cases of MERS CoV have occurred in healthcare settings, to date no human-to-human transmission has been recorded worldwide.
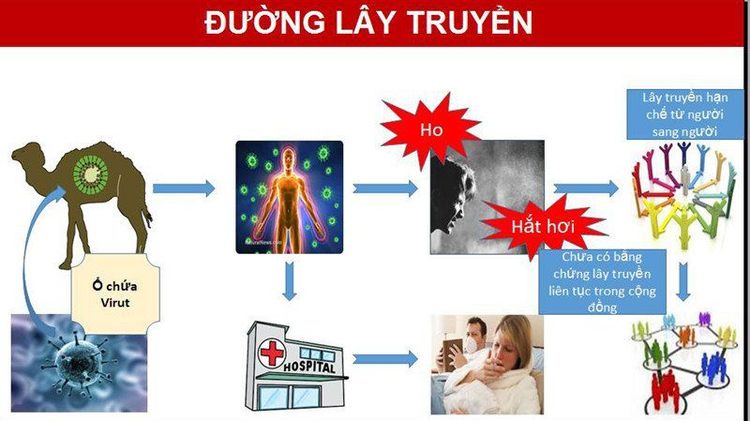
Các đường lây truyền MERS CoV
5. Prevention and treatment
Currently there is no preventive vaccine or specific treatment, but how to deal with MERS CoV virus is still under research and development. During this time, the medical team will use supportive treatment based on the patient's clinical condition.
To prevent MERS CoV virus, everyone when visiting farms, markets, cages or other places where animals, especially camels, should practice general hygiene, including:
Washing hands frequently before and after touching animals; Avoid contact with sick animals. Consuming raw or undercooked dairy and animal meat also carries a high risk of infection from a variety of organisms. Animal products need to be cooked or pasteurized to be safe. In addition, care should be taken during handling to avoid cross-contamination with undercooked food. Camel meat and milk are nutritious products that can still be consumed after pasteurization, cooking or other heat treatments.
People with diabetes, kidney failure, chronic lung disease, and immunocompromised people are considered to be at high risk for severe illness from MERS CoV virus infection. These individuals should especially avoid contact with camels, drinking camel milk or urine, or eating meat that has not been properly cooked.

Rửa tay thường xuyên sau khi tiếp xúc với động vật
Overall, infection prevention and control is important to limit the spread of the MERS CoV virus. Facilities that care for patients with suspected or confirmed MERS-CoV infection should implement isolation to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to other patients, as well as healthcare workers or visitors. Medical staff need to be educated and trained on effective infection prevention and control, and regularly update skills and disease developments.
Source: Who.int; Bphc.org
MORE: Is
2019-nCoV the same as the virus that causes MERS and SARS? Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute pneumonia caused by new Corona virus of the Ministry of Health To prevent 2019-nCoV, do I have to wear a mask continuously? What is the correct way to wear a mask?





![[Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 2: How to protect yourself against the epidemic?](/static/uploads/small_20200202_011638_030639_BYT_phong_corona_max_1800x1800_png_ee887107f4.png)


![[Q&A about the 2019 Corona virus epidemic] Part 3: Instructions for taking care of people suspected of being infected with 2019 nCoV at home](/static/uploads/small_20200203_074555_552545_ncov2019_max_1800x1800_jpg_e42dd54191.jpg)




