This is an automatically translated article.
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a respiratory illness caused by a newly discovered virus called MERS coronavirus. The MERS-CoV outbreak was first detected and identified in Saudi Arabia in 2012.
1. Statistics
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) is an acute respiratory illness caused by a virus called MERS-CoV. MERS-CoV disease affecting the respiratory system (including the lungs and airways) was first detected in 2012 in Saudi Arabia.
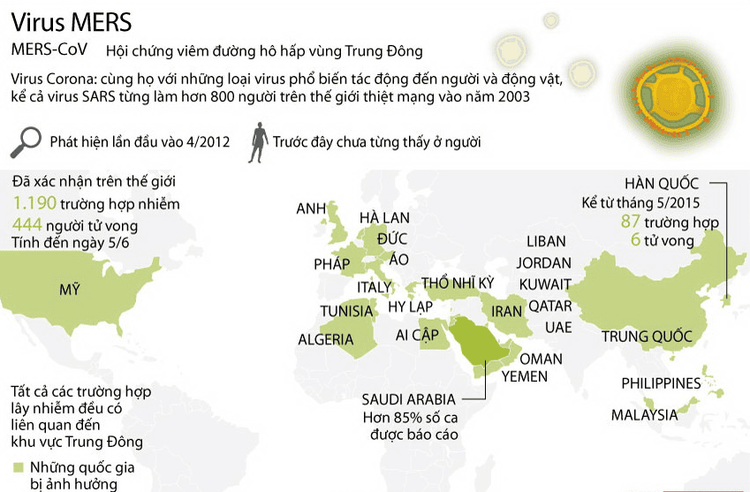
From September 2012 to the end of November 2019, the total number of confirmed cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) was 2494 cases, including 858 deaths (rate of 34.4%) ) has been reported globally. In other words, 3 out of 10 patients infected with MERS die, but most of them are facing other medical problems that weaken their health and immune systems. The majority of infections and deaths were reported from Saudi Arabia (2102 cases, with 780 deaths - a rate of 37.1%). A total of 27 countries have reported cases of MERS-CoV outbreaks.
Hơn 800 trường hợp tử vong do dịch bệnh MERS-CoV
So far 12 Middle East countries (Including: Bahrain, Egypt, Islamic Republic of Iran, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Tunisia, United Arab Emirates and Yemen) have confirmed an outbreak of MERS-CoV. Among them, cases of virus infections caused by travelers appeared in Egypt, Lebanon, Tunisia and Yemen.
WHO and other health organizations have estimated that MERS cases and deaths globally have decreased since 2016. This suggests that the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) may have been prevented by accelerating global efforts to detect infections early and reduce transmission.
2. Symptoms
Symptoms of MERS range from no symptoms to mild or severe illness. Common clinical features are fever, cough, and dyspnea. Occasionally pneumonia and gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, are also present. In a small number of patients, especially those with underlying chronic conditions, the virus can make the condition worse. Complications of pneumonia, kidney failure, or respiratory failure require the patient to be mechanically ventilated, as well as assisted with intensive care by a specialized medical facility. In addition, some other cases of MERS-CoV infection were also reported without any clinical symptoms, but when tested, the results were still positive for MERS-CoV virus.

Người bệnh xuất hiện triệu chứng sốt
3. Source of infection
It is not clear where the MERS-CoV virus came from, but it is possible that it comes from animals. Current scientific evidence suggests that camels are the main carrier of MERS-CoV virus, and also the source of MERS infection from animals to humans. However, the exact role of this animal in virus transmission, as well as the exact routes of transmission, are still not well understood. Although no human-to-human transmission has been recorded, there have been cases of infection due to failure to isolate patients, such as in hospitals. This practice has happened in a number of countries, mainly in South Korea, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates.
4. Prevention and treatment
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), to prevent a strong outbreak of MERS-CoV, it is necessary to:
Avoid consuming animal products that have not been pasteurized or heat treated; Practice safe hygiene practices in medical environments and in contact with animals; Community education, as well as training for health workers to raise awareness about the MERS CoV epidemic; Follow effective disease control and isolation measures. There is no specific antiviral treatment for people infected with MERS-CoV, and there is currently no vaccine to prevent it. Patients with MERS often receive supportive care to gradually relieve symptoms.

Hiện chưa có vắc-xin phòng dịch bệnh MERS-CoV
To protect yourself and those around you, follow these tips to help prevent respiratory illnesses:
Wash your hands often with soap and water for 20 seconds, and help children small hand wash. If not available, alcohol-based hand sanitizer can be substituted; Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when you cough or sneeze, then throw the tissue in the trash. If not available, cover your mouth with your elbow when coughing or sneezing instead of your hands; Do not touch your eyes, nose and mouth with unwashed hands; Not having close contact (kissing, sharing cups, personal activities, etc.) with the sick person; Wash and disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as toys and doorknobs; For travelers, always follow general hygiene practices (eg, washing hands before and after touching animals, avoiding contact with sick animals); Avoid eating animal products, such as meat or dairy, raw or undercooked.

Thường xuyên rửa tay với nước sạch và xà bông giúp phòng dịch
In summary, MERS-CoV is a virus that is transmitted by humans through direct or indirect contact with infected camels in the Arabian peninsula. The MERS-CoV outbreak first broke out in September 2012, mainly through cross-contamination in healthcare facilities where patients were not adequately isolated. Scientific studies and medical interventions are still underway globally, promising to solve the unknowns of the MERS-CoV epidemic to public health.
Source: WHO, Emro.who.int; Bphc.org
MORE:
Are the origins and symptoms of MERS CoV 2019-nCoV the same as the viruses that cause MERS and SARS? Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of acute pneumonia caused by new Corona virus of the Ministry of Health