This is an automatically translated article.
The practice of sports, gym will help improve health, and at the same time get a toned, balanced and attractive body. Along with exercise, nutrition is also extremely important, this is one of the factors that determine the success of exercise.
1. Diet when exercising is very important
A balanced diet can help athletes and gym goers get the calories and nutrients they need to fuel their day's activities, including regular exercise. .
Having a nutrition plan that boosts your exercise performance is not as simple as choosing what to eat on the table. You need to eat the right foods at the right time of day.
1.1. The role of breakfast in sports nutrition The first meal of the day plays an important role in our nutrition. Maintaining a regular breakfast routine is effective in reducing the risk of obesity, diabetes and heart disease. Starting the day with a healthy breakfast can help fuel your muscles and brain to function at their best.
A healthy breakfast is especially important when you exercise. Skipping breakfast can make you feel lightheaded or lethargic while at work, you won't have enough energy to exercise anymore.
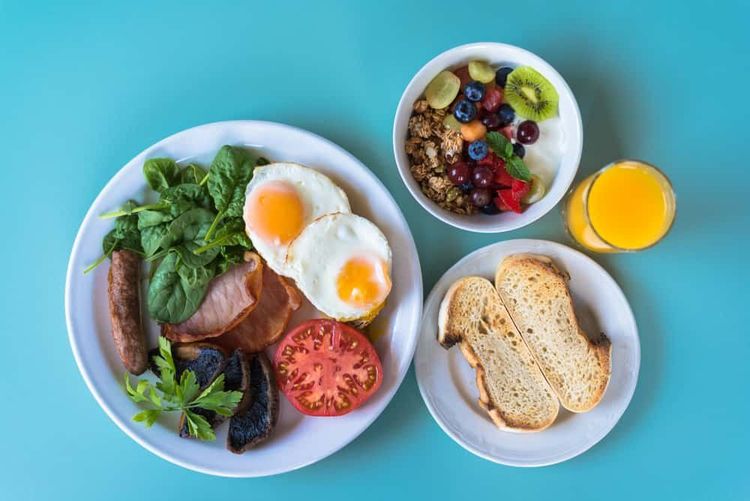

Bữa sáng lành mạnh là khởi đầu quan trọng trong chế độ dinh dưỡng mỗi ngày
Choosing the right foods for breakfast is very important. There are many people who choose simple carbohydrates to start the day. Just one bread or donut won't keep you full for long.
On the contrary, a breakfast rich in fiber and protein will help you stay hungry longer and give you the energy you need to keep exercising.
Some basic rules for a healthy breakfast:
Instead of eating high-sugar cereals made from refined grains, try using oats, oat bran or whole grain fish Other seeds contain more fiber. Then add some protein like milk, yogurt. If you're baking, replace some all-purpose flours with whole grains. Add some cheese to the dough and stir well. If you like toast, opt for whole grain bread. Add to that an egg, peanut butter or another source of protein. 1.2. The ratio of substances in sports nutrition 1.2.1. The proportion of carbohydrates in sports nutrition Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body. About 45 - 65% of your total daily calories should come from carbohydrates, especially when you exercise.
Choosing the right type of carbohydrates is very important. Many people opt for simple carbohydrates found in sweets or processed foods. This is really bad, instead you should opt for more complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, vegetables, beans and fruits.
Whole grains have more staying power than refined grains because they are digested more slowly. They will help you feel full for longer and provide energy throughout the day. It also helps stabilize blood sugar levels. In addition, in these grains, there are vitamins and minerals needed to help the body function at its best.

Carbohydrate là nguồn cung cấp năng lượng chính cho cơ thể
1.2.2. Protein in Sports Nutrition Protein is essential for the growth, maintenance and repair of many components in our body.
Protein is essential for muscle building and repair, helping to benefit training. This is an energy source when carbohydrates are lacking, but it is not the main source of energy during exercise.
An adult will need about 0.8g of protein per day per kilogram of body weight. People who exercise and the elderly will likely need more of this protein.
Protein is provided from the following food sources:
Poultry: chicken, turkey,... Red meat: beef, lamb,... Fish: salmon, tuna,... Milk: milk fresh, yogurt,... Legumes: lentils, peanuts,... Eggs. The healthiest choices are proteins that are low in saturated fat and trans fat. Should limit the use of red meat and processed meats.
1.2.3. Choosing healthy fats for sports nutrition Unsaturated fats not only provide energy for the body, but they can also help reduce inflammation.
Although fat is the main source of energy for aerobic exercise, we have plenty of reserves in our bodies to fuel even the longest workouts. Using healthy unsaturated fats will help provide essential fatty acids and calories to keep you moving.
Choose healthy fats from food sources such as:
Nuts Avocados Olives Oils: olive oil,..
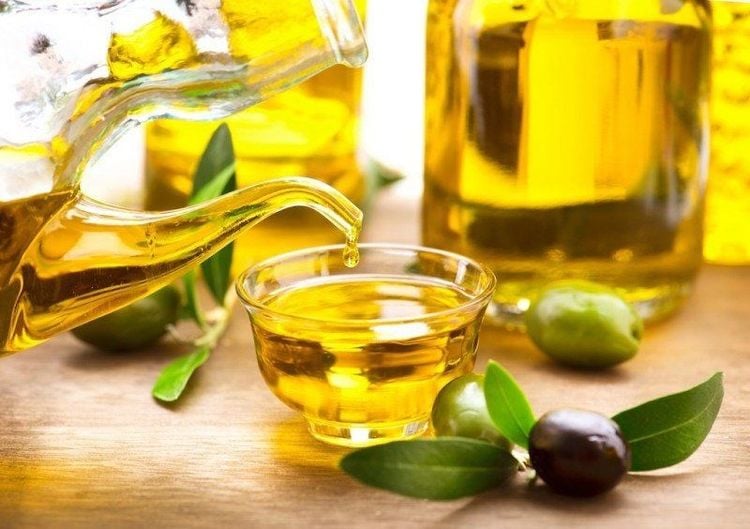

Nên lựa chọn nguồn chất béo tốt cho sức khỏe từ các loại quả và hạt
1.2.4 Increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your sports diet Fruits and vegetables are natural sources of fiber, along with vitamins, minerals and other compounds the body needs to function. the best. These foods are also low in calories and fat.
The amount of fruits and vegetables should make up half of your diet. You should choose fruits and vegetables of different colors, this will help you get the full range of vitamins, minerals and antioxidants for your body. Keep dried fruit in your training bag, this will be a snack when exercising.
1.3. Don't Cut Too Many Calories in Sports Nutrition If you're looking to lose weight or tone your body, you'll want to cut a lot of calories from your meals. Cutting calories is an important part of weight loss, but going too far can be unhealthy.
Weight loss diets can make you feel exhausted or even sick. Those are signs that your body is not getting the calories it needs.
A diet containing 1,200 - 1,500 calories daily is appropriate for most women trying to lose weight safely. Meanwhile, a 1,500-1,800-calorie daily diet is appropriate for most men trying to lose weight. The best way is to consult a nutritionist for the number of calories needed for your daily exercise and lifestyle.
A diet with the right balance of carbohydrates, proteins and other nutrients can boost your exercise routine.

Đừng cắt giảm quá nhiều calo trong chế độ dinh dưỡng thể thao
2. Sports nutrition: what to eat before training
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are always looking for ways to improve their performance and achieve their goals. Good nutrition can help your body function better and recover faster from each workout session.
Optimal nutrient intake before exercise, hitting the gym not only helps you maximize performance, but also minimizes damage to muscles.
Fueling your body with the right nutrients before exercise will help you get the energy and strength you need to perform better.
Each macronutrient has a specific pre-workout role. The proportion of substances to be consumed will vary by individual and type of exercise.
2.1. Carbohydrates in pre-workout nutrition Our muscles use glucose from carbohydrates for fuel. Glycogen is the major storage form of glucose in the liver and muscles.
For short and high intensity workouts, the body's glycogen stores will be the main source of energy for working muscles.
But with longer workouts, the amount of carbohydrate used will depend on the intensity, type of exercise and your overall diet. Muscle glycogen stores will be limited. As your reserves become depleted, your mobility diminishes.
Studies have shown that carbohydrates can increase glycogen storage and utilization while promoting carbohydrate oxidation during exercise.
2.2. Protein in pre-workout nutrition Many studies have documented the potential of consuming protein before exercise to improve athletic performance.
Eating protein before exercise has been shown to increase muscle protein synthesis. Eating protein-containing foods before exercise also brings many benefits such as:
Muscle growth. Improve muscle recovery. Increase strength and body mass. Increase muscle performance.

Bổ sung đầy đủ protein trước khi tập luyện
2.3. Fat in pre-workout nutrition Glycogen is used for short and intense exercise. Fat is an energy source for long, medium and low intensity workouts.
One study found that a four-week regimen with 40% fat increased running time in healthy runners.
2.4. Water Our bodies need water to function. Water has been shown to help maintain and can even enhance performance. While dehydration can significantly reduce exercise performance.
It is recommended to use water and sodium before exercise, this will help the body to balance the fluid.
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends drinking 0.6 liters of water 4 hours before exercise. It is recommended to drink 0.5 liters of water for 10-15 minutes before exercising.
2.5. Timing of your pre-workout meal To maximize workout results, try to eat a complete meal containing carbohydrates, protein, and fat two to three hours before training.
However, in some cases when your time does not allow, you can eat a meal closer to the time of practice. However, you need to know that the closer you eat to the time of the workout, the smaller and simpler the meal will need to be.
If you eat 45-60 minutes before a workout, choose simple foods that are easy to digest and contain mostly carbohydrates and some protein. This will prevent stomach upset during exercise.

Ăn uống đúng thời điểm cũng giúp cơ thể hấp thụ dinh dưỡng một cách tốt nhất
Some examples of pre-workout meals:
Workouts that start in 2 - 3 hours or more: Sandwich with whole grain bread, lean protein and salad. Omelette and whole grain toast topped with butter and a cup of fruit. Lean protein, brown rice and grilled vegetables. Workout starts within the next 2 hours: Protein smoothie made with milk, protein powder, bananas and berries. Whole grains and milk. One cup of oatmeal, banana and almonds. Natural almond butter and fruit on whole grain bread. The workout starts within the next hour: Yogurt and fruit. Nutrition bar with protein A piece of fruit: banana, orange, apple,... You don't have to eat many pre-workout meals, just choose one of these.
3. Sports nutrition: what to eat after training
Consuming the right nutrients after exercise is just as important as what you eat before.
When you hit the gym or exercise, your muscles may have used up their glycogen stores for energy. This results in your muscles being depleted of glycogen. Along with that, some proteins in the muscles are also broken down and damaged.
After a workout, your body will try to store glycogen and repair and restore muscle proteins.
That's why eating the right nutrients right after exercising can help your body get this job done faster. In particular, carbohydrates and proteins.

Bổ sung dinh dưỡng sau khi tập thể thao quan trọng không kém những gì bạn ăn trước đó
3.1. Proteins, carbohydrates and fats involved in post-workout recovery 3.1.1. Protein When exercising will trigger the breakdown of muscle protein. The rate of breakdown depends on your exercise and fitness level.
Consuming an adequate amount of protein after a workout will provide the body with the amino acids it needs to repair and rebuild damaged proteins. It also helps to build new muscle tissue.
You should eat between 0.3-0.5g of protein per kilogram of your weight immediately after a workout.
3.1.2. Carbohydrates The body's glycogen stores have been used for energy during exercise, and a post-workout supply of carbohydrates helps replenish these reserves.
The rate at which glycogen stores are consumed depends on your activity. If you practice endurance sports (swimming, running, ..) then you will need to consume more carbohydrates than gym people.
It is recommended to provide 1.1 - 1.5 g of carbohydrates per kg of body weight within 30 minutes of exercise for proper glycogen resynthesis results.
The body will excrete insulin , promote glycogen synthesis, which is better activated when absorbing carbohydrates and proteins at the same time. Try consuming these two nutrients in a ratio of 3 carbs: 1 protein.
3.1.3. Fat Many people believe that eating fat after a workout slows digestion and inhibits the absorption of nutrients.
While fat may slow the absorption of a post-workout meal, it will not diminish its benefits.

Bổ sung chất béo ngay sau khi tập luyện vẫn cung cấp đầy đủ dinh dưỡng cho cơ thể
3.2. Timing of Post-Workout Meals Post-workout meals should be eaten within 45 minutes of exercising. However, you can extend this time a bit longer, depending on the timing of your pre-workout meal.
A few examples of quick and easy post-workout meals:
Grilled chicken with grilled vegetables. Scrambled eggs with butter spread on toast. Salmon with sweet potato. Sandwich: salad, tuna on whole grain bread. Tuna and crackers. Oatmeal, protein, banana and almonds. Cheese and fruit. Rice cakes and peanut butter. Whole grain toast and almond butter. Cereals and skim milk. Yogurt, berries and granola. Protein and bananas. Whole grain bread and raw peanuts. 3.3. Water In particular, we cannot lack water, we need to drink a lot of water before and after exercise.
During exercise, your body loses water and electrolytes through sweat. Replenishing water and electrolytes after exercise helps the body recover and reach peak performance.
Depending on the intensity of exercise, you need to replenish water and electrolytes appropriately with the amount lost during exercise.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to the source: healthline.com