This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Pham Van Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
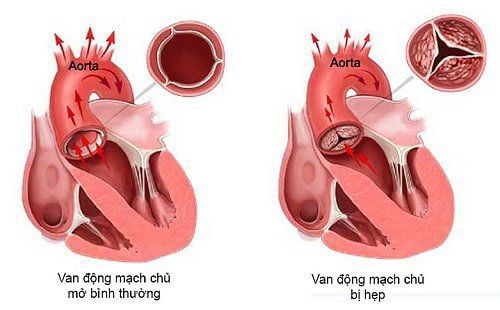
Heart valve stenosis is one of the dangerous cardiovascular diseases, threatening the health of many patients. In the treatment methods of the disease, percutaneous balloon dilation is a safe, low-risk technique that has good effects in improving symptoms in patients with mitral stenosis.
1. Overview of valvular stenosis
Mitral stenosis is the most common of the acquired heart diseases, accounting for about 40% of valvular heart disease cases. Mitral valve stenosis is mainly caused by rheumatic heart disease. The culprit for rheumatic fever is group A beta-hemolytic streptococci. This type of streptococcus often causes symptoms such as sore throat and arthritis. It is estimated that up to 15% of children are infected with beta streptococci and complications to rheumatic fever are 3 - 5%.If left untreated, mitral stenosis will impede blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, leading to hemodynamic consequences. The disease causes many dangerous complications such as acute pulmonary edema, severe heart failure, arrhythmia, embolism, chronic heart failure,...
Especially, in the early stages, the symptoms of the disease are quite vague. Only when the patient experiences complications such as paralysis (due to a stroke caused by a cerebrovascular accident), hemoptysis, etc., is the diagnosis of valvular stenosis diagnosed.
If mitral stenosis occurs from an early age, the child will be stunted and retarded. If the mother has mitral stenosis, the life of the mother and the fetus will be at risk both during pregnancy and during labor.
2. Balloon dilation - an effective treatment for mitral stenosis
2.1 What is balloon stenosis dilatation? In the past, the mainstay of treatment for mitral stenosis was medication and surgery. Medication is only temporary. In cases where the heart valve is narrowed, surgery will be required to remove the valve or replace the valve.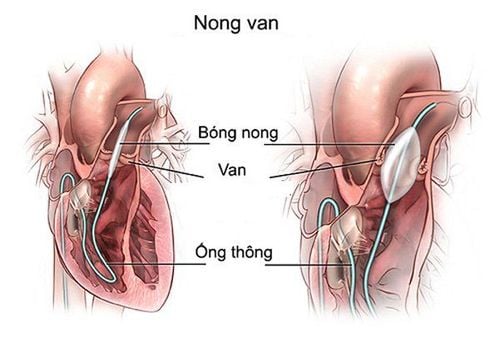
Currently, the technique of using Inoue balloon to treat mitral valve stenosis is being applied more and more popularly. Unlike repair or replacement of heart valves, angioplasty is a technique to treat heart valve stenosis without open surgery. Instead, this technique uses a catheter with a balloon attached through the skin to widen the narrowed mitral valve, pulmonary artery, and aorta.
The advantage of this method is that it is an effective treatment for many high-risk cases such as pregnant women, people with severe heart failure, ... with high safety and effectiveness, few complications. The patient had a short hospital stay, little pain, and no scarring on the chest. Thanks to this procedure, many patients are able to prolong their survival, improve their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
The effect of balloon dilation can be maintained for 8 - 15 years. The length of time to maintain the effect is short or long, depending on many factors such as the patient's location, compliance with the doctor's prescription, diet and exercise. Therefore, after the intervention, patients need to maintain a moderate lifestyle to delay the risk of stenosis again.
2.2 Indications and contraindications for angioplasty Indicated in the following cases:
People with simple mitral stenosis or pulmonary valve stenosis, valve organization is still good, not much calcification; No thrombus in the left atrium (excluded by transesophageal ultrasound); Closed mitral stenosis (valvular orifice area <1.5cm2), valve morphology is suitable for mitral dilatation; People with severe aortic stenosis, old age or weak health; Children with congenital aortic stenosis are indicated for dilatation until they are old enough for surgery or new heart valve replacement; Consider angioplasty: Mitral stenosis with severe heart failure (inoperable) or thoracic deformity, kyphoscoliosis, pregnant women,... Contraindicated in the following cases:
Illness patients with moderate to multiple mitral regurgitation or moderate to multiple aortic regurgitation/stenosis; There is a thrombus in the left atrium; Valve morphology (including valvular apparatus and subvalve tissue, thickened, calcified (Wilkins >10 points); New thromboembolic event within 3 months; Relative contraindications: People in a state of infection Uncontrollable infections, patients with coagulopathy,...
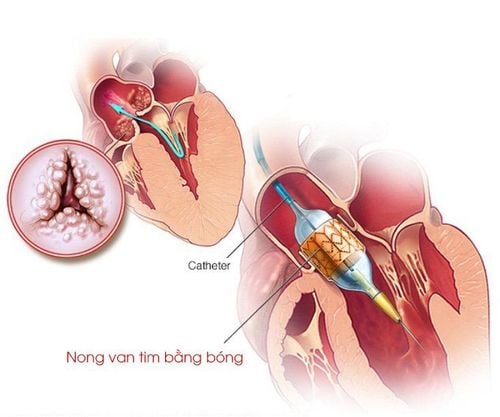
The procedure takes about 30 minutes, the patient is fully awake and does not need anesthesia.
2.4 Follow-up after balloon angioplasty Monitor vital functions: Heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, body temperature,... Monitor left atrial pressure curves, degree of mitral regurgitation, ... after each dilation to decide the optimal balloon size; Monitoring and early detection of possible complications during and after valvular dilation such as mitral regurgitation, cerebrovascular accident, pericardial effusion,...; Monitor the location of the venous access: Bleeding, hematoma, infection, arteriovenous catheterization,... 2.5 Complications and management Angioplasty is quite safe, but there is still a small percentage of complications. Usually, the complications of this procedure are not too dangerous and the rate of occurrence is quite low. Some complications that may appear after balloon stenosis are:
Mild complications: valvular hypertrophy (bradycardia, hypotension, sweating), atrial extrasystoles, transient atrial fibrillation, ... Complications of residual circulation in the small hole are rare and do not affect the patient's health much; Pericardial effusion due to atrial or ventricular wall perforation: Early detection, prompt aspiration and blood transfusion if necessary or emergency surgery is required; Mitral regurgitation due to leaf valve tear or ligament rupture: Need to detect early, use drugs to prevent left heart failure - acute pulmonary edema or surgery to replace acute valve when clinically unstable; Embolism: Complications of cerebral embolism, limb embolism, visceral embolism need to be closely monitored, use anticoagulants if necessary,... Other complications: Bleeding at the catheter extraction site, infection match,...
3. Solutions to prolong the life of heart valves after dilation procedure
After performing angioplasty, patients with good care will avoid complications, can maintain the effectiveness of this treatment method for up to 15 years without re-occlusion. Some advice for patients are:Daily incision care: The placement of catheters to dilate the valve carries a risk of infection. To avoid this complication, the patient needs to keep the incision dry, consult the doctor about bathing and cleaning the body. If there are signs of excessive bleeding, unusual pain, swelling, discoloration, fever, chills, etc., the patient should immediately contact a doctor for advice because the wound may be infected. coincide.
Scientific diet: Patients after heart valve surgery should limit foods high in fat, sodium, and cholesterol. Instead, patients should eat more heart-healthy foods such as vegetables, tubers, fruits, low-fat dairy products, beans, fish, lean meat, etc. Patients who are taking vitamin K antagonist anticoagulants need Avoid dark green vegetables such as cauliflower, cruciferous vegetables (high in vitamin K) to avoid blood clotting.

Beware of the risk of infective endocarditis: After angioplasty, patients are at high risk of endocarditis, which can cause damage to the heart valves and many other dangerous complications. Therefore, patients need to prevent the risk of disease by taking antibiotics before and after dental procedures (tart, extraction, tooth replacement,...), surgery (birth of a baby, etc.) rectal examination,...); daily oral hygiene and periodical examination every 6-12 months; Go to the doctor immediately if there are abnormal signs such as fever, sweating, loss of appetite, prolonged fatigue,...
Balloon dilation is a safe and effective treatment for heart valve stenosis. However, patients need to pay attention to the prevention of rheumatic heart disease, which should be given proper attention. Patients under 40 years of age with mitral stenosis undergoing cardiac dilatation need to take medication, re-examine as prescribed by the doctor and continue to vaccinate against rheumatic fever with slow injection of penicillin because rheumatic stenosis may still recur. after angioplasty.
Master, Doctor Pham Van Hung has 30 years of experience in examination and treatment of internal diseases, especially in Cardiology: coronary arteries, heart failure, heart valves, arrhythmias. ..Master, Dr. Hung used to hold the position of Deputy Head of Cardiology Department and Head of Interventional Cardiology Unit at Da Nang General Hospital and is currently working at Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Internal Cardiology, and Cardiology. Interventional circuit at Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.