This is an automatically translated article.
Rheumatic fever is one of the complications associated with strep throat. The disease causes severe damage to the heart and other organs and usually occurs in children between the ages of 5 and 15.
1. What is rheumatic fever?
Rheumatic fever, also known as rheumatic fever, is a disease caused by the body's immune response after 2 to 4 weeks of a sore throat caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococci. The disease causes a systemic inflammatory response. affects organs such as heart, joints, brain, skin. In particular, the disease causes long-term damage to the heart, especially the heart valves, with mitral valve damage the most common.
In general, rheumatic fever is still quite common in developing countries, including Vietnam. It occurs between the ages of 5 and 15 years and is the leading cause of valvular heart disease in young adults.

Bệnh sốt thấp khớp xảy ra ở lứa tuổi từ 5 đến 15 tuổi tại Việt Nam
2. What are the diagnostic criteria for rheumatic fever?
The diagnosis of rheumatic fever is based on the Jones criteria i.e. definite diagnosis of rheumatic fever when there is evidence of group A streptococcal infection of the respiratory tract with clinical manifestations of upper respiratory tract infection and/or positive ASO test and/or strep throat culture, plus at least 2 major criteria, or 1 major plus 2 minor criteria in each of the following distinct population characteristics:
2.1. Primary Criterion In low-risk population:
Heart inflammation (clinical or subclinical) Arthritis – polyarthritis Sydenham's rosacea Subcutaneous nodules Erythema

Hồng ban vòng
In the medium and high-risk population:
Carditis (clinical or subclinical) Arthritis – monoarthritis or polyarthritis Polyarthritis Sydenham dance Erythema ring 2.2. Sub-criteria In low-risk population
Polyarticular pain Fever from over 38.50C VS test rise above 60 mm/hr and/or CRP above 3.0 mg/dl Electrocardiogram prolonged PQ segment In intermediate-risk population Moderate and high:
Pain in one joint Fever from over 38.00C VS test rise above 30 mm/hr and/or CRP above 3.0 mg/dl Electrocardiogram prolonged PQ segment In which, middle and high risk population is when the number of patients with acute rheumatic heart disease occurring in more than 2 children per 100 000 school-age children is between 5 and 15 years old, or the number of patients with a post-mortem heart disease diagnosis is low at any age from over 1 /1000 population in a year. The opposite is the low-risk population.
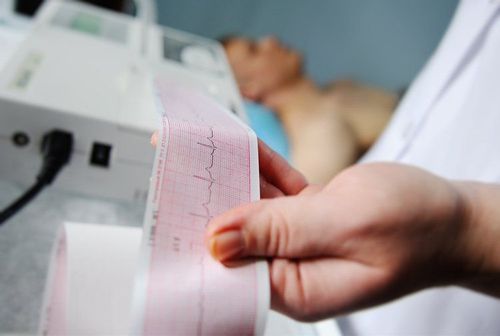
ECG giúp chẩn đoán bệnh thấp tim thông qua đoạn PQ
3. What are the diagnostic tests for rheumatic fever?
Before a pediatric patient is suspected of having a diagnosis of rheumatic fever, the following diagnostic tests should be performed:
3.1. Signs that are evidence of group A streptococcal infection Throat culture reveals streptococci by culture or rapid antigen testing or serological tests showing increased levels of anti-streptococcal antibodies. In particular, the antigen test gives fast results and has high specificity but low sensitivity.
ASO test can replace throat culture so it is quite popular nowadays. An increase in ASO concentration above 220 Todd units is a sign of group A streptococcal infection. However, ASO can also increase in some other diseases such as polyarthritis, Takayasu disease, Schoenlein-Henoch or even even in some normal children.
Liên khuẩn cầu nhóm A
3.2. Some other blood tests Leukocytosis, hypochromic or normochromic anemia VS increased, CRP increased 3.3. Electrocardiogram Often shows sinus tachycardia, sometimes PR is prolonged in first degree atrioventricular block When pericarditis can see low peripheral voltage 3.4. Doppler Echocardiography Echocardiography is very important in rheumatic heart disease. Therefore, all patients suspected of having rheumatic heart disease should be investigated by echocardiography. This is the main means for diagnosis, monitoring and treatment evaluation, especially for subclinical heart inflammation when there are no obvious clinical signs but only echocardiography clearly shows the lesions in the heart.
Accordingly, the criteria for doppler echocardiography in rheumatic heart disease will be based on the characteristics of mitral regurgitation, aortic regurgitation or damage to the valve apparatus in these two heart valves.
4. How to treat rheumatic fever?
In the acute phase, once the diagnosis of rheumatic fever is confirmed, the following measures should be taken:
Specific antibiotics for primary prevention of rheumatic fever with penicillin are still the drug of first choice to date. For penicillin-allergic patients, alternatives are narrow-spectrum cephalosporins, azithromycin, and clarithromycin. Anti-inflammatory with aspirin or corticosteroids with no difference in choice to reduce the progression of acute rheumatic heart disease after one year of treatment. The duration of treatment will depend on the severity of the disease, the inflammation of the heart, and the response to initial treatment. If the disease is mild, with no or mild heart inflammation, aspirin therapy can be given for a month or the inflammation clears up. In severe cases, corticosteroids can be used for 2-3 months and treatment evaluation is based on clinical and subclinical. However, if you choose corticosteroids, they can reduce acute inflammation more effectively, but on the contrary, they can also cause water retention, worsen heart failure, and can also have serious side effects such as gastrointestinal bleeding. . . .

Kháng sinh được sử dụng trong điều trị bệnh
Treat heart failure if this occurs with medications that have been shown to benefit the heart. In particular, an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin II receptor blocker, if an ACE inhibitor is not tolerated, gradually increase the dose to the therapeutic dose for heart failure. Diuretics can be added in the presence of fluid overload. At the same time, digoxin will be indicated for symptomatic treatment if the above treatment measures are not effective or to control the ventricular response if atrial fibrillation occurs. However, digoxin should be used with caution because the heart of rheumatic patients is very sensitive, so the initial dose should be half of the usual dose. In addition, the patient also needs to rest in bed, lie with the head elevated, limit salty foods and breathe oxygen if the oxygen level in the blood is low.
5. How can rheumatic fever be prevented in the future?
It is extremely important to remind patients and families of the need and respect for secondary rheumatic heart disease when the patient is discharged from the hospital. Because once rheumatic fever recurs in the future, the damage to the heart will become more severe, the function of the heart is no longer guaranteed and the risk of death is high.
In which, antibiotic treatment with penicillin is still the most effective regimen for prevention of recurrence. The low occupancy period is at least 5 years or until the age of 21 and choose the longest period. This is done more seriously in subjects with high risk factors for recurrent rheumatic heart disease:
Severe polyvalvular rheumatic disease Frequent recurrence Low family history of disease High population density Article low economic and educational background High risk of streptococcus infection

Định kỳ kiểm tra sức khỏe giúp sớm phát hiện bệnh lý
In summary, rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can cause damage to the heart after a strep throat infection without proper treatment. The above information will help improve understanding of this disease, actively prevent rheumatic fever by adhering to the treatment of strep throat infection with a course of antibiotics according to the right regimen.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.