This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Pharmacist Dinh Thi My Hanh - Faculty of Pharmacy - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Melatonin is a hormone in the body that plays a role in sleep. The production and release of melatonin in the brain is connected to the time of day, increasing when it is dark and decreasing when it is morning. The production of melatonin in the body decreases with age.
1. Uses of Melatonin
Melatonin is also available as a dietary supplement, usually in pill or capsule form. Most melatonin supplements are usually made in a lab.
Melatonin can be used for sleep disorders, such as: Insomnia and Jet lag (a syndrome of circadian rhythm disturbances of the body, caused by time zone changes without synchronization. the body's learning is delayed to adjust to the new cycle of daylight and darkness at night).
Research on the use of melatonin in specific conditions shows:
Sleep rhythm disturbances in the blind: Melatonin may help improve these disorders in adults and children. Late sleep phase (late sleep-wake phase sleep disorder). In this disorder, your bedtime is 2 hours or more behind your usual bedtime. As a result, you will fall asleep later and wake up later. Research shows that melatonin reduces the time it takes to fall asleep in adults and children with this condition. Insomnia: Research shows that melatonin can slightly reduce the time it takes to fall asleep. However, its effect on sleep quality. Melatonin may be more beneficial for older adults with melatonin deficiency. Jet lag syndrome: Evidence suggests that melatonin can improve jet lag symptoms. Shift Work Sleep Disorders: There is no research demonstrating that melatonin can improve daytime sleep quality and duration in night shift workers. Sleep disorders in children: Small studies have suggested melatonin may help treat sleep disorders in children with certain disabilities. However, the often recommended initial treatment is to practice good bedtime habits. Consult your doctor before giving melatonin to your child. Some research shows that melatonin can reduce confusion and restlessness at night in people with Alzheimer's disease. However, there is no evidence that melatonin improves cognitive performance. The body can produce enough melatonin on demand. However, research has shown that supplementing with melatonin can help improve sleep and is safe for short-term use. Melatonin can be used to treat late sleep phase and circadian rhythm sleep disorders in blind people, helping to relieve insomnia.
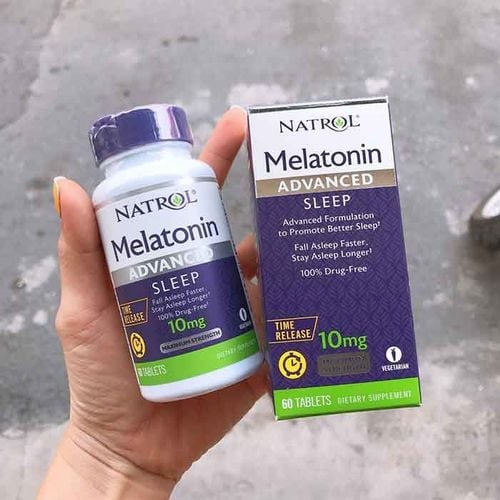

Melatonin là thực phẩm bổ sung có thể sử dụng cho các chứng rối loạn giấc ngủ
2. Safety and side effects
Melatonin taken orally in appropriate doses is generally safe. However, melatonin can also cause some side effects such as:
Headache ; Dizzy; Nausea; Sleepy. Some of the less common melatonin side effects may include: Short-lasting feelings of depression, mild tremors, mild anxiety, stomach cramps, irritability, decreased alertness, confusion, or disorientation direction.
Because melatonin can cause daytime drowsiness, patients should not drive or use machines for 5 hours after taking it.
Do not use melatonin if you have an autoimmune disease.
3. Drug interactions
Possible drug interactions include:
Anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, herbs and supplements: These drugs, herbs, and supplements decrease blood clotting. Combining melatonin with these substances may increase the risk of bleeding. Antiepileptic drugs: Melatonin may inhibit the effects of antiepileptic drugs and increase the frequency of seizures, especially in children with neurological disabilities. Blood pressure medications: Melatonin may worsen blood pressure in people taking blood pressure medications. Central nervous system (CNS) depressants: Using melatonin with these drugs may cause an additional sedative effect. Diabetes medications: Melatonin can affect sugar levels. If you take diabetes medication, talk to your doctor before using melatonin. Birth control pills: Using birth control pills along with melatonin might increase the sedative effects and increase the possible side effects of melatonin. Substances that interact with cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) and cytochrome P450 2C19 (CPY2C19) enzymes. Caution should be exercised if melatonin is used concomitantly with medications such as diazepam or other products that are affected and metabolized by these enzymes. Fluvoxamine (Luvox): A drug used to treat obsessive-compulsive disorder that can increase melatonin levels, causing unwanted excessive sleepiness. Immunosuppressants: Melatonin may stimulate immune function and interfere with immunosuppressive therapy. Drugs that lower the seizure threshold: Taking melatonin with these drugs may increase the risk of seizures. In summary, if you have any concerns about potential interactions between melatonin and medications you are taking, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using
Reference information: mayoclinic.org