This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.
Acute appendicitis is one of the dangerous surgical emergencies. Children with acute appendicitis are often more difficult to diagnose than adults, so when they see signs of appendicitis, they need to go to medical centers for timely examination and treatment.
1. Is acute appendicitis in children dangerous?
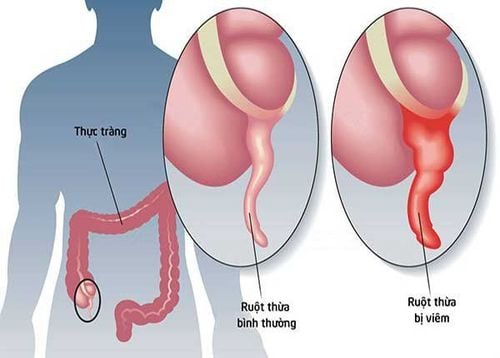
Acute appendicitis is the most common emergency in pediatric practice. Diagnosing appendicitis in children can be difficult, especially in young children. The examination and monitoring of clinical progress is the most important factor for diagnosis and indication for surgery. In 90% of cases the appendix is located in the right iliac fossa.
Appendicitis is divided into 2 types: uncomplicated appendicitis and complicated appendicitis.
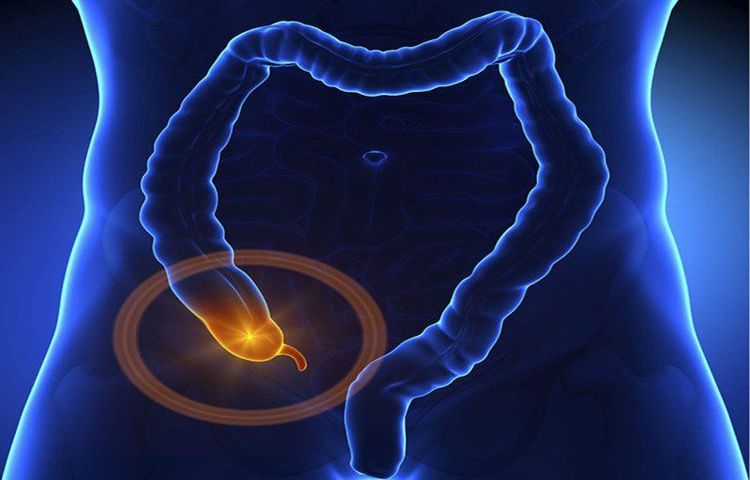
2. Diagnosis of appendicitis
Steps to diagnose appendicitis are as follows:2.1. Ask the disease Abdominal pain: Pain in the epigastrium or around the navel, pain spreading down the right iliac fossa. Mild fever 37.50C - 38.50C is common. High fever is common when appendicitis is complicated. Vomiting, nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, diarrhea. Urinary disorders: Urinary frequency, painful urination are common signs in appendicitis, appendicitis, and bladder irritation. 2.2. Examination Abdominal examination: Pain, resistance/reaction to the right iliac fossa wall; palpate a mass in the right iliac fossa. McBurney score (+). Schotkin-Blumberg(+), Rovsing(+) rebound. Rectal examination: If the patient is suspected of appendicitis in the pelvic region. Complications: Water-electrolyte disorders, shock, sepsis, intestinal obstruction... 2.3. Subclinical examination Abdominal ultrasound : Image of appendicitis: Diameter > 6mm, wall thickness > 3mm, pressure not collapsing, surrounding fat infiltrate, pressing ultrasound probe causes pain Abdominal X-ray unprepared : Indicated when gastrointestinal perforation is suspected (subdiaphragmatic crescent) or intestinal obstruction (manifested by the level of fluid in the small intestine). Complete blood cell analysis: Routine, WBC usually high, Neutrophil predominate. Other tests: CRP/CRP hs increased, electrolytes, blood amylase/lipase (helps to rule out pancreatitis),... In case of clinical suspicion of appendicitis but ultrasound, the test is inconclusive. If possible, a CT scan of the abdomen can be performed for diagnosis.
3. Treatment of acute appendicitis in children
Principles of treatment of acute appendicitis in resuscitated children with complications and appendectomy.
Medical resuscitation includes: Anti-shock, rehydration, electrolytes, antipyretic, pain relief, use of antibiotics and nasogastric drainage if there is a complication of intestinal obstruction, fasting.

3.1. Surgery The treatment for acute appendicitis is usually the removal of the inflamed appendix and there are two types of surgery:
Laparoscopic surgery has many advantages such as being able to view the entire abdomen allowing exclusion of differential diagnoses, small incision, less pain, minimal complications, shorter hospital stay compared to open surgery. Open surgery is applied when the patient is contraindicated for laparoscopic surgery. Uncomplicated appendicitis: appendectomy. Appendicitis : appendectomy, abdominal lavage ± abdominal drainage. Appendiceal abscess: drain the abscess ± appendectomy (if found). Tests performed during surgery: Antibiotic culture, biochemistry of abdominal fluid, pathology when needed. After surgery, the patient was rehydrated with electrolytes and continued to take antibiotics for 5-7 days.
3.2. Deferred surgery This method is indicated when in the case of appendiceal mass, serious medical disease is not suitable for surgery. At this time, the patient will be given antibiotics, and drained under the guidance of ultrasound or computed tomography and selected the appropriate time for surgery.
Appendicitis in children is one of the diseases that can seriously affect the health and life of children, especially in cases of acute inflammation. Therefore, when there are signs of the disease, parents should take the child to the medical center for examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.