This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Doctor Ngo Viet Thang - Gastroenterologist, Department of General Surgery, Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Acute appendicitis is an acute infection of the appendix. Acute appendicitis is potentially fatal due to complications related to appendicitis because it is not diagnosed correctly and treated promptly.
1. Is acute appendicitis dangerous?
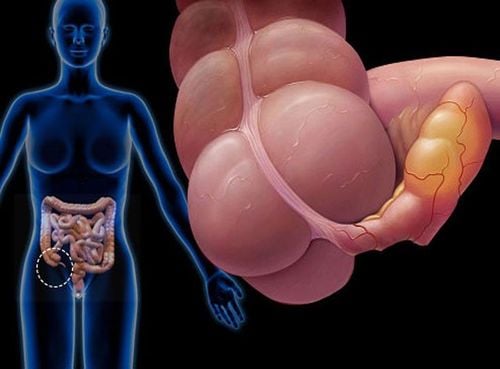
The appendix is a small, finger-shaped organ that arises from the first segment of the large intestine in the right iliac fossa. Although the appendix is an organ whose exact function is unknown, a disorder in this organ can become a disease. This is a very common surgical emergency at the age of 20 - 30. Although acute appendicitis has a typical clinical picture, but based on clinical evidence alone, the diagnosis of acute appendicitis can give results. erroneous results up to 30%. In the case of considering clinical signs, combined with ultrasound, this error rate can be reduced to 15% and if computed tomography (CT scan) is applied, the error rate can be reduced. down to only 7%.
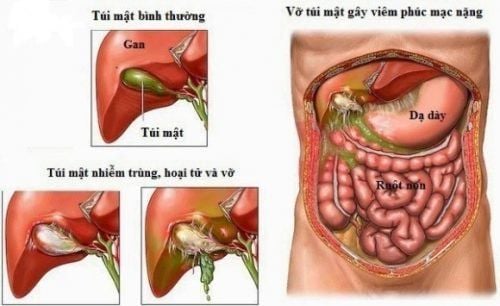
Acute appendicitis if not properly diagnosed and treated promptly, the inflamed appendix may burst, causing pus to spread to the abdomen, causing appendicitis peritonitis and a few other complications, threatening threaten the patient's life.
2. Complications from acute appendicitis
2.1. Total peritonitis
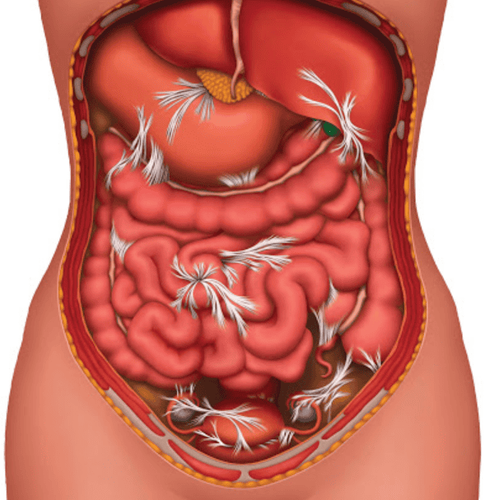
Generalized peritonitis is a dangerous complication of acute appendicitis, which occurs when the ruptured appendix flows into the abdomen.
Clinically, signs of severe systemic infection can be observed. Regarding local symptoms, the patient presented with pain throughout the abdomen, dyspepsia, difficult bowel movements, abdominal distention due to intestinal paralysis, and reactions in the abdominal wall spreading throughout the abdomen.
Viêm phúc mạc toàn bộ
2.2. Appendiceal abscess
Acute appendicitis leads to a ruptured appendix, but surrounded by the omentum, the loops of intestine become a barrier to localize the inflammation, preventing it from spreading to the abdomen.
Clinically show signs that the patient still has right iliac fossa pain and high fever. On examination of the right iliac fossa, a non-movable, smooth-surfaced mass can be observed that is tender and painful when pressed. Laboratory tests revealed an elevated white blood cell count. Appendiceal abscess is likely to rupture into the abdomen, causing second-stage peritonitis.
2.3. Appendices bunch
This is a complication of acute appendicitis that occurs in cases where the patient has good resistance, the loops of intestine and the omentum have the ability to enclose the appendix, preventing its spread.
Clinical symptoms are pain and fever decrease, the right iliac fossa appears firm, non-moving, mildly tender, no reaction in the abdominal wall. Laboratory tests showed that the white blood cell count gradually decreased back to normal. Appendiceal masses have the potential to progress in two directions, either dissolving or forming an appendix abscess.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.