This is an automatically translated article.
Low levels of progesterone can cause various problems, especially for women, especially pregnant women. However, there are many possible treatments that can help with the condition. Hormone therapy can be a long-term option for many people, especially postmenopausal women.
1. What is Progesterone?
Progesterone is a hormone found in women. It is produced mainly in the ovaries after ovulation each month. This hormone is an important part of the menstrual cycle and the maintenance of fertility. Progesterone helps regulate the menstrual cycle. But the main job of this hormone is to prepare the uterus for pregnancy. After each month's ovulation, progesterone helps thicken the lining of the uterus in preparation for a fertilized egg. If no egg is fertilized, progesterone levels drop and menstruation begins. If there is a fertilized egg attached to the wall of the uterus, progesterone will help maintain the uterine lining throughout the pregnancy.Progesterone is essential for breast development and lactation. It complements some of the effects of estrogen, another female hormone. It also works with testosterone, a precursor to adrenal hormones.
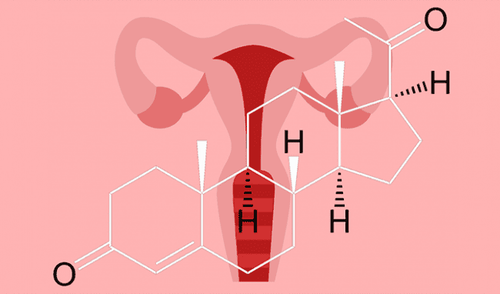
Progesterone là một loại hormone được sản xuất bởi buồng trứng ở phụ nữ
2. Should I be concerned about low progesterone levels?
Progesterone plays an extremely important role during pregnancy and childbirth. If the amount of progesterone in your body is not enough for this process, you will have difficulty getting pregnant and maintaining a pregnancy.
When one of the ovaries releases an egg, the amount of progesterone in a woman's body increases. This hormone helps thicken the uterus to prepare it for the reception of a fertilized egg. If the lining of the uterus is not thick enough, the egg will not implant.
Symptoms from having too low a progesterone level in a non-pregnant woman can include:
Headaches or migraines Mood changes, including anxiety and depression Irregular periods Having low amounts Low progesterone can also cause abnormal uterine bleeding in women who are not pregnant. Irregular periods or amenorrhea can indicate that the ovaries are not working properly and that there is a shortage of progesterone.
If you become pregnant, you will still need progesterone to maintain the condition of your uterus until the baby is born. The body will increase production of progesterone, which will lead to symptoms of pregnancy including breast pain and nausea. If progesterone levels are too low, the uterus won't be able to hold the baby until the due date. During pregnancy, symptoms caused by low progesterone levels include heavy bleeding and miscarriage.
Low progesterone could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy. This can cause miscarriage or stillbirth.
Without the amount of progesterone to replenish, estrogen will become the dominant hormone. This will cause symptoms:
Weight gain Loss of sex drive, mood swings and depression PMS PMS, irregular menstrual cycle, heavy periods Breast pain, cystic fibrosis Uterus Gallbladder problems
Progesterone thấp có thể gây biến chứng đau vú ở phụ nữ
3. Test test
The progesterone test (PGSN) can help your doctor see if your progesterone levels are too low. This is a simple blood test and does not require any preparation.
The test can tell you why you are having trouble getting pregnant. It can also confirm whether or not your egg has been released. PGSN testing is also used in the monitoring of hormone replacement therapy or the status of a high-risk pregnancy. Progesterone levels during pregnancy are usually higher than normal. And the concentration will be even higher if you have more than one fetus.
Men, children, and postmenopausal women all have lower levels of the hormone progesterone than women who are pregnant. Progesterone levels are considered “normal” depending on a person's age and sex. In women, other factors that affect progesterone levels are whether they are pregnant or menstruating. Progesterone levels fluctuate throughout the menstrual period. Progesterone levels will peak 7 days before your period and levels will vary throughout the day.
Underactive ovaries reduce the quality of progesterone production. During menopause, it is normal for estrogen and progesterone levels to drop.
4. What can I do when my progesterone levels are too low?
You probably won't experience any symptoms when your progesterone levels are low, and you won't need treatment either. But if you want to have a baby, hormone therapy can work. Hormone therapy increases progesterone levels and thickens the lining of the uterus. This will help improve your chances of having a healthy pregnancy and staying pregnant until your due date.
Menstrual irregularities and irregular bleeding can be improved with hormone therapy. For severe symptoms of menopause, hormone therapy involves a combination of estrogen and progesterone. Women who use only estrogen and no progesterone have an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
Liệu pháp hormone giúp làm gia tăng lượng progesterone trong cơ thể người bệnh
Progesterone treatment options include:
Creams and gels that can be applied topically or inserted into the vagina Suppositories, often used to treat low progesterone causing fertility problems. Oral medications, such as Provera Hormone therapy (whether estrogen alone or a combination of estrogen and progesterone) can ease symptoms such as:
Hot flashes Night sweats Vaginal dryness With For some women, progesterone can also help improve mood. Oral progesterone also provides a soothing sensation and eases sleep.
Hormone therapy can increase your risk of:
Heart attack and stroke Blood clots Gallbladder problems Some types of breast cancer
Your doctor will advise you not to use hormone therapy if you have a history of conditions such as:
Breast cancer Endometrial cancer Liver disease Blood clots Stroke
Phụ nữ mắc ung thư vú không nên sử dụng liệu pháp hormone
Natural remedies to increase progesterone levels include:
Boosting vitamins B and C, which are essential in maintaining progesterone levels Eat plenty of zinc-containing foods like shellfish (clams, mussels .. .) Manage stress levels, as when stressed your body releases cortisol instead of progesterone. This is because most menopausal symptoms are caused by a drop in estrogen levels.
Using hormone replacement therapy has some risks, so it is important to consult a doctor. Some prescription drugs are designed to work with your body in a similar way to your body's natural hormones. They are sometimes called “biocompatible” hormones. But while it sounds perfectly fine, they carry the same risks as other prescription formulations.
It is important to see a specialist to find out what treatment is best for you. It may take a few weeks to see results from hormone therapy. Check in with your doctor regularly to reassess your treatment plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to the source: healthline.com